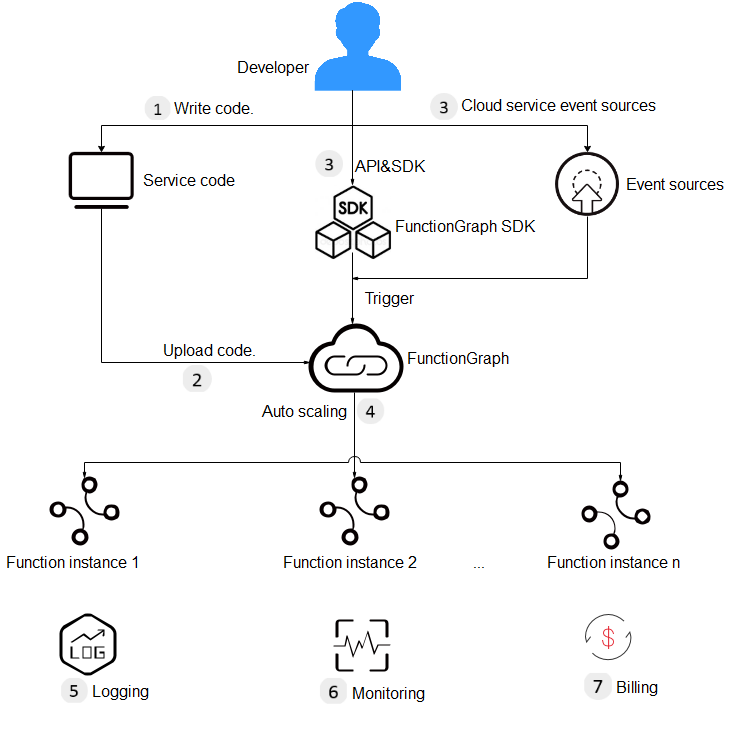
Process of Using FunctionGraph
FunctionGraph allows you to run your code without provisioning or managing servers, while ensuring high availability and scalability. All you need to do is upload your code and set execution conditions, and FunctionGraph will take care of the rest. You pay only for what you use and you are not charged when your code is not running.
To quickly create a function using FunctionGraph, do as follows:
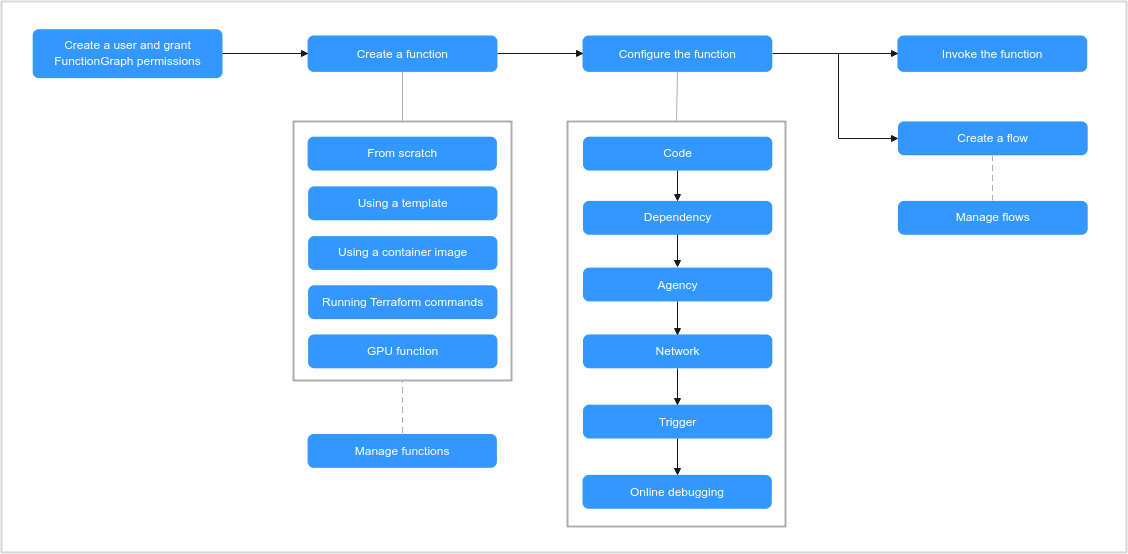
- Create a user and grant FunctionGraph permissions: Ensure that the login user has the FunctionGraph Administrator permission.
- Create a function: Create a function from scratch, using a template, by running Terraform commands, or with an image.
- Configure the function: Configure function code, dependencies, public network or VPC access, agency permissions, triggers, and online debugging.
- Invoke the function: Functions can be triggered through RESTful APIs or cloud service event sources.
- Flow: Create and manage function flows.
Process
The following shows the details:
- Write code.
Write code in Node.js, Python, Java, C#, PHP, Go, Cangjie, or custom runtimes. For details, see FunctionGraph Developer Guide.
- Upload code.
Upload the service code. You can edit code online or upload code files. For details, see Configuring Function Code and Configuring Dependencies.
- Trigger functions by API calls or cloud service events.
Functions are triggered by API calls or cloud service events. For details, see Configuring Triggers.
- Implement auto scaling.
FunctionGraph scales automatically during function execution based on the number of requests without the need for configurations. For details about concurrency restrictions, see Notes and Constraints.
- View logs.
View run logs of function as FunctionGraph is interconnected with Log Tank Service (LTS). For details, see Configuring and Viewing Function Invocation Logs.
- View monitoring information.
View graphical monitoring information. FunctionGraph is interconnected with Cloud Eye. For details, see FunctionGraph Metrics.
- Check your bills.
After function execution is complete, you will be billed based on the number of function execution requests and execution duration. For details, see .Bills.
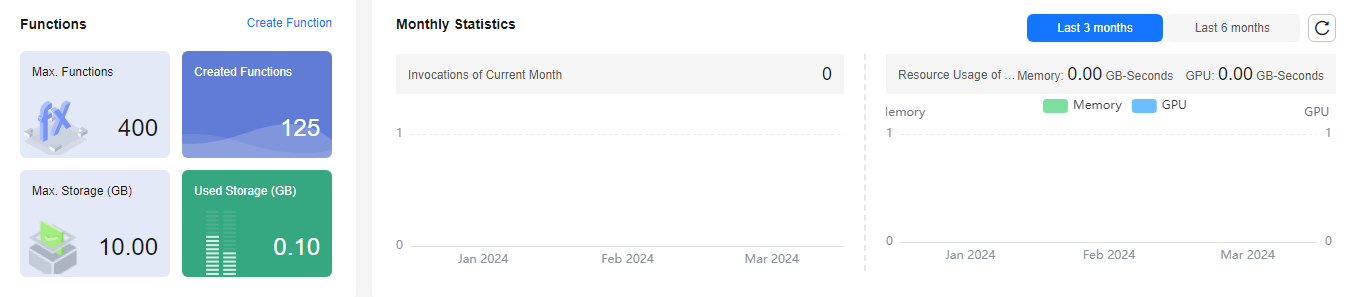
Introduction to Dashboard
- View your created functions/function quota, used storage/storage quota, and monthly invocations and resource usage.
Figure 3 Monthly statistics
- View tenant-level metrics, including invocations, top 10 functions by invocation, errors, top 10 functions by error, duration, and throttles.
Table 1 describes the function metrics.
Table 1 Function metrics Metric
Unit
Description
Invocations
Count
Total number of invocation requests, including invocation errors and throttled invocations. In case of asynchronous invocation, the count starts only when a function is executed in response to a request.
The 10 Functions with the Most Invocations
-
Top 10 functions by invocation in the last day, last 3 days, or a custom period.
Duration
ms
Maximum duration: the maximum duration all functions are executed at a time within a period.
Minimum duration: the minimum duration all functions are executed at a time within a period.
Average duration: the average duration all functions are executed at a time within a period.
Errors
Count
Number of times that your functions failed with error code 200 being returned. Errors caused by function syntax or execution are also included.
The 10 Functions with the Most Errors
-
Top 10 functions by error in the last day, last 3 days, or a custom period.
Throttles
Count
Number of times that FunctionGraph throttles your functions due to the resource limit.
- View flow metrics, including the number of invocations, duration, number of errors, and number of running workflows.
Metric
Unit
Description
Invocations
Count
Total number of invocation requests, including successful, failed, and ongoing requests. In case of asynchronous invocation, the count starts only when a flow executes in response to a request.
Duration
ms
Average time taken to execute a flow in a specified period.
Errors
Count
Number of times that flows failed to be executed.
Running Workflows
Count
Number of ongoing flow executions.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot