Maximum Number of Pods That Can Be Created on a Node
Calculation of the Maximum Number of Pods on a Node
The maximum number of pods that can be created on a node is calculated based on the cluster type.
|
Network Model |
Maximum Number of Pods on a Node |
Recommended Configuration |
|---|---|---|
|
Tunnel network |
None |
|
|
VPC network |
The smaller value between the Maximum Number of Pods on a Node and Number of Reserved Pod IP Addresses Per Node |
To ensure that new pods run smoothly on a node, verify that the maximum number of pods on the node does not exceed the number of allocatable pod IP addresses. If the node lacks sufficient pod IP addresses, new pods will not function properly. |
|
Cloud Native Network 2.0 (for CCE Turbo clusters) |
The smaller value between the maximum number of pods on a node and the number of network interfaces on a node in a CCE Turbo cluster |
To ensure new pods run smoothly on a node, make sure that the number of pods on the node does not exceed the number of network interfaces on it. If there are not enough network interfaces available on the node, the new pods may not function properly. |
Number of Reserved Pod IP Addresses Per Node
When creating a cluster in the VPC network model, follow the rules for managing pod IP addresses and specify the number of pod IP addresses that each node can allocate using alpha.cce/fixPoolMask.
The maximum number of pods that can be created on a node is determined by the number of pod IP addresses available for allocation. In a containerized environment, each pod requires its own unique IP address. If the node runs out of reserved pod IP addresses, new pods cannot be created. If hostNetwork: true is configured in the YAML file, pods will use the host network instead of the reserved pod IP addresses. For details, see Pod IP Address Allocation Differences Between the Container Network and Host Network.
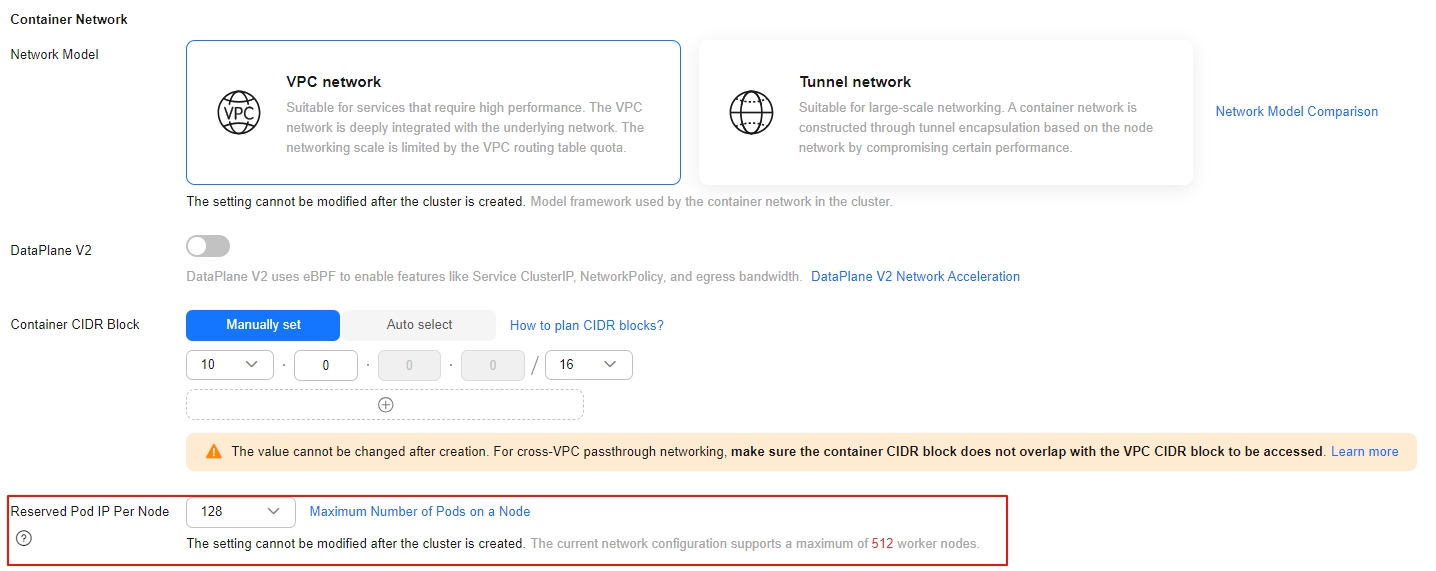
By default, each node in a cluster is assigned a CIDR block from which pod IP addresses are allocated. The usable number of IP addresses for pods within this block is typically the total number of addresses in the CIDR block minus three reserved addresses (including the network address, gateway address, and broadcast address). For example, in the preceding figure, the usable number of IP addresses for pods is 125 (128 – 3).
Maximum Number of Pods on a Node
When creating a node, you can configure the maximum number of pods (Max. Pods) that can be created on the node. This parameter is a configuration item of kubelet and determines the maximum number of pods that can be created by kubelet.

For nodes in the default node pool (DefaultPool), the maximum number of pods cannot be changed after the nodes are created.
After a node in a custom node pool is created, you can modify Max. Pods in the node pool configuration to change the maximum number of pods on the node. For details, see Configuring a Node Pool.

Table 1 lists the default maximum number of pods on a node based on node specifications.
Number of Node Network Interfaces (Available Only for CCE Turbo Clusters)
In a CCE Turbo cluster, ECS nodes use supplementary network interfaces and BMS nodes use network interfaces. The maximum number of pods that can be created on a node depends on the number of network interfaces that can be used by the node.

Pod IP Address Allocation Differences Between the Container Network and Host Network
When creating a pod, you can select the container network or host network for the pod.
- Container network (default): Each pod is assigned an IP address from the container network by the cluster networking add-ons.
- Host network: Pods with hostNetwork: true configured directly use the network of the host. For details, see Configuring hostNetwork for Pods. After the configuration, the pods use the ports on the host and their IP address is identical to that of the host, without relying on the IP addresses of the container network. When using a host network, avoid conflicts between the pod ports and service ports on the host. Use a host network only if a particular application requires access to a specific port on the host.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





