Overview
Huawei Cloud IoT Device Access (IoTDA) allows you to connect your physical devices to the cloud, where you can collect device data and deliver commands to devices for remote control. It can also work with other Huawei Cloud services to help you quickly develop IoT solutions.
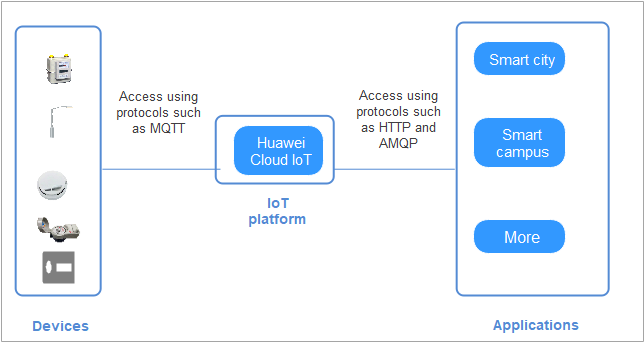
A complete IoT solution consists of the IoT platform, devices, and applications.
- The IoT platform is located between applications and devices. It harmonizes differences between device interfaces to enable quick device access. It provides robust capabilities to help you develop diverse IoT solutions.
- Devices can access the platform via fixed broadband (FBB), 2G/3G/4G/5G, Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT), and Wi-Fi networks. They can report service data to the platform using mainstream protocols or industry protocols, such as Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT), Lightweight Machine-to-Machine (LwM2M) over Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). Devices can also receive commands from the platform.
- Applications call application programming interfaces (APIs) provided by the platform to implement services such as data collection, command delivery, and device management.
Features
Devices can connect to the platform directly or through industrial gateways or home gateways. The platform supports multi-network access, multi-protocol access, and serialized Agent access, preventing issues caused by complex, diversified, and fragmented device access. It also provides comprehensive device management capabilities, simplifies management of device fleets, and improves management efficiency. The following table describes the IoTDA functions.
|
Category |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Device access |
Native protocol access |
You can connect devices to the platform using MQTT, CoAP, LwM2M, and HTTPS protocols. |
|
Serial device SDKs |
IoT Device SDK and IoT Device SDK Tiny in languages such as C and Java are supported. For details, see Introduction to IoT Device SDKs. |
|
|
Industry protocol access |
You can connect devices to the platform through edge gateways using Modbus and OPC Unified Architecture (OPC UA) and using industry protocols based on plug-ins. |
|
|
Device access authentication |
Authentication modes such as one-device-one-secret and X.509 certificates are supported. |
|
|
- |
- |
|
|
Device management |
Device lifecycle management |
You can add, delete, modify, and query devices, manage device status, freeze and unfreeze devices, and manage child devices. |
|
Device groups and tags |
You can group devices or add tags to them. For details, see Groups. |
|
|
Product models |
You can define a product model (profile) for devices. For details, see Product Model Definition. |
|
|
Device shadows |
You can configure and query device shadows. For details, see Device Shadow. |
|
|
OTA upgrade |
You can upgrade device software and firmware. For details, see OTA Upgrade. |
|
|
Device file upload |
Devices can upload files to Object Storage Service (OBS) and request files from the cloud. For details, see File Uploads. |
|
|
Batch device operations |
You can perform batch operations on devices, including device registration, software/firmware upgrades, and command delivery. For details, see Create a Batch Task. |
|
|
Message communications |
Bidirectional transparent transmission |
Device messages can be pushed to applications using HTTP and AMQP. Applications can deliver messages to devices asynchronously. |
|
Product model topic communications |
Applications and devices communicate with each other based on the properties, commands, and events defined in the product model in a decoupled mode. |
|
|
Custom topic communications |
You can customize topics for bidirectional message communications. |
|
|
Data parsing and conversion |
You can develop codecs online to parse and convert device data. |
|
|
Command delivery |
Commands can be delivered to online devices in synchronous mode. In the NB-IoT scenario, commands can be delivered in asynchronous mode. For details, see Command Delivery. |
|
|
Rules |
Data forwarding |
Data can be forwarded to Huawei Cloud Kafka, OBS, GaussDB, Data Ingestion Service (DIS), Distributed Message Service (DMS), and ROMA Connect. For details, see Rules. |
|
Device linkage |
You can create rules for device linkage control. For details, see Rules. |
|
|
Data forwarding |
The platform can forward data reported by devices to applications through HTTP or AMQP. |
|
|
Monitoring and O&M |
Logging |
The console provides message tracing, integrates with Log Tank Service (LTS) for log analysis, and integrates with Cloud Trace Service (CTS) for log audit. For details, see Monitoring and O&M. |
|
Alarm reporting |
The platform provides notifications and management of system alarms (such as threshold alarms) and alarms triggered by device rules by integrating with Application Operations Management (AOM). For details, see Alarms. |
|
|
Metric monitoring |
The platform provides monitoring reports of tenant-level service metrics (such as device status, commands, subscription and push, and message transfer) by integrating with AOM. For details, see Reports. |
Security and Data Protection
IoTDA established an end-to-end trustworthy security system. It is graded level-4 of China's Multi-Level Protection Scheme 2.0 and obtains international security certifications such as ISO27001, ISO27017, ISO27018, and CSA STAR. It complies with European Union's General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR).
- Device security: It provides a one-device-one-secret authentication mechanism to prevent unauthorized access and supports device security check.
- Data transmission: Secure transmission channels are provided based on Transport Layer Security (TLS), Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS), and DTLS+.
- Platform security: Threat defense is performed on the entire Huawei Cloud. Huawei Cloud security service products or components and security research department are fully leveraged to build a comprehensive security defense system that covers security analysis, design, coding, testing, and defense.
- Data protection: It complies with GDPR.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





