NGINX Ingress Controller
Introduction
Kubernetes uses kube-proxy to expose Services and provide load balancing. The implementation is at the transport layer. When it comes to Internet applications, where a bucket-load of information is generated, forwarding needs to be more fine-grained, precisely and flexibly controlled by policies and load balancers to deliver higher performance.
This is where ingresses enter. Ingresses provide application-layer forwarding functions, such as virtual hosts, load balancing, SSL proxy, and HTTP routing, for Services that can be directly accessed outside a cluster.
Kubernetes has officially released the Nginx-based Ingress controller. CCE Nginx Ingress controller directly uses community templates and images. The NGINX Ingress Controller generates Nginx configuration and stores the configuration using ConfigMap. The configuration will be written to Nginx pods through the Kubernetes API. In this way, the Nginx configuration is modified and updated. For details, see How the Add-on Works.
Open-source community: https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx
- Starting from version 2.3.3, NGINX Ingress Controller only supports TLS v1.2 and v1.3 by default. If the TLS version is earlier than v1.2, an error will occur during the negotiation process between the client and Nginx Ingress. If more versions of TLS are needed, see TLS/HTTPS.
- When installing the NGINX Ingress Controller, you can specify Nginx parameters. These parameters take effect globally and are contained in the nginx.conf file. You can search for the parameters in ConfigMaps. If the parameters are not included in ConfigMaps, the configurations will not take effect.
- Do not manually modify or delete the load balancer and listener that are automatically created by CCE. Otherwise, the workload will be abnormal. If you have modified or deleted them by mistake, uninstall the nginx-ingress add-on and re-install it.
How the Add-on Works
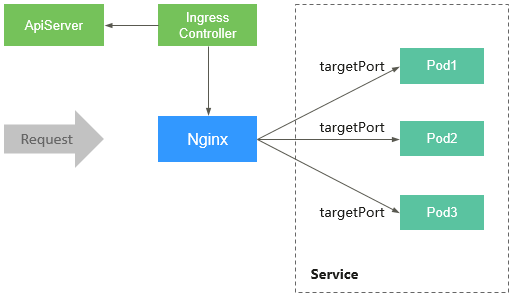
An Nginx ingress consists of the ingress object, ingress controller, and Nginx. The ingress controller assembles ingresses into the Nginx configuration file (nginx.conf) and reloads Nginx to make the configuration changes apply. When it detects that the pod in a Service changes, it dynamically changes the upstream server group configuration of Nginx. In this case, the Nginx process does not need to be reloaded. Figure 1 shows how this add-on works.
- An ingress is a group of access rules that forward requests to specified Services based on domain names or URLs. Ingresses are stored in the object storage service etcd and are added, deleted, modified, and queried through APIs.
- The ingress controller monitors the changes of resource objects such as ingresses, Services, endpoints, secrets (mainly TLS certificates and keys), nodes, and ConfigMaps in real time and automatically performs operations on Nginx.
- Nginx implements load balancing and access control at the application layer.
Precautions
- For clusters earlier than v1.23, kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx" must be added to the annotation of the ingress created through the API.
- A dedicated load balancer must be of the network type (TCP/UDP) and support private networks (with a private IP address).
- If the node where NGINX Ingress Controller runs and containers on this node cannot access Nginx ingress, you need to configure anti-affinity for the workload pods and Nginx Ingress Controller. For details, see Configuring Anti-Affinity Between a Workload and Nginx Ingress Controller.
- During the NGINX Ingress Controller pod upgrade, 10s are reserved for deleting the NGINX Ingress Controller at the ELB backend.
- The timeout duration for the graceful exit of the NGINX Ingress Controller is 300s. If the timeout duration is longer than 300s during the upgrade of the NGINX Ingress Controller, persistent connections will be disconnected, and connectivity will be interrupted for a short period of time.
Prerequisites
Before installing this add-on, you have one available cluster and there is a node running properly. If no cluster is available, create one according to Buying a CCE Standard/Turbo Cluster.
Installing the Add-on
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons, locate NGINX Ingress Controller on the right, and click Install.
- On the Install Add-on page, configure the specifications as needed.
You can adjust the number of add-on pods and resource quotas as required. High availability is not possible with a single pod. If an error occurs on the node where the add-on instance runs, the add-on will fail.
- Configure the add-on parameters.
- Ingress Class: Enter a controller name. The name of each controller in the same cluster must be unique and cannot be set to cce (which is the unique identifier of the ELB ingress controller.) When creating an ingress, you can specify the controller name to declare which controller should manage this ingress.
- Add-on Namespace: Select a namespace for the ingress controller.
- Load Balancer: Select a shared or dedicated load balancer. If no load balancer is available, create one. The load balancer has at least two listeners, and ports 80 and 443 are not occupied by listeners.
- Admission Check: Admission control is performed on Ingresses to ensure that the controller can generate valid configurations. Admission verification is performed on the configuration of Nginx Ingresses. If the verification fails, the request will be intercepted. For details about admission verification, see Access Control.
- Admission check slows down the responses to Ingress requests.
- Only add-ons of version 2.4.1 or later support admission verification.
- Nginx Parameters: You can configure the nginx.conf file, which will affect all managed ingresses. You can select GUI or YAML. GUI is supported by the NGINX Ingress Controller of version 2.2.75, 2.6.26, 3.0.1, or later.
To configure custom parameters supported by the Kubernetes community, choose YAML and find the related parameters in ConfigMaps. For example, you can use the keep-alive-requests parameter to describe how to set the maximum number of requests for keeping active connections to 100.
{ "keep-alive-requests": "100" }
- If the configured parameters are not listed in ConfigMaps, the configurations will not take effect.
- The parameter value must be a string. Otherwise, the installation fails.
The table below shows parameters can be configured on the GUI of the NGINX Ingress Controller add-on of version 2.2.75, 2.6.26, 3.0.1, and later.Nginx Parameter
Description
Default Value
Maximum Worker Connections
Specifies the maximum number of connections that can be concurrently processed by each NGINX worker process. This parameter is used to control the load of worker processes. In a high-concurrency environment, you are advised to set this parameter to a large value to ensure system stability. Such connections include client connections and connections to backend servers.
65536
Maximum Keepalive Requests
Controls how many requests can be processed by a keepalive connection. If requests exhaust the limit, the connection is closed.
100
Maximum Keepalive Connections to the Upstream Server
Activates the cache for connections to upstream servers. This parameter sets how many idle keepalive connections can be stored in the cache of each worker process. If the idle connections stored in a process exhaust the limit, the connections that are not used for the longest time will be closed.
320
Maximum Keepalive Timeout of the Upstream Server
Specifies the timeout for a keepalive connection between an upstream server and a backend server, in seconds. During this period, NGINX Ingress Controller can maintain connections for reuse. This reduces the overhead required for establishing new connections and significantly improves performance in high QPS scenarios.
900
Request Timeout
Specifies the timeout for connecting the client to the proxy server, in seconds. If the client cannot access the backend server within 10 seconds, NGINX Ingress Controller will return a 502 Bad Gateway error. It applies to scenarios where the connection speed is high.
10
Maximum Request Body Size
Specifies the maximum size of the request body that Nginx can send to the backend server through the proxy. This applies to file uploads and large data form submissions. If the size of any request body exceeds the limit, a 413 Payload Too Large error will be returned.
20m
Allow the Backend to Return Server Headers
Typically, NGINX Ingress Controller eliminates the server header information sent by a backend server to a client, which identifies the server. However, if this parameter is set to true, the NGINX Ingress Controller will transmit the server header information directly from the backend server to the client. To prevent revealing the server type and version, it is recommended that you disable this feature.
Disable
Allow Underscores in Headers
Some HTTP headers may contain underscores (_), such as X_Custom-Header, but this is not recommended according to Request For Comments (RFC) standards. So underscores are not allowed by many servers by default. You can activate this parameter if you require underscores in certain headers, such as when third-party services or clients use underscores in their header information.
Disable
Generate a Request ID
After a request is received, NGINX Ingress Controller generates a unique request ID. This ID is usually recorded in logs or transferred to a backend server through header information. This is useful for tracing and debugging requests, especially for locating problems in distributed systems.
Enable
Ignore Invalid Headers
By default, NGINX Ingress Controller rejects HTTP requests that contain an invalid header. With this setting enabled, NGINX Ingress Controller will ignore invalid headers and keep on processing requests. It is useful for clients that do not fully comply with the HTTP standard.
Enable
Reuse Ports
Enabling SO_REUSEPORT allows multiple processes or threads to be bound to the same {IP}:{Port}. This can effectively improve the concurrent performance of servers, especially for those with multi-core CPUs. With this function enabled, a port can accept more new connections.
Enable
Allow Server Information in Request Body
Disables the server information added to a response header by NGINX Ingress Controller by default. The information usually contains the NGINX version. Disabling this option helps hide server information, enhancing security and preventing attackers from using the version information to attack the system.
Disable
Automatically Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Disables automatic redirection from HTTP to HTTPS. For example, if you want to use HTTPS only for specific pages, such as the login page, and HTTP for other pages, you can disable the default redirection using this option.
Disable
CPU Affinity of Worker Threads
Automatically allocates worker processes to specific CPU cores to improve the performance of multi-core systems. For example, on a multi-core server, some worker processes can be bound on a specific CPU core. This reduces context switching and improves processing efficiency.
Auto
- Enabling Indicator Collection: If the add-on version is 2.4.12 or later, Prometheus monitoring metrics can be collected.
- Default certificate of the server: Select an IngressTLS or kubernetes.io/tls key to configure the default certificate when the NGINX Ingress Controller is started. If no secret is available, click Create TLS Secret. For details, see Creating a Secret. For details about the default server certificate, see Default SSL Certificate.
- 404 Service: By default, the 404 service provided by the add-on is used. To customize the 404 service, enter the namespace/service name. If the service does not exist, the add-on installation will fail.
- Adding a TCP/UDP Service: By default, NGINX Ingress Controller can forward only external HTTP and HTTPS traffic. You can add TCP/UDP port mapping to forward external TCP/UDP traffic to services in the cluster. For more information about adding TCP/UDP services, see Exposing TCP and UDP services.
- Protocol: Select TCP or UDP.
- Service Port: specifies the port used by the ELB listener. The port number ranges from 1 to 65535.
- Target Service Namespace: Select the namespace where the Service is in.
- Destination Service: Select an existing Service. Any Services that do not match the search criteria will be filtered out automatically.
- Destination Service Port: Select the access port of the destination Service.
- If the cluster version is v1.19.16-r5, v1.21.8-r0, v1.23.6-r0, or later, the TCP/UDP hybrid protocols can be configured.
- If the cluster version is v1.19.16-r5, v1.21.8-r0, v1.23.6-r0, v1.25.2-r0, or later, you can configure the TCP/UDP hybrid protocols to use the same external port.
- (Optional) Extended Parameter Settings: additional extended parameters of the add-on If the extended parameter settings conflict with the default settings, the extended parameter settings will be prioritized.
- extraArgs: additional configurable startup parameters of the nginx-ingress-controller component. For details about the startup parameters supported by the community, see the documentation.
- extraInitContainers: initial container configuration of nginx-ingress-controller. This parameter is supported by add-on 2.2.82, 2.6.32, 3.0.8 and later, with optimized kernel settings by default.
- maxmindLicenseKey: Maxmind license key, which can be used to download GeoLite2 databases. This parameter is supported by add-on 2.2.82, 2.6.32, 3.0.8, and later. It is mandatory for NGINX Ingress Controller to configure the use-geoip2 capability.
- Configure deployment policies for the add-on pods.
- Scheduling policies do not take effect on add-on pods of the DaemonSet type.
- When configuring multi-AZ deployment or node affinity, ensure that there are nodes meeting the scheduling policy and that resources are sufficient in the cluster. Otherwise, the add-on cannot run.
Table 1 Configurations for add-on scheduling Parameter
Description
Multi-AZ Deployment
- Preferred: Deployment pods of the add-on will be preferentially scheduled to nodes in different AZs. If all the nodes in the cluster are deployed in the same AZ, the pods will be scheduled to different nodes in that AZ.
- Equivalent mode: Deployment pods of the add-on are evenly scheduled to the nodes in the cluster in each AZ. If a new AZ is added, you are advised to increase add-on pods for cross-AZ HA deployment. With the Equivalent multi-AZ deployment, the difference between the number of add-on pods in different AZs will be less than or equal to 1. If resources in one of the AZs are insufficient, pods cannot be scheduled to that AZ.
NOTE:
The equivalent mode supports only the pods in the kube-system and monitoring namespaces.
- Forcible: Deployment pods of the add-on are forcibly scheduled to nodes in different AZs. There can be at most one pod in each AZ. If nodes in a cluster are not in different AZs, some add-on pods cannot run properly. If a node is faulty, add-on pods on it may fail to be migrated.
Node Affinity
- Not configured: Node affinity is disabled for the add-on.
- Specify node: Specify the nodes where the add-on is deployed. If you do not specify the nodes, the add-on will be randomly scheduled based on the default cluster scheduling policy.
- Specify node pool: Specify the node pool where the add-on is deployed. If you do not specify the node pools, the add-on will be randomly scheduled based on the default cluster scheduling policy.
- Customize affinity: Enter the labels of the nodes where the add-on is to be deployed for more flexible scheduling policies. If you do not specify node labels, the add-on will be randomly scheduled based on the default cluster scheduling policy.
If multiple custom affinity policies are configured, ensure that there are nodes that meet all the affinity policies in the cluster. Otherwise, the add-on cannot run.
Toleration
Using both taints and tolerations allows (not forcibly) the add-on Deployment to be scheduled to a node with the matching taints, and controls the Deployment eviction policies after the node where the Deployment is located is tainted.
The add-on adds the default tolerance policy for the node.kubernetes.io/not-ready and node.kubernetes.io/unreachable taints, respectively. The tolerance time window is 60s.
For details, see Configuring Tolerance Policies.
- Click Install.
Installing Multiple NGINX Ingress Controllers
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons, locate the installed NGINX Ingress Controller, and click New.
- On the page displayed, reconfigure the add-on parameters. For details, see Installing the Add-on.
- Click Install.
- Wait until the installation instruction is delivered. Go back to Add-ons, click Manage, and view the installed add-on instance on the add-on details page.
Components
|
Component |
Description |
Resource Type |
|---|---|---|
|
cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<Controller name>-controller (The controller name in versions earlier than 2.5.4 is cceaddon-nginx-ingress-controller.) |
Nginx-based ingress controller that provides flexible routing and forwarding for clusters. |
Deployment |
|
cceaddon-nginx-ingress-<Controller name>-backend (The controller name in versions earlier than 2.5.4 is cceaddon-nginx-ingress-default-backend.) |
Default backend of the Nginx ingress. The message "default backend - 404" is returned. |
Deployment |
Configuring Anti-Affinity Between a Workload and Nginx Ingress Controller
To avoid a situation where the node running NGINX Ingress Controller and its containers cannot access the Nginx Ingress Controller, you should set up anti-affinity between the workload and Nginx Ingress Controller. This means that the workload pods cannot be scheduled to the same node as the Nginx Ingress Controller.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:aplpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: nginx
imagePullSecrets:
- name: default-secret
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions: # Implement anti-affinity through the label of the NGINX Ingress Controller pods.
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- nginx-ingress #If multiple NGINX Ingress Controllers are installed in the cluster, the label value is nginx-ingress-<Controller name>.
- key: component
operator: In
values:
- controller
namespaces:
- kube-system
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot