StorageClasses are resource objects that define storage types in Kubernetes. They enable dynamic provisioning of storage volumes. Once you modify the parameter settings of a StorageClass, it can automatically provision and adjust storage resources based on service requirements. When you specify a StorageClass name (StorageClassName) in a PVC, Kubernetes will automatically provision a PV and the underlying storage resources based on the requirements declared in the PVC. If no matching PV is found in the cluster, Kubernetes will call the target provisioner specified in the StorageClass to create a new PV and storage resources. This simplifies the process of manually creating and maintaining PVs. The StorageClass defines default parameters for storage provisioning. If there are conflicts between the StorageClass settings and the PVC settings, the PVC settings will take precedence.
If CCE's default StorageClasses (listed in Table 3) do not meet your service needs, you can customize StorageClasses by setting parameters such as reclaim policies and binding modes.
Creating a StorageClass
CCE allows you to create a StorageClass via the console or kubectl. kubectl provides additional parameters for enhanced flexibility. Choose a method that best suits your needs.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- Choose Storage in the navigation pane. In the right pane, click the Storage Classes tab. Click Create Storage Class in the upper right corner. In the dialog box displayed, configure parameters.
Figure 1 Create StorageClass
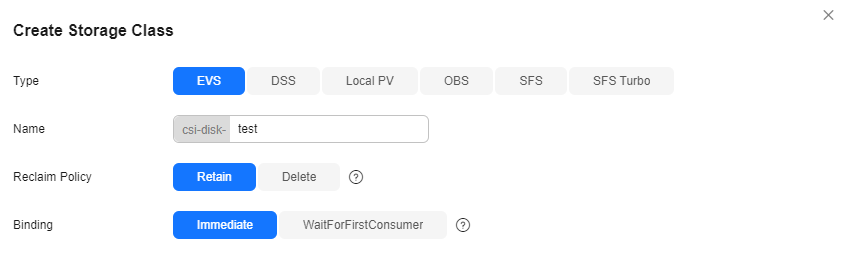
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Type |
The type of the underlying storage. |
|
Name |
The StorageClass name. The name of a StorageClass must be unique within a cluster. |
|
Reclaim Policy |
The policy for reclaiming the underlying storage when the PVC is deleted. For details, see PV Reclaim Policy.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, its associated underlying storage resources are deleted and the PV resources are removed. Exercise caution if you select this option.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, the associated PV and underlying storage resources are retained and need to be manually deleted.
|
|
Binding |
When a PV is dynamically created, either immediately or with a delay.
- Immediate: When a PVC is created, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC immediately, without delay. Local PVs do not support Immediate.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: When a PVC is created, it is not immediately bound to a PV. Instead, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC only after the pod that requires the PVC is scheduled. OBS, SFS, and SFS Turbo do not support WaitForFirstConsumer.
|
- Click Create. On the Storage Classes tab, view the created StorageClass and its information.
This section provides several StorageClass templates. You can choose the one that best suits your needs to quickly create a StorageClass resource.
- Use kubectl to access the cluster (Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl).
- Create a YAML file for the StorageClass. The file name is customizable.
vim evs-storageclass.yaml
The file content is as follows:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-disk-evs
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false" # (Optional) Specify the default StorageClass in a cluster. Only one default StorageClass is allowed per cluster.
provisioner: everest-csi-provisioner
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: disk.csi.everest.io
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
everest.io/disk-volume-type: GPSSD2
everest.io/enterprise-project-id: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx # The specified enterprise project ID. This parameter is only available for accounts with an enterprise project enabled.
everest.io/passthrough: 'true'
everest.io/disk-iops: '3000' # This parameter is only available for General Purpose SSD v2 disks.
everest.io/disk-throughput: '100' # This parameter is only available for General Purpose SSD v2 disks.
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: true
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
mountOptions: [] # This parameter is optional and is supported only by certain StorageClasses. If it is not supported by the specified StorageClass, delete this parameter.
Table 1 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
metadata.annotations.storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class |
The default StorageClass. Configure only one default StorageClass per cluster. If multiple default StorageClasses exist, CCE will not report an error, but the behavior may be unpredictable.
- true: The current StorageClass is the default one. If StorageClassName is not explicitly specified when you create a PVC, CCE will use the default StorageClass.
- false or not set: The current StorageClass is not the default one.
|
|
provisioner |
The storage resource provisioner. CCE storage is provided by Everest. You can only enter everest-csi-provisioner. |
|
parameters |
The configuration parameters of a StorageClass. For details, see Table 2. |
|
reclaimPolicy |
The policy for reclaiming the underlying storage when the PVC is deleted. For details, see PV Reclaim Policy. If this parameter is not specified, the default value Delete will be used.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, its associated underlying storage resources will be deleted and the PV resources will be removed. Exercise caution if you select this option.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, both of the PV and its associated underlying storage resources will be retained and the PV is marked as released. If you manually delete the PV afterwards, the underlying storage resources will not be deleted. To bind the PV to a new PVC, you need to remove the original binding information from the PV.
|
|
allowVolumeExpansion |
Whether the PVs provisioned by a StorageClass can be dynamically expanded by modifying the PVC. The default value is false.
This parameter is used to enable dynamic capacity expansion. Whether this function applies depends on the underlying storage add-on. If the underlying storage add-on does not support dynamic capacity expansion, the capacity cannot be expanded even if this parameter is set to true. Only EVS and SFS Turbo (without subdirectories or with limited subdirectories) support dynamic capacity expansion. |
|
volumeBindingMode |
How a volume is bound when a PV is dynamically created. The value can be Immediate or WaitForFirstConsumer.
- Immediate: When a PVC is created, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC immediately, without delay.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: When a PVC is created, it is not immediately bound to a PV. Instead, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC only after the pod that requires the PVC is scheduled.
|
|
mountOptions |
Parameters used to mount volumes, which control the mounting behavior (such as read-only and buffer policies). You can configure mount options for EVS disks. For details, see Configuring EVS Mount Options. |
Table 2 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Description |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name |
Yes |
The driver type. If an EVS disk is used, the parameter value is fixed at disk.csi.everest.io. |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype |
Yes |
The file system type used by a CSI driver to create storage volumes. If an EVS disk is used, the parameter value can be ext4. |
|
everest.io/disk-volume-type |
Yes |
EVS disk type. All letters are in uppercase.
- SAS: high I/O
- SSD: ultra-high I/O
- GPSSD: general-purpose SSD
- ESSD: extreme SSD
- GPSSD2: general-purpose SSD v2, which is supported when the Everest version is 2.4.4 or later and the everest.io/disk-iops and everest.io/disk-throughput annotations are configured
|
|
everest.io/enterprise-project-id |
No |
The ID of the enterprise project to which the underlying storage resources belong. This parameter is available only to enterprise accounts with enterprise projects enabled. Set this parameter to the enterprise project to which the cluster belongs or the default enterprise project to centrally manage resources. For more details, see Enterprise Management.
To obtain an enterprise project ID, log in to the EPS console, click the name of the target enterprise project, and copy the enterprise project ID.
NOTE:
To use this function, the Everest add-on must be upgraded to v1.2.33 or later.
|
|
everest.io/passthrough |
Yes |
The parameter value is fixed at true. This indicates that the EVS device type is SCSI. No other parameter values are allowed. |
|
everest.io/disk-iops |
No |
The IOPS of the underlying storage. This parameter is only available for General Purpose SSD v2 disks.
|
|
everest.io/disk-throughput |
No |
The throughput of the underlying storage. This parameter is only available for General Purpose SSD v2 disks. The value ranges from 125 MiB/s to 1,000 MiB/s. The maximum value is a quarter of IOPS.
If the throughput is greater than 125 MiB/s, extra throughput will be billed. For details, see Price Calculator. |
- Create the StorageClass.
kubectl apply -f evs-storageclass.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-disk-evs created
- Check details of csi-disk-evs.
kubectl describe sc csi-disk-evs
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Name: csi-disk-evs
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"allowVolumeExpansion":true,"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"csi-disk-evs"},......
- Use kubectl to access the cluster (Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl).
- Create a YAML file for the StorageClass. The file name is customizable.
vim sfs-storageclass.yaml
The file content is as follows:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-nas-sfs3
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false" # (Optional) Specify the default StorageClass in a cluster. Only one default StorageClass is allowed per cluster.
provisioner: everest-csi-provisioner
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: nas.csi.everest.io
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: nfs
everest.io/share-access-level: rw
everest.io/share-access-to: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx
everest.io/sfs-version: 'sfs3.0' # This parameter is only required for general purpose file systems (SFS 3.0 Capacity-Oriented) and its value is fixed at sfs3.0.
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: false
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
mountOptions: [] # This parameter is optional and is supported only by certain StorageClasses. If it is not supported by the specified StorageClass, delete this parameter.
Table 3 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
metadata.annotations.storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class |
The default StorageClass. Configure only one default StorageClass per cluster. If multiple default StorageClasses exist, CCE will not report an error, but the behavior may be unpredictable.
- true: The current StorageClass is the default one. If StorageClassName is not explicitly specified when you create a PVC, CCE will use the default StorageClass.
- false or not set: The current StorageClass is not the default one.
|
|
provisioner |
The storage resource provisioner. CCE storage is provided by Everest. You can only enter everest-csi-provisioner. |
|
parameters |
The configuration parameters of a StorageClass. For details, see Table 4. |
|
reclaimPolicy |
The policy for reclaiming the underlying storage when the PVC is deleted. For details, see PV Reclaim Policy. If this parameter is not specified, the default value Delete will be used.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, its associated underlying storage resources will be deleted and the PV resources will be removed. Exercise caution if you select this option.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, both of the PV and its associated underlying storage resources will be retained and the PV is marked as released. If you manually delete the PV afterwards, the underlying storage resources will not be deleted. To bind the PV to a new PVC, you need to remove the original binding information from the PV.
|
|
allowVolumeExpansion |
Whether the PVs provisioned by a StorageClass can be dynamically expanded by modifying the PVC. The default value is false.
This parameter is used to enable dynamic capacity expansion. Whether this function applies depends on the underlying storage add-on. If the underlying storage add-on does not support dynamic capacity expansion, the capacity cannot be expanded even if this parameter is set to true. Only EVS and SFS Turbo (without subdirectories or with limited subdirectories) support dynamic capacity expansion. |
|
volumeBindingMode |
How a volume is bound when a PV is dynamically created. The value can be Immediate or WaitForFirstConsumer. SFS supports only Immediate.
- Immediate: When a PVC is created, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC immediately, without delay.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: When a PVC is created, it is not immediately bound to a PV. Instead, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC only after the pod that requires the PVC is scheduled.
|
|
mountOptions |
Parameters used to mount volumes, which control the mounting behavior (such as read-only and buffer policies). You can configure mount options for SFS file systems. For details, see Configuring SFS Volume Mount Options. |
Table 4 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Description |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name |
Yes |
The driver type. If SFS is used, the parameter value is fixed at nas.csi.everest.io. |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype |
Yes |
The file system type used for mounting the storage volume. If SFS is used, the value can be nfs. |
|
everest.io/share-access-level |
Yes |
The parameter value is fixed at rw. This indicates that the SFS data is readable and writable. |
|
everest.io/share-access-to |
Yes |
The VPC ID of the cluster.
To obtain the ID, go to the cluster overview page, find VPC in the Networking Configuration pane, hover over the target VPC, and copy the VPC ID. |
|
everest.io/share-is-public |
No |
The parameter value is fixed at false. This indicates that the file is shared to private.
When you use a general purpose file system (SFS 3.0 Capacity-Oriented), there is no need to configure this parameter. |
|
everest.io/sfs-version |
No |
This parameter is only required for general purpose file systems (SFS 3.0 Capacity-Oriented) and its value is fixed at sfs3.0. |
- Create the StorageClass.
kubectl apply -f sfs-storageclass.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-nas-sfs3 created
- Check details of csi-nas-sfs3.
kubectl describe sc csi-nas-sfs3
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Name: csi-nas-sfs3
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"allowVolumeExpansion":true,"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"false"},...
- Use kubectl to access the cluster (Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl).
- Create a YAML file for the StorageClass. The file name is customizable.
vim sfsturbo-storageclass.yaml
The file content is as follows:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-sfsturbo-test1
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false" # (Optional) Specify the default StorageClass in a cluster. Only one default StorageClass is allowed per cluster.
provisioner: everest-csi-provisioner
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: sfsturbo.csi.everest.io
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: nfs
everest.io/reclaim-policy: retain-volume-only
everest.io/share-expand-type: bandwidth
everest.io/share-source: sfs-turbo
everest.io/share-volume-type: STANDARD
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: true
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
Table 5 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
metadata.annotations.storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class |
The default StorageClass. Configure only one default StorageClass per cluster. If multiple default StorageClasses exist, CCE will not report an error, but the behavior may be unpredictable.
- true: The current StorageClass is the default one. If StorageClassName is not explicitly specified when you create a PVC, CCE will use the default StorageClass.
- false or not set: The current StorageClass is not the default one.
|
|
provisioner |
The storage resource provisioner. CCE storage is provided by Everest. You can only enter everest-csi-provisioner. |
|
parameters |
The configuration parameters of a StorageClass. For details, see Table 6. |
|
reclaimPolicy |
The policy for reclaiming the underlying storage when the PVC is deleted. For details, see PV Reclaim Policy. If this parameter is not specified, the default value Delete will be used.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, its associated underlying storage resources will be deleted and the PV resources will be removed. Exercise caution if you select this option.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, both of the PV and its associated underlying storage resources will be retained and the PV is marked as released. If you manually delete the PV afterwards, the underlying storage resources will not be deleted. To bind the PV to a new PVC, you need to remove the original binding information from the PV.
|
|
allowVolumeExpansion |
Whether the PVs provisioned by a StorageClass can be dynamically expanded by modifying the PVC. The default value is false.
This parameter is used to enable dynamic capacity expansion. Whether this function applies depends on the underlying storage add-on. If the underlying storage add-on does not support dynamic capacity expansion, the capacity cannot be expanded even if this parameter is set to true. Only EVS and SFS Turbo (without subdirectories or with limited subdirectories) support dynamic capacity expansion. |
|
volumeBindingMode |
How a volume is bound when a PV is dynamically created. The value can be Immediate or WaitForFirstConsumer. SFS Turbo supports only Immediate.
- Immediate: When a PVC is created, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC immediately, without delay.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: When a PVC is created, it is not immediately bound to a PV. Instead, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC only after the pod that requires the PVC is scheduled.
|
Table 6 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Description |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name |
Yes |
The driver type. If SFS Turbo is used, the parameter value is fixed at sfsturbo.csi.everest.io. |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype |
Yes |
The file system type used for mounting the storage volume. If SFS Turbo is used, the value can be nfs. |
|
everest.io/share-expand-type |
No |
The expansion type. The default value is bandwidth, indicating an enhanced file system.
This field has been deprecated and is no longer effective. |
|
everest.io/share-source |
Yes |
The parameter value is fixed at sfs-turbo. |
|
everest.io/share-volume-type |
No |
The SFS Turbo StorageClass. The default value is STANDARD, indicating both the standard and standard enhanced editions.
This field has been deprecated and is no longer effective. |
|
everest.io/reclaim-policy |
No |
Whether to retain subdirectories when deleting a PVC. This parameter must be used with reclaimPolicy. This parameter is available only when the PV reclaim policy is Delete. Options:
- retain-volume-only: When a PVC is deleted, the PV is deleted, but its associated subdirectories are retained.
- delete: When a PVC is deleted, the PV and its associated subdirectories are also deleted.
NOTE:
When a subdirectory is deleted, only the absolute path of the subdirectory specified in the PVC is deleted. The parent directory is retained.
|
- Create the StorageClass.
kubectl apply -f sfsturbo-storageclass.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-sfsturbo-test1 created
- Check details of csi-sfsturbo-test1.
kubectl describe sc csi-sfsturbo-test1
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Name: csi-sfsturbo-test1
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"allowVolumeExpansion":false,"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"false"},...
- Use kubectl to access the cluster (Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl).
- Create a YAML file for the StorageClass. The file name is customizable.
vim obs-storageclass.yaml
The file content is as follows:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-obs-test1
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false" # (Optional) Specify the default StorageClass in a cluster. Only one default StorageClass is allowed per cluster.
provisioner: everest-csi-provisioner
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: obs.csi.everest.io
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: s3fs
everest.io/obs-volume-type: STANDARD
everest.io/enterprise-project-id: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx # The specified enterprise project ID. This parameter is only available for accounts with an enterprise project enabled.
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
mountOptions: [] # This parameter is optional and is supported only by certain StorageClasses. If it is not supported by the specified StorageClass, delete this parameter.
Table 7 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
metadata.annotations.storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class |
The default StorageClass. Configure only one default StorageClass per cluster. If multiple default StorageClasses exist, CCE will not report an error, but the behavior may be unpredictable.
- true: The current StorageClass is the default one. If StorageClassName is not explicitly specified when you create a PVC, CCE will use the default StorageClass.
- false or not set: The current StorageClass is not the default one.
|
|
provisioner |
The storage resource provisioner. CCE storage is provided by Everest. You can only enter everest-csi-provisioner. |
|
parameters |
The configuration parameters of a StorageClass. For details, see Table 8. |
|
reclaimPolicy |
The policy for reclaiming the underlying storage when the PVC is deleted. For details, see PV Reclaim Policy. If this parameter is not specified, the default value Delete will be used.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, its associated underlying storage resources will be deleted and the PV resources will be removed. Exercise caution if you select this option.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, both of the PV and its associated underlying storage resources will be retained and the PV is marked as released. If you manually delete the PV afterwards, the underlying storage resources will not be deleted. To bind the PV to a new PVC, you need to remove the original binding information from the PV.
|
|
volumeBindingMode |
How a volume is bound when a PV is dynamically created. The value can be Immediate or WaitForFirstConsumer. OBS supports only Immediate.
- Immediate: When a PVC is created, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC immediately, without delay.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: When a PVC is created, it is not immediately bound to a PV. Instead, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC only after the pod that requires the PVC is scheduled.
|
|
mountOptions |
Parameters used to mount volumes, which control the mounting behavior (such as read-only and buffer policies). You can configure mount options for OBS volumes. For details, see Configuring OBS Mount Options. |
Table 8 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Description |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name |
Yes |
The driver type. If OBS is used, the parameter value is fixed at obs.csi.everest.io. |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype |
Yes |
The instance type, which can be obsfs or s3fs.
- obsfs: a parallel file system
- s3fs: an object bucket
|
|
everest.io/obs-volume-type |
Yes |
The OBS StorageClass.
- If fsType is set to s3fs, standard buckets (STANDARD) and infrequent access buckets (WARM) are supported.
- This parameter is invalid when fsType is set to obsfs.
|
|
everest.io/enterprise-project-id |
No |
The ID of the enterprise project to which the underlying storage resources belong. This parameter is available only to enterprise accounts with enterprise projects enabled. Set this parameter to the enterprise project to which the cluster belongs or the default enterprise project to centrally manage resources. For more details, see Enterprise Management.
To obtain an enterprise project ID, log in to the EPS console, click the name of the target enterprise project, and copy the enterprise project ID.
NOTE:
To use this function, the Everest add-on must be upgraded to v1.2.33 or later.
|
- Create the StorageClass.
kubectl apply -f obs-storageclass.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-obs-test1 created
- Check details of csi-obs-test1.
kubectl describe sc csi-obs-test1
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Name: csi-obs-test1
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"false"},......
- Use kubectl to access the cluster (Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl).
- Create a YAML file for the StorageClass. The file name is customizable.
vim dss-storageclass.yaml
The file content is as follows:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-disk-dsstest
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false" # (Optional) Specify the default StorageClass in a cluster. Only one default StorageClass is allowed per cluster.
provisioner: everest-csi-provisioner
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: disk.csi.everest.io
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
everest.io/disk-volume-type: SSD
everest.io/passthrough: 'true'
everest.io/resource-type: dss
everest.io/enterprise-project-id: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx # The specified enterprise project ID. This parameter is only available for accounts with an enterprise project enabled.
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: false
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
Table 9 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
metadata.annotations.storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class |
The default StorageClass. Configure only one default StorageClass per cluster. If multiple default StorageClasses exist, CCE will not report an error, but the behavior may be unpredictable.
- true: The current StorageClass is the default one. If StorageClassName is not explicitly specified when you create a PVC, CCE will use the default StorageClass.
- false or not set: The current StorageClass is not the default one.
|
|
provisioner |
The storage resource provisioner. CCE storage is provided by Everest. You can only enter everest-csi-provisioner. |
|
parameters |
The configuration parameters of a StorageClass. For details, see Table 10. |
|
reclaimPolicy |
The policy for reclaiming the underlying storage when the PVC is deleted. For details, see PV Reclaim Policy. If this parameter is not specified, the default value Delete will be used.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, its associated underlying storage resources will be deleted and the PV resources will be removed. Exercise caution if you select this option.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, both of the PV and its associated underlying storage resources will be retained and the PV is marked as released. If you manually delete the PV afterwards, the underlying storage resources will not be deleted. To bind the PV to a new PVC, you need to remove the original binding information from the PV.
|
|
allowVolumeExpansion |
Whether the PVs provisioned by a StorageClass can be dynamically expanded by modifying the PVC. The default value is false.
This parameter is used to enable dynamic capacity expansion. Whether this function applies depends on the underlying storage add-on. If the underlying storage add-on does not support dynamic capacity expansion, the capacity cannot be expanded even if this parameter is set to true. Only EVS and SFS Turbo (without subdirectories or with limited subdirectories) support dynamic capacity expansion. |
|
volumeBindingMode |
How a volume is bound when a PV is dynamically created. The value can be Immediate or WaitForFirstConsumer.
- Immediate: When a PVC is created, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC immediately, without delay.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: When a PVC is created, it is not immediately bound to a PV. Instead, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC only after the pod that requires the PVC is scheduled.
|
Table 10 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Description |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name |
Yes |
The driver type. If DSS is used, the parameter value is fixed at disk.csi.everest.io. |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype |
Yes |
The file system type. The value can only be ext4. |
|
everest.io/disk-volume-type |
Yes |
The dedicated storage, which must be specified in uppercase.
- SAS: high I/O
- SSD: ultra-high I/O
|
|
everest.io/passthrough |
Yes |
The parameter value is fixed at true. This indicates that the DSS device type is SCSI. No other values are allowed. |
|
everest.io/resource-type |
Yes |
The resource type. The parameter value is fixed at dss. |
|
everest.io/enterprise-project-id |
No |
The ID of the enterprise project to which the underlying storage resources belong. This parameter is available only to enterprise accounts with enterprise projects enabled. Set this parameter to the enterprise project to which the cluster belongs or the default enterprise project to centrally manage resources. For more details, see Enterprise Management.
To obtain an enterprise project ID, log in to the EPS console, click the name of the target enterprise project, and copy the enterprise project ID.
NOTE:
To use this function, the Everest add-on must be upgraded to v1.2.33 or later.
|
- Create the StorageClass.
kubectl apply -f dss-storageclass.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-disk-dsstest created
- Check details of csi-disk-dsstest.
kubectl describe sc csi-disk-dsstest
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Name: csi-disk-dsstest
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"false"},...
- Use kubectl to access the cluster (Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl).
- Create a YAML file for the StorageClass. The file name is customizable.
vim local-storageclass.yaml
The file content is as follows:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: csi-local-test
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false" # (Optional) Specify the default StorageClass in a cluster. Only one default StorageClass is allowed per cluster.
provisioner: everest-csi-provisioner
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: local.csi.everest.io
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
volume-type: persistent
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
Table 11 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
metadata.annotations.storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class |
The default StorageClass. Configure only one default StorageClass per cluster. If multiple default StorageClasses exist, CCE will not report an error, but the behavior may be unpredictable.
- true: The current StorageClass is the default one. If StorageClassName is not explicitly specified when you create a PVC, CCE will use the default StorageClass.
- false or not set: The current StorageClass is not the default one.
|
|
provisioner |
The storage resource provisioner. CCE storage is provided by Everest. You can only enter everest-csi-provisioner. |
|
parameters |
The configuration parameters of a StorageClass. For details, see Table 12. |
|
reclaimPolicy |
The policy for reclaiming the underlying storage when the PVC is deleted. For details, see PV Reclaim Policy. If this parameter is not specified, the default value Delete will be used.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, its associated underlying storage resources will be deleted and the PV resources will be removed. Exercise caution if you select this option.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, both of the PV and its associated underlying storage resources will be retained and the PV is marked as released. If you manually delete the PV afterwards, the underlying storage resources will not be deleted. To bind the PV to a new PVC, you need to remove the original binding information from the PV.
|
|
volumeBindingMode |
How a volume is bound when a PV is dynamically created. The value can be Immediate or WaitForFirstConsumer. Local PVs support only WaitForFirstConsumer.
- Immediate: When a PVC is created, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC immediately, without delay.
- WaitForFirstConsumer: When a PVC is created, it is not immediately bound to a PV. Instead, the storage resources and PV are created and bound to the PVC only after the pod that requires the PVC is scheduled.
|
Table 12 Parameters
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Description |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name |
Yes |
The driver type. If a local PV is used, the parameter value is fixed at local.csi.everest.io. |
|
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype |
Yes |
The file system type. The value can only be ext4. |
|
volume-type |
Yes |
The volume type. The value can only be persistent. |
- Create the StorageClass.
kubectl apply -f dss-storageclass.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-local-test created
- Check details of csi-local-test.
kubectl describe sc csi-local-test
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Name: csi-local-test
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"false"},...
Applications of Custom StorageClasses
The following provides typical applications of custom StorageClasses:
- Meeting customized requirements and simplifying batch operations: You can customize parameters such as reclaimPolicy and volumeBindingMode to flexibly meet diverse service needs. This avoids the need for repeated parameter configuration when batch-creating PVCs, thereby simplifying the operation process and improving management efficiency.
- Supporting smooth migration and reducing modification costs: When migrating from a custom-built Kubernetes cluster or Kubernetes services of another cloud vendor to CCE, you can create a StorageClass with the same name as that in the original environment. This allows the storageClassName in the YAML file or Helm chart to remain unchanged, effectively avoiding the operational burden and error risks associated with manually modifying a large number of configurations. For example, if the StorageClass used before the migration is named disk-standard, you can copy the YAML file of the StorageClass csi-disk, change its name to disk-standard, and create the StorageClass again.
- Setting the default StorageClass: When creating a StorageClass, you can set it as the default by using metadata.annotations.storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class. After the setting, you do not need to explicitly specify storageClassName when creating a PVC. CCE will automatically use the default StorageClass, simplifying resource declaration.
- Associating a StorageClass with an enterprise project for unified resource management: When creating a StorageClass, you can associate it with an enterprise project by specifying parameters.everest.io/enterprise-project-id. This links the underlying storage resources to the enterprise project, facilitating subsequent resource classification management and cost accounting.
Helpful Links
Before using a new StorageClass, you only need to specify it in the storageClassName field of the target PVC. The parameter settings of the StorageClass will be used by default. If there are conflicts between the StorageClass settings and those specified in the PVC, the PVC's settings will take precedence.
To simplify the manual creation and maintenance of PVs, see the following resources:







