Usage
Process

Procedure
- Use FunctionGraph to create a custom authentication function.
Figure 2 Function list - Creating a function
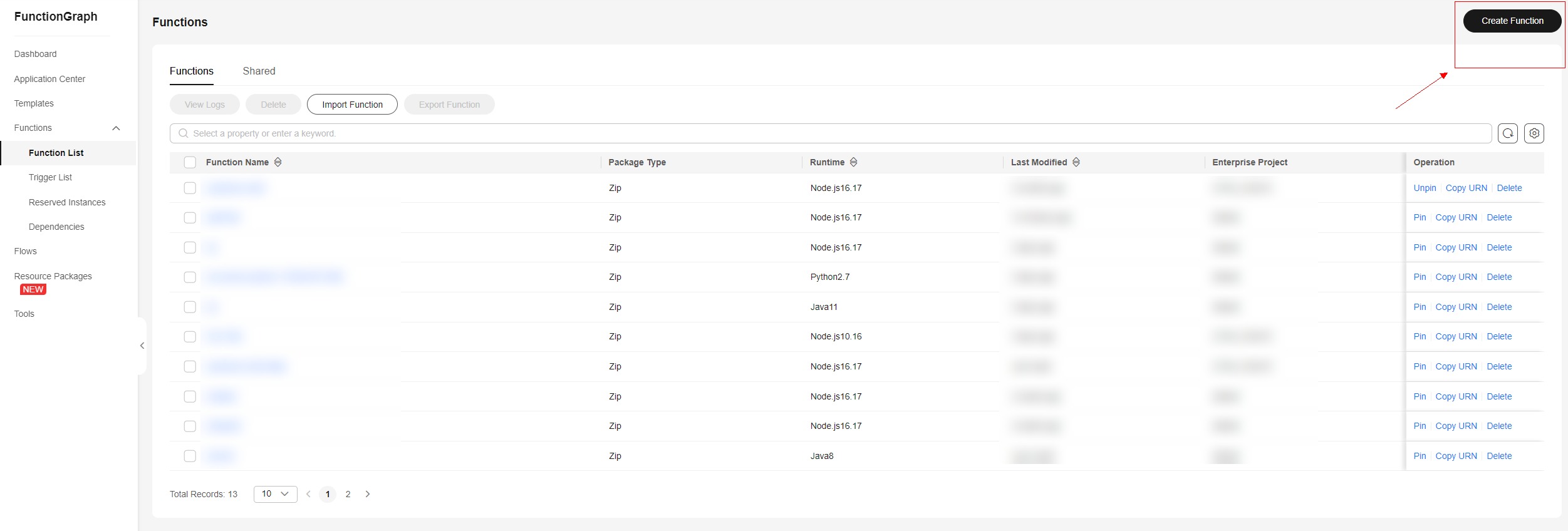 Figure 3 Creating a function - Parameters
Figure 3 Creating a function - Parameters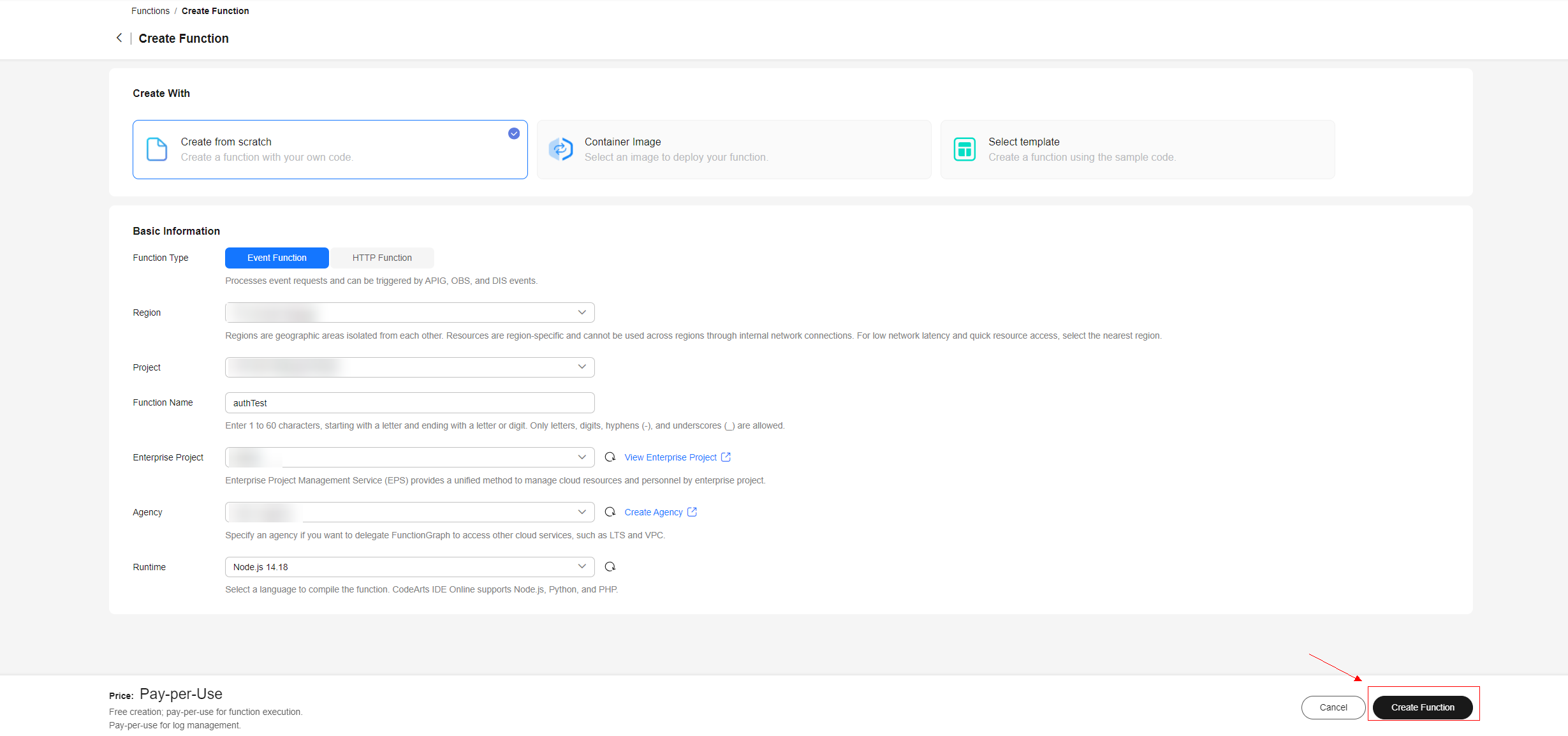
- Configure custom authentication on the console for storage, management, and maintenance. You can configure up to 10 custom authenticators and choose one as the default.
Figure 4 Custom authentication - Creating an authenticator
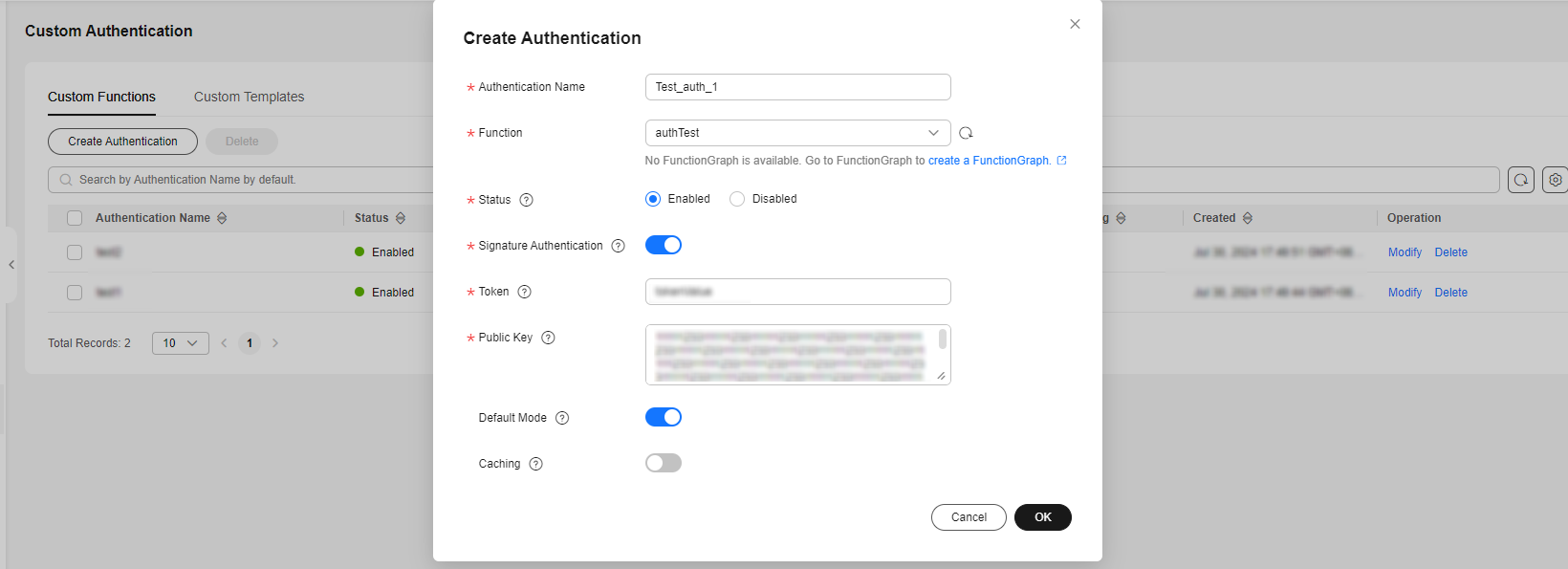
Table 1 Custom authentication parameters Parameter
Mandatory
Description
Authentication Name
Yes
Definition: Name of the custom authenticator.
Function
Yes
Definition: Function corresponding to the custom authenticator.
Range: Functions created in 1.
Status
Yes
Definition: Activation status of the authenticator. Activate an authenticator before using it.
Default Value: Disabled
Signature Authentication
Yes
Definition: After this function is enabled, the authentication information that does not meet the signature requirements will be rejected to reduce invalid function calls.
Default Value: Enabled
Token
No
Definition: Token for signature authentication. Used to check whether a device's signature information is valid.
Public Key
No
Definition: Public key for signature authentication. Used to check whether a device's signature information is valid.
Default Mode
Yes
Definition: After this function is enabled, if the username in an authentication request does not contain the authorizer_name parameter, this authenticator is used.
Default Value: Disabled
Caching
Yes
Definition: After this function is enabled, FunctionGraph authentication results can be cached for 300 minutes to 1 day.
Default Value: Disabled
- The device initiates a CONNECT request using MQTT. The request must carry the username parameter, which contains optional parameters related to custom authentication.
- Username format requirements: Remove braces ({}) and separate each parameter by a vertical bar (|). Do not add vertical bars (|) in the parameter content.
{device-identifier}|authorizer-name={authorizer-name}|authorizer-signature={token-signature}|signing-token={token-value} Example: 659b70a0bd3f665a471e5ec9_auth|authorizer-name=Test_auth_1|authorizer-signature=***|signing-token=tokenValueTable 2 Description of the username parameter Parameter
Mandatory
Description
device-identifier
Yes
Definition: Device identifier. Recommended value: device ID.
authorizer-name
No
Definition: Custom authenticator name, which must be the same as the configured authenticator. If this parameter is not carried, the system will use either the default custom authenticator (if configured) or the original secret/certificate authentication mode.
authorizer-signature
No
Definition: Signature required for signature verification.
Range: Obtain the value by encrypting the private key and signing-token. The value must be the same as the authentication name used in 2.
signing-token
No
Definition: Token required for signature verification.
Value Range: The value must be the same as the token value used in 2.
- Run the following command to obtain authorizer-signature:
echo -n "123456" | openssl dgst -sha256 -sign key.pem -sigopt rsa_padding_mode:pss -sigopt rsa_pss_saltlen:-1 | openssl base64
Table 3 Command parameters Parameter
Description
echo -n {signing-token}
Run the echo command to output the value of signing-token and use the -n parameter to remove the newline character at the end. The value of signing-token must be the same as that of the token in 2.
openssl dgst -sha256 -sign
Hash the input data with the SHA-256 algorithm.
{private key}
Private key encrypted using the RSA algorithm. You can upload a private key file in .pem or .key format.
rsa_padding_mode:pss
Use the Probabilistic Signature Scheme (PSS) padding mode.
-sigopt rsa_pss_saltlen:-1
Set the salt length to the maximum value (automatically determined based on the private key size).
openssl base64
Encode the signature result using Base64 for transmission and storage.
- Username format requirements: Remove braces ({}) and separate each parameter by a vertical bar (|). Do not add vertical bars (|) in the parameter content.
- When receiving an authentication request, IoTDA determines whether to use the custom authentication mode based on the username parameter and related configuration.
- The system checks whether the username carries the custom authentication name. If yes, the authenticator processing function is matched based on the name. If no, the default custom authenticator is used to match the authentication processing function. If no matching is found, the original key/certificate authentication mode is used.
- The system checks whether signature verification is enabled. If yes, the system checks whether the signature information carried in the username can be verified. If the verification fails, an authentication failure message is returned.
- After the processing function is matched, the device authentication information (that is, the input parameter event of 5) is carried and an authentication request is sent to FunctionGraph through the function URN.
- Develop based on the processing function created with FunctionGraph in 1. Example for using the function and the JSON format of the returned result:
exports.handler = async (event, context) => { console.log("username=" + event.username); // Enter the validation logic. // Returned JSON format (fixed) const authRes = { "result_code": 200, "result_desc": "successful", "refresh_seconds": 300, "device": { "device_id": "myDeviceId", "provision_enable": true, "provisioning_resource": { "device_name": "myDeviceName", "node_id": "myNodeId", "product_id": "myProductId", "app_id": "customization0000000000000000000", "policy_ids": ["657a4e0c2ea0cb2cd831d12a", "657a4e0c2ea0cb2cd831d12b"] } } } return JSON.stringify(authRes); }Request parameters (event, in JSON format) of the function:
{ "username": "myUserName", "password": "myPassword", "client_id": "myClientId", "certificate_info": { "common_name": "", "fingerprint": "123" } }Table 4 Request parameters Parameter
Type
Mandatory
Description
username
String
Yes
The username field in the MQTT CONNECT message, the format of which is the same as that of the username field in 3.
password
String
Yes
password parameter in the MQTT CONNECT message.
client_id
String
Yes
clientId parameter in the MQTT CONNECT message.
certificate_info
JsonObject
No
Device certificate information in the MQTT CONNECT message.
Table 5 certificate_info parameters Parameter
Type
Mandatory
Description
common_name
String
Yes
Common name parsed from the device certificate carried by the device.
fingerprint
String
Yes
Fingerprint information parsed from the device certificate carried by the device.
Table 6 Returned parameters Parameter
Type
Mandatory
Description
result_code
Integer
Yes
Authentication result code. If 200 is returned, the authentication is successful.
result_desc
String
No
Description of the authentication result.
refresh_seconds
Integer
No
Cache duration of the authentication result, in seconds.
device
JsonObject
No
Device information when the authentication is successful. When self-registration is enabled, the platform creates a device based on the device information provided if the corresponding device ID does not exist.
Table 7 Device parameters Parameter
Type
Mandatory
Description
device_id
String
Yes
Definition: Globally unique device ID. Mandatory in both self-registration and non-self-registration scenarios. If this parameter is carried, the platform sets the device ID to the value of this parameter. Recommended format: product_id_node_id.
Range: The value can contain up to 128 characters. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed. You are advised to use at least 4 characters.
provision_enable
Boolean
No
Definition: Self-registration switch.
Default Value: false
provisioning_resource
JsonObject
Mandatory in the self-registration scenario
Definition: Self-registration parameters.
Table 8 provisioning_resource self-registration parameters Parameter
Type
Mandatory
Description
device_name
String
No
Definition: Device name, which uniquely identifies a device in a resource space.
Range: The value can contain up to 256 characters. Only letters, digits, and special characters (_?'#().,&%@!-) are allowed. You are advised to use at least 4 characters.
Min. characters: 1
Max. characters: 256
node_id
String
Yes
Definition: Device identifier. This parameter is set to the IMEI, MAC address, or serial number. It contains 1 to 64 characters, including letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_). (Note: Information cannot be modified once it is hardcoded to NB-IoT modules. Therefore, the node ID of an NB-IoT must be globally unique.)
Range: The value can contain up to 64 characters. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed. You are advised to use at least 4 characters.
product_id
String
Yes
Definition: Unique ID of the product associated with the device. The value is allocated by IoTDA after the product is created. Range: The value can contain up to 256 characters. Only letters, digits, and special characters (_?'#().,&%@!-) are allowed. You are advised to use at least 4 characters.
Min. characters: 1
Max. characters: 256
app_id
String
Yes
Definition: Resource space ID, which specifies the resource space to which the created device belongs.
Range: The value can contain up to 36 characters. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed.
policy_ids
List<String>
No
Definition: Topic policy ID.
Figure 5 Compiling a function - Deployment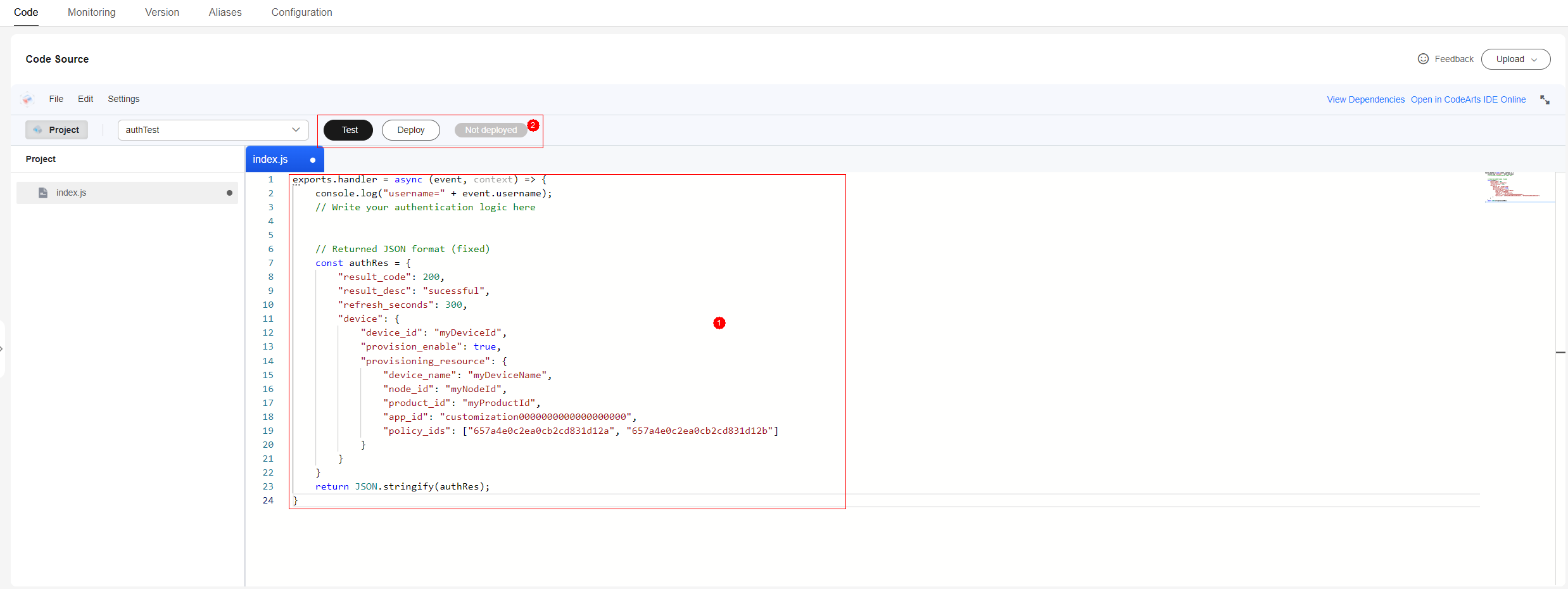
- After receiving the result, FunctionGraph checks whether the self-registration is required. If yes, FunctionGraph triggers automatic device registration. By default, all self-registered devices are authenticated using secrets, which are randomly generated. After receiving the authentication result, IoTDA proceeds with the subsequent process.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





