Obtaining the Client Source IP Address for a Container
When using containers, clients may communicate with them through multiple proxy servers. However, this can cause issues with transferring the clients' source IP addresses to the containers' services. This section describes how to effectively obtain the client source IP address from a container based on different network solutions provided by CCE clusters.
Description
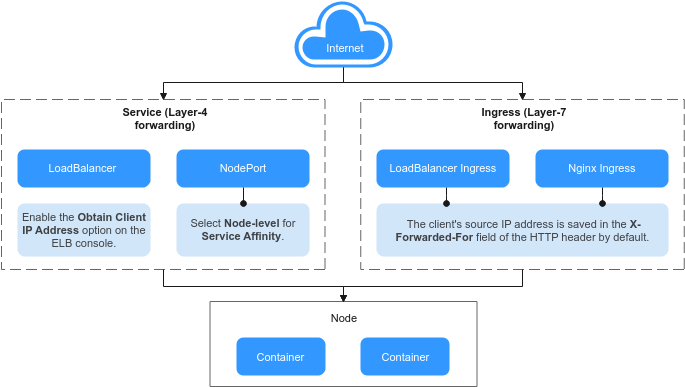
The method for obtaining source client IP addresses may vary with the network settings. The following shows some typical network configurations and their corresponding solutions:
- Ingress Layer-7 forwarding: When accessing an application at Layer-7, the client's source IP address is automatically saved in the X-Forwarded-For field of the HTTP header. No additional configurations are needed to obtain the client's source IP address.
- Service Layer-4 forwarding: The method and principle for obtaining the source IP addresses will depend on the type of Services being used.
- LoadBalancer Service: A load balancer is used as the traffic entry. Both shared and dedicated load balancers are supported.
- For a shared load balancer, you need to enable the function of obtaining client IP addresses on the listeners.
- By default, the function of obtaining client IP addresses is enabled for a dedicated load balancer listener.
- NodePort Service: Container ports are mapped to node ports, which are used as the entry for external services. The capability of obtaining client source IP addresses depends on the service affinity.
- In a cluster-level service affinity for a NodePort Service, traffic is forwarded within the cluster, which means the backend containers of the Service cannot access the client's source IP address.
- In a node-level service affinity for a NodePort Service, the traffic can directly reach the container without any forwarding. This allows the backend containers of the Service to obtain the source IP address of the client.
- LoadBalancer Service: A load balancer is used as the traffic entry. Both shared and dedicated load balancers are supported.
LoadBalancer Ingress
For the ELB Ingresses (using HTTP- or HTTPS-compliant), the function of obtaining the source IP addresses of the client is enabled by default. No other operation is required.
A client source IP address is placed in the X-Forwarded-For field of the HTTP header by the load balancer. The format is as follows:
X-Forwarded-For: <client-source-IP-address>, <proxy-server-1-IP-address>, <proxy-server-2-IP-address>, ...
The first IP address obtained from the X-Forwarded-For field is the client source IP address.
Nginx Ingress
- For an Nginx ingress that uses a dedicated load balancer, transparent transmission of source IP addresses is enabled by default. This means that you can easily obtain the source IP address of the client without any additional configurations.
- For an Nginx ingress that uses a shared load balancer, perform the following steps to obtain the source IP address of the client:
- Take the Nginx workload as an example. Before configuring the source IP address, obtain the access logs. nginx-c99fd67bb-ghv4q indicates the pod name.
kubectl logs nginx-c99fd67bb-ghv4q
Information similar to the following is displayed:
... 10.0.0.7 - - [17/Aug/2023:01:30:11 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 19 "http://114.114.114.114:9421/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/115.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/115.0.1901.203" "100.125.**.**"
100.125.**.** specifies the CIDR block of the load balancer, indicating that the traffic is forwarded through the load balancer.
- Enable Transfer Client IP Address. This operation is required only when shared load balancers are used. For dedicated load balancers, source IP address-based transparent transmission is enabled by default.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region and a project. - Choose Service List > Networking > Elastic Load Balance.
- On the Elastic Load Balance page, click the name of the target load balancer.
- Click the Listeners tab, locate the row containing the target listener, and click Edit. If modification protection exists, disable the protection on the basic information page of the listener and try again.
- Enable Transfer Client IP Address.
- Click
- Access the workload again and view the new access log.
... 10.0.0.7 - - [17/Aug/2023:02:43:11 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "http://114.114.114.114:9421/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/115.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/115.0.1901.203" "124.**.**.**"
The source IP address of the client is obtained.
You can enable WAF for the load balancers used by Nginx Ingress Controllers in clusters, but different WAF modes will affect how Nginx Ingress Controllers obtain the real client IP addresses.
- Load balancer access in WAF cloud CNAME access mode
When using the cloud CNAME access mode, requests go through WAF and are checked for protection before being sent to the load balancer. This means that even if the load balancer has transparent transmission of source IP addresses enabled, the client will receive the back-to-source IP address of WAF. Consequently, the Nginx Ingress Controller is unable to obtain the real client IP address by default. In this case, you can edit the NGINX Ingress Controller add-on and add the following configuration to the add-on parameters:
{ "enable-real-ip": "true", "use-forwarded-headers": "true", "proxy-real-ip-cidr": <Back-to-source IP address you obtained from WAF> }
- Load balancer access in the cloud WAF mode
This mode is transparent access (non-inline deployment) and supports only dedicated load balancers. In this mode, Nginx Ingress Controllers can obtain the real client IP address by default.
LoadBalancer
- CCE Clusters (using VPC or Tunnel network): Source IP addresses can be obtained when either a shared or dedicated load balancer is used.
- CCE Turbo Clusters (using the Cloud Native Network 2.0): Source IP addresses can be obtained for dedicated load balancers, and for shared load balancers with hostNetwork enabled.
VPC and Container Tunnel Network Models
To enable the function of obtaining the source IP address on the console, perform the following steps:
- When creating a LoadBalancer Service on the CCE console, set Service Affinity to Node-level instead of Cluster-level.
- Go to the ELB console and enable the function of obtaining the client IP address of the listener corresponding to the load balancer. Transparent transmission of source IP addresses is enabled for dedicated load balancers by default. You do not need to manually enable this function.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region and a project. - Choose Service List > Networking > Elastic Load Balance.
- On the Elastic Load Balance page, click the name of the target load balancer.
- Click the Listeners tab, locate the row containing the target listener, and click Edit. If modification protection exists, disable the protection on the basic information page of the listener and try again.
- Enable Transfer Client IP Address.
- Click
Cloud Native 2.0 Network Model (CCE Turbo Clusters)
- For workloads with hostNetwork enabled, you can set Service Affinity to Node-level to obtain the source IP addresses.
- For other workloads, you cannot set Service Affinity to Node-level, so the source IP addresses cannot be obtained.
Dedicated load balancers are recommended. External access can be directly sent to containers. By default, transparent transmission of source IP addresses is enabled for dedicated load balancers. You do not need to manually enable Transfer Client IP Address on the ELB console. Instead, you only need to select a dedicated load balancer when creating a LoadBalancer Service on the CCE console.
NodePort
Set the service affinity of a NodePort Service to Node-level instead of Cluster-level. That is, set spec.externalTrafficPolicy of the Service to Local.
In clusters using Cloud Native 2.0 networks, if NodePort Services are used, only workloads with hostNetwork enabled support node-level service affinity. Therefore, only such workloads can obtain source IP addresses.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





