Forwarding Device Data to OBS for Long-Term Storage
Scenarios
If you want to store data reported by devices for a long term, you can either forward the data to applications or to Object Storage Service (OBS) for storage.
In this example, data reported by all devices is forwarded to OBS.
Creating an OBS Bucket
- Log in to Huawei Cloud and visit OBS.
- Click Access Console to go to the OBS console.
- Click Create Bucket in the upper right corner of the page, select bucket specifications as required, and click Create Now.
Figure 1 Purchasing OBS

Configuring IoTDA
Using IoTDA, you can create a product model, register a device, and set a data forwarding rule to forward data reported by the device to OBS.
Creating a rule
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose , and click Create Rule in the upper left corner.
- Set the parameters based on the table below. The following parameter values are only examples. You can create a rule by referring to Data Forwarding and click Create Rule.
Parameter
Description
Rule Name
Customize a name, for example, iotda-obs.
Description
Enter a rule description, for example, forwarding data to OBS for storage.
Data Source
Select Device property.
Trigger
Device property reported is automatically populated.
Resource Spaces
Select All resource spaces.
Figure 2 Rules triggered by property reporting - Forwarding data to OBS
- Click the Set Forwarding Target tab, and then click Add to set a forwarding target.
Parameter
Description
Forwarding Target
Select Object Storage Service (OBS).
Region
Select the region where OBS is located. If IoTDA is not authorized to access the service in this region, configure cloud service access authorization as prompted.
OBS Bucket
Select the bucket where data is to be stored. If no OBS bucket is available, create one on the OBS console.
Figure 3 Creating a forwarding target - to OBS in JSON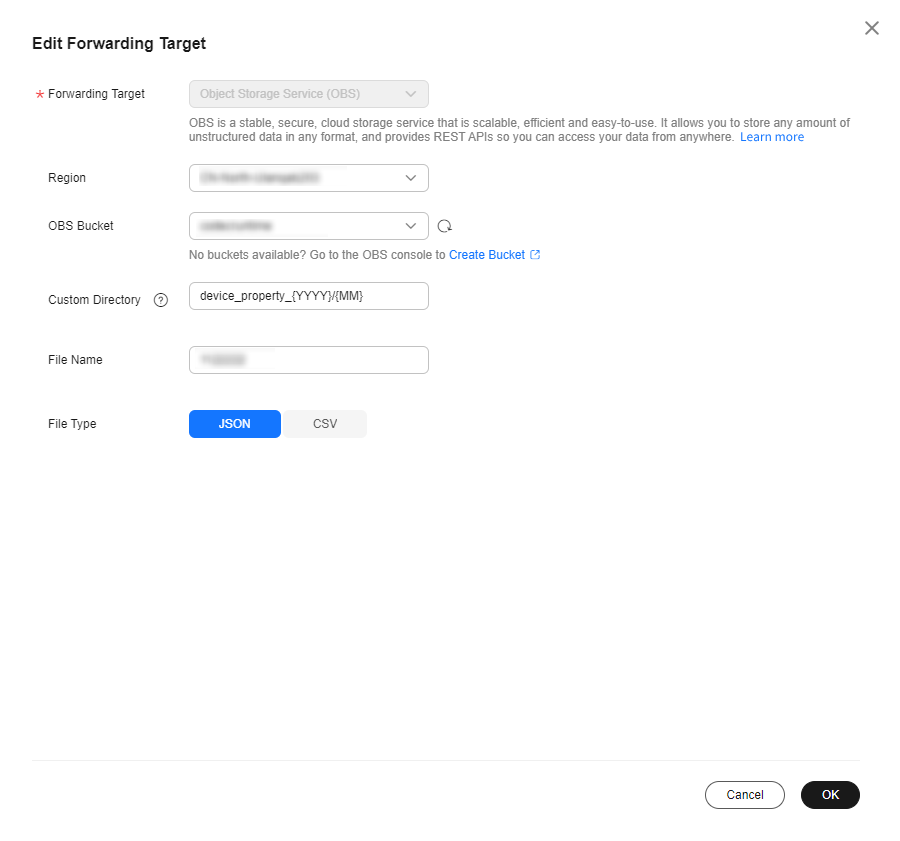
- Click Enable Rule to activate the configured data forwarding rule.
Figure 4 Enabling a rule - Forwarding data to OBS

Verifying the Configurations
- You can use a registered physical device to access the platform and enable the device to report data.
- You can also use a simulator to report data by simulating a device. For details, see Developing an MQTT-based Smart Street Light Online.
Log in to the OBS console, and click the bucket name. On the Objects page, you can view the data reported by the device.

You can also use the OBS API Downloading Objects to read files.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





