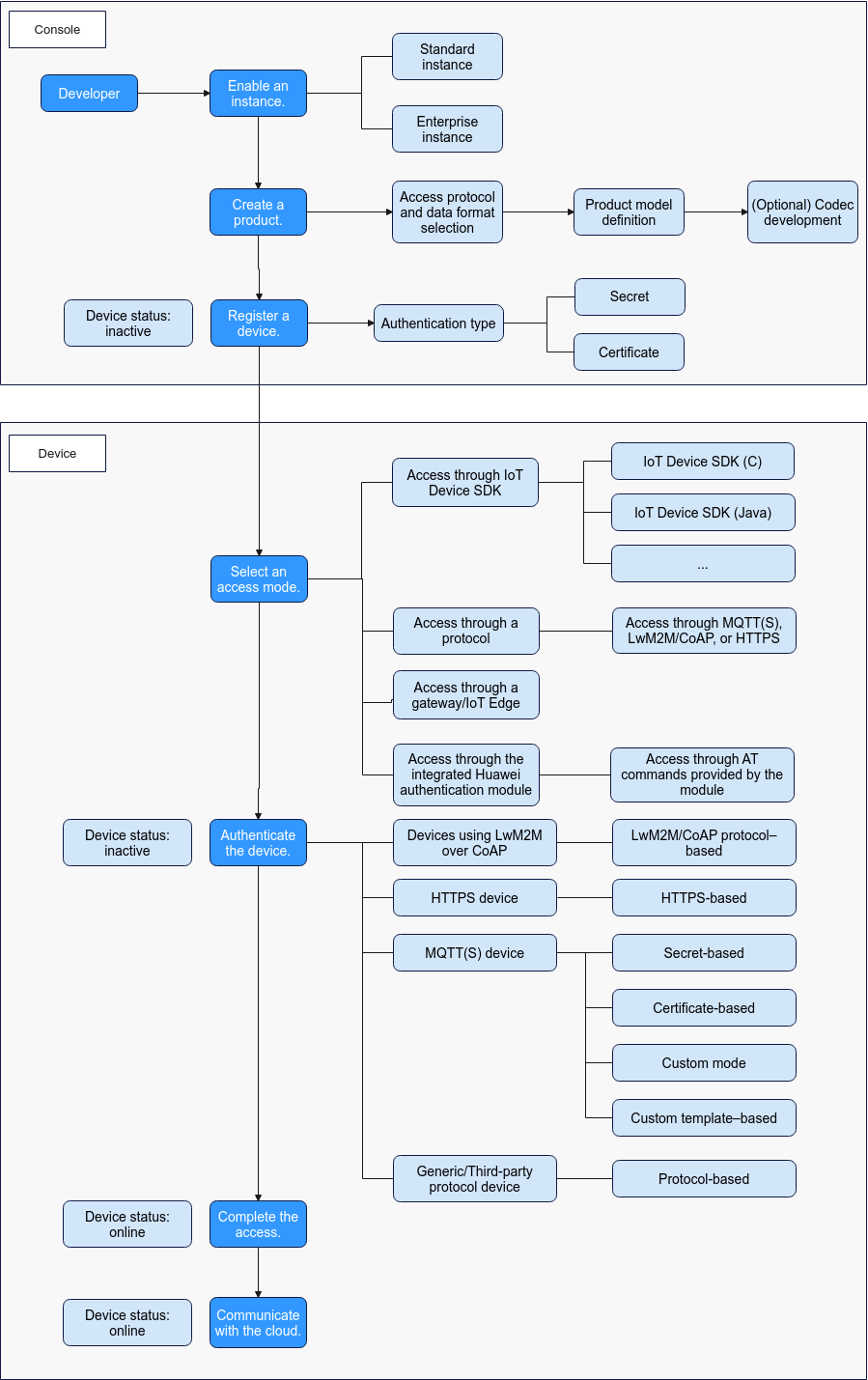
Device Access
Process
You can use various protocols to access Huawei Cloud IoTDA, including:
- Common native protocols: MQTT(S), HTTPS, and LwM2M/CoAP(S)
- Standard protocols for access through gateways or IoT Edge: Modbus, OPC UA, OPC DA, ONVIF, GB28181, and LoRa
- Common protocols in some industries: JT808 (vehicle terminal communication protocol), SL651 (hydrological monitoring data communication protocol), and HJ212 (environmental protection industry data transmission standard protocol)
- TCP proprietary protocols and third-party protocols
For more protocols, see Device Access Protocols.
TLS
IoTDA supports Transport Layer Security (TLS) for encrypted communication and secure client connections. When TLS is utilized, clients can transmit the Server Name Indication (SNI) and access domain name during device connection establishment, which is essential for features like custom domain names, device self-registration, and custom authentication.
|
Protocol |
Operations Supported |
Supported TLS Version |
Port |
|---|---|---|---|
|
MQTT |
Publish/Subscribe |
Not applicable |
1883 |
|
MQTTS |
Publish/Subscribe |
1.1, 1.2, and 1.3 |
8883 |
|
MQTT over WebSocket (WSS) |
Publish/Subscribe |
TLS 1.2 |
443 |
|
HTTPS |
Publish |
TLS 1.2 |
443 |
|
CoAP |
Report and deliver |
Not applicable |
5683 |
|
CoAPS |
Report and deliver |
DTLS 1.2 |
5684 |
Access via Device-side SDKs
IoTDA offers device SDKs for seamless integration with Huawei Cloud, supporting functions like file uploading/downloading, automatic reconnection, OTA upgrades, data reporting, and time synchronization. The SDKs are available in C, C#, Java, Android, Go, Python, and ArkTS for HarmonyOS development. For details, see Device SDKs.
Access via Native Protocols
Devices can connect to IoTDA using native protocols such as MQTT(S), HTTPS, CoAP(S), or LwM2M. When a device employs the binary format, its data must be converted between binary and JSON formats using the codec deployed on the platform for communication with IoTDA.
|
Protocol |
Operations Supported |
Transport Layer |
Power Consumption |
Applicable Network |
Feature |
Common Usage Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Upstream and downstream |
TCP |
Low |
Unstable/High-latency |
Lightweight and low power consumption; publish/subscribe model for one-to-many communication; persistent sessions |
Recommended industry protocol for persistent connection scenarios. It can be used in IoT systems that require bidirectional communication, device control, or high scalability, such as smart city, Internet of Vehicles (IoV), energy, electric power, and Industry 4.0 solution. |
|
|
Upstream only |
TCP |
High |
Stable and high-bandwidth |
Various data formats available; one-way communication for client-initiated requests; stateless with independent requests |
Scenarios where data is integrated with existing web services (such as apps and web pages) or requires high readability. |
|
|
Upstream and downstream |
UDP |
Very low |
Extremely low bandwidth/High packet loss rate |
Designed for restricted devices; lightweight and multicast; low costs; binary format (CBOR) |
This technology is commonly employed on low-power devices with limited resources, such as water meters and electricity meters, as well as on devices with extremely restricted resources like battery-powered sensors or those operating solely on UDP networks. |
Access via Huawei-certified Modules
Huawei-certified modules are integrated with the IoT Device SDK Tiny and have passed Huawei certification tests. They comply with Huawei AT command specifications. You can send and receive data with a few clicks using AT commands, greatly reducing device interconnection workload and device commissioning period.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





