Cluster Upgrade Overview
CCE strictly complies with community consistency authentication. It releases three Kubernetes versions each year and offers a maintenance period of at least 24 months after each version is released. CCE ensures the stable running of Kubernetes versions during the maintenance period.
To ensure your service rights and benefits, upgrade your Kubernetes clusters before a maintenance period ends. You can check the Kubernetes version of your cluster on the cluster list page and check whether a new version is available. Proactive cluster upgrades help you:
- Reduce security and stability risks: During the iteration of Kubernetes versions, known security and stability vulnerabilities are continuously fixed. Long-term use of EOS clusters will result in security and stability risks to services.
- Experience the latest functions: During the iteration of Kubernetes versions, new functions and optimizations are continuously released. For details about the features of the latest version, see Release Notes for CCE Cluster Versions.
- Minimize compatibility risks: During the iteration of Kubernetes versions, APIs are continuously modified and functions are deprecated. If a cluster has not been upgraded for a long time, more O&M assurance investment will be required when the cluster is upgraded. Periodic upgrades can effectively mitigate compatibility risks caused by accumulated version differences. It is a good practice to upgrade a patch version every quarter and upgrade a major version to the latest version every year.
- Obtain more effective technical support: CCE does not provide security patches or issue fixing for EOS Kubernetes cluster versions, and does not ensure technical support for the EOS versions.
Cluster Upgrade Path
CCE clusters evolve iteratively based on the community Kubernetes version. A CCE cluster version consists of the community Kubernetes version and the CCE patch version. Therefore, two cluster upgrade paths are provided.
- Upgrading a Kubernetes version
Source Kubernetes Version
Target Kubernetes Version
v1.13 or earlier
Not supported
v1.15
v1.19
v1.17
v1.19
v1.19
v1.21 or v1.23
v1.21
v1.23
v1.23
v1.25, v1.27, or v1.28
v1.25
v1.27 or v1.28
v1.27
v1.28
v1.28
v1.29
v1.29
v1.30
- A version that has been end of maintenance cannot be directly upgraded to the latest version. You need to upgrade such a version for multiple times, for example, from v1.15 to v1.19, v1.23, and then to v1.27 or v1.28.
- A Kubernetes version can be upgraded only after the patch is upgraded to the latest version. CCE will automatically generate an optimal upgrade path on the console based on the current cluster version.
- Upgrading a patch version
Patch version management is available for CCE clusters of v1.19 or later to provide new features and fix bugs and vulnerability for in-maintenance clusters without requiring a major version upgrade.
After a new patch version is released, you can directly upgrade any patch version to the latest patch version. For details about the release history of patch versions, see Patch Version Release Notes.
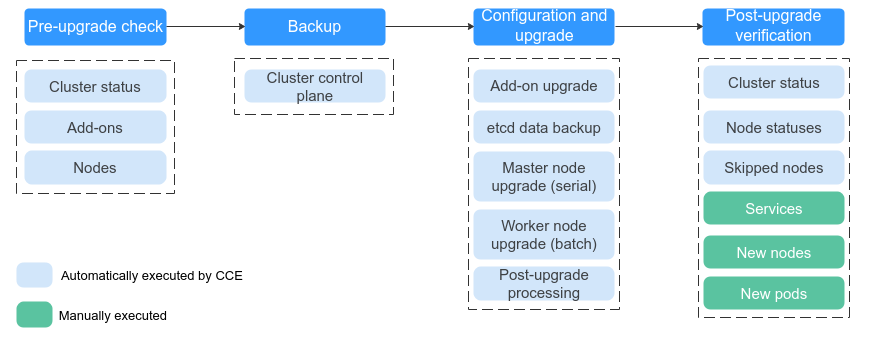
Cluster Upgrade Process
The cluster upgrade process involves pre-upgrade check, backup, upgrade, and post-upgrade verification.
After determining the target version of the cluster, read the precautions carefully and prevent function incompatibility during the upgrade.
- Pre-upgrade check
Before a cluster upgrade, CCE checks mandatory items such as the cluster status, add-ons, workload compatibility, and nodes to ensure that the cluster meets the upgrade requirements. For more details, see Pre-upgrade Check. If any check item is abnormal, rectify the fault as prompted on the console.
- Backup
You can use disk snapshots to back up master node data, including CCE component images, component configurations, and etcd data. Back up data before an upgrade. If unexpected cases occur during an upgrade, you can use the backup to quickly restore the cluster.
Backup Type
Backup Object
Backup Mode
Backup Duration
Rollback Duration
Description
etcd data backup
etcd data
Automatic backup during an upgrade
1-5 minutes
2 hours
Mandatory. The data is automatically backed up during an upgrade.
CBR cloud server backup
Master node disks, including component images, configurations, logs, and etcd data
One-click backup on a web page (manually triggered)
20 minutes to 2 hours (based on the cloud backup tasks in the current region)
20 minutes
This function is gradually replaced by EVS snapshot backup.
EVS snapshot backup
Master node disks, including component images, configurations, logs, and etcd data
One-click backup on a web page (manually triggered)
1-5 minutes
20 minutes
This function is coming soon.
After this function is released, it will replace CBR cloud server backup.
- Configuration and upgrade
Configure parameters before an upgrade. CCE has provided default settings, which can be modified as needed. After the configuration, upgrade add-ons, master nodes, and worker nodes in sequence.
- Add-on Upgrade Configuration: Add-ons that have been installed in your cluster are listed. During the cluster upgrade, CCE automatically upgrades the selected add-ons to be compatible with the target cluster version. You can click Set to re-define the add-on parameters.
If an add-on is marked with
 on its right side, the add-on cannot be compatible with both the source and target versions of the cluster upgrade. In this case, CCE will upgrade the add-on after the cluster upgrade. The add-on may be unavailable during the cluster upgrade.
on its right side, the add-on cannot be compatible with both the source and target versions of the cluster upgrade. In this case, CCE will upgrade the add-on after the cluster upgrade. The add-on may be unavailable during the cluster upgrade. - Node Upgrade Configuration
- Max. Nodes for Batch Upgrade: You can configure the maximum number of nodes to be upgraded in a batch.
Node pools will be upgraded in sequence. Nodes in node pools will be upgraded in batches. One node is upgraded in the first batch, two nodes in the second batch, and the number of nodes to be upgraded in each subsequent batch increases by a power of 2 until the maximum number of nodes to be upgraded in each batch is reached. The next cluster is upgraded after the previous one is upgraded. By default, 20 nodes are upgraded in a batch, and the number can be increased to the maximum of 120.
- Node Priority: You can customize node upgrade priorities. If the priorities are not specified, CCE will perform the upgrade based on the priorities generated by the default policy.
- Add Upgrade Priority: You can custom the priorities for upgrading node pools. If the priorities are not specified, CCE will preferentially upgrade the node pool with the least number of nodes based on the default policy.
- Add Node Priority: You can custom the priorities for upgrading nodes in a node pool. If the priorities are not specified, CCE will preferentially upgrade the node with lightest load (calculated based on the number of pods, resource request rate, and number of PVs) based on the default policy.
- Scope of Node Upgrade Batches: By default, this parameter is set to a cluster, but it can be customized.
- If the scope is set to a cluster, the upgrade batch will remain unchanged throughout the entire upgrade process.
- If the scope is set to node pools, the upgrade batch will be reset for each node pool separately.
- Max. Nodes for Batch Upgrade: You can configure the maximum number of nodes to be upgraded in a batch.
- Add-on Upgrade Configuration: Add-ons that have been installed in your cluster are listed. During the cluster upgrade, CCE automatically upgrades the selected add-ons to be compatible with the target cluster version. You can click Set to re-define the add-on parameters.
- Post-upgrade verification
After an upgrade, CCE will automatically check items including the cluster status and node status. You need to manually check services, new nodes, and new pods to ensure that the cluster functions properly after the upgrade. For details, see Performing Post-Upgrade Verification.
Upgrade Modes
|
Upgrade Mode |
Description |
Upgrade Scope |
Advantage |
Constraint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In-place upgrade |
Kubernetes components, network components, and CCE management components are upgraded on nodes. During an upgrade, service pods and networks are not affected. Nodes are upgraded in batches. Only the nodes that have been upgraded can be used to schedule services. |
|
The one-click upgrade does not need to migrate services. This ensures service continuity. |
In-place upgrade is supported only in clusters of v1.15 or later. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





