Monitoring Center FAQ
Indexes
- Why Is There No Data on Monitoring Center?
- How Do I Disable Monitoring Center?
- Why Are Custom Metrics Not Displayed on Monitoring Center?
- Why Is Resource Information Not Displayed in the Node List for 1 to 2 Minutes After a prometheus-server Pod Is Restarted When the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on Is Deployed with Local Data Storage Enabled?
- Why There Are Two Sets of Data After a kube-state-metrics Pod Is Restarted When the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on Is Deployed with Local Data Storage Enabled?
- Why Does the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on with Local Data Storage Enabled Fail to Report Metrics?
- Why Does the Workload/Node CPU Usage Displayed in Monitoring Center Exceed 100%?
- Why Is 403 Displayed in Collection Endpoint Access? How Do I Handle It?
Why Is There No Data on Monitoring Center?
- Possible cause 1: The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on is abnormal.
Access the Add-ons page on the cluster console and check whether the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on is in the Running state.
Figure 1 Checking the add-on status
If the add-on is not running normally, locate the fault based on the events.
Figure 2 Viewing add-on events
- Possible cause 2: The AOM instance interconnected with the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on is deleted.
Access the Add-ons page on the cluster console and check the configuration of the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on.
Figure 3 Editing the add-on configuration
Ensure that AOM Instance is not left empty.
Figure 4 Viewing the AOM instance
- Possible cause 3: There was rate limiting or blocking when metrics are reported to AOM.
- On the cluster console or at the cluster backend, check whether the RemoteWriteAOMPending event exists in the Kubernetes events. If the event exists, the reporting to AOM is blocked. You are advised to increase the number of shards of the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on. For details, see Adjusting the Number of Shards for Prometheus-based Data Collection. If your cluster scale is large, you are advised to perform optimization by referring to Configuring the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on in a Large-Scale Cluster.
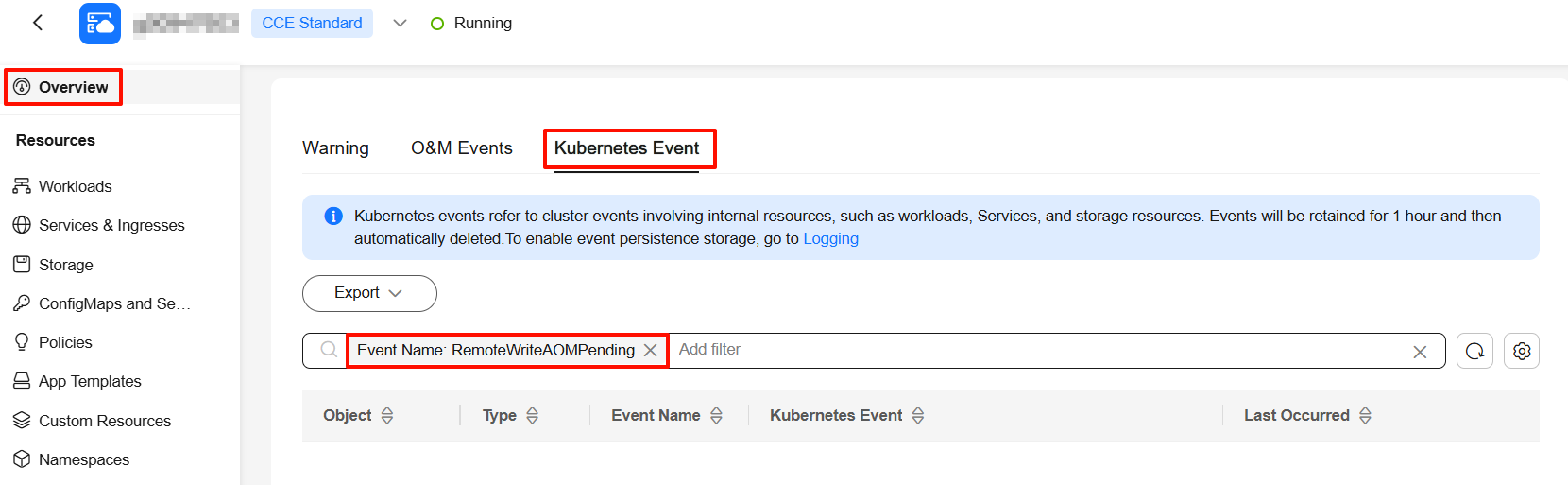
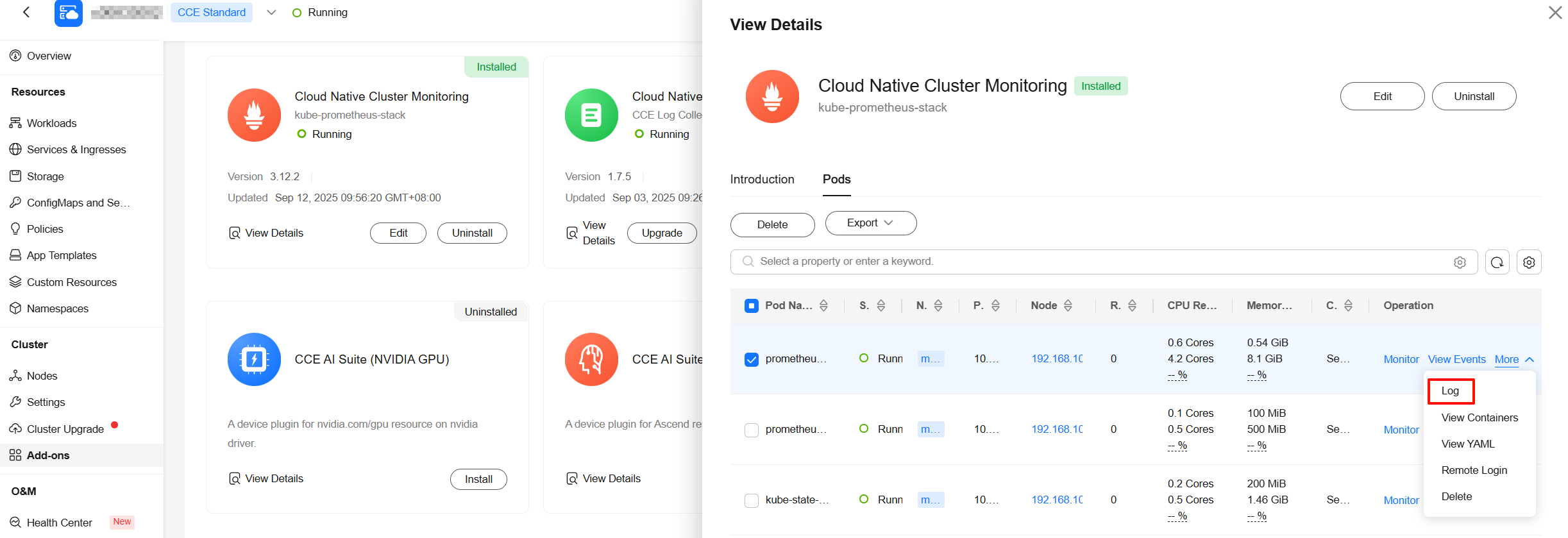
- Go to the Add-ons page, click Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring, and click the Pods tab. Then, locate the prometheus-lightweight workload (multiple pods may be displayed if there are multiple shards, so view each pod separately) and choose More > Log in the Operation column. Check whether there are logs related to metric reporting errors or 429 Too Many Requests. If yes, contact AOM engineers to locate and rectify the fault.
- On the cluster console or at the cluster backend, check whether the RemoteWriteAOMPending event exists in the Kubernetes events. If the event exists, the reporting to AOM is blocked. You are advised to increase the number of shards of the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on. For details, see Adjusting the Number of Shards for Prometheus-based Data Collection. If your cluster scale is large, you are advised to perform optimization by referring to Configuring the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on in a Large-Scale Cluster.
How Do I Disable Monitoring Center?
To disable Monitoring Center, uninstall the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on on the Add-ons page or disable the option for interconnecting with AOM.
Why Are Custom Metrics Not Displayed on Monitoring Center?
Monitoring Center currently does not display custom metrics. To view custom metrics, you can create a dashboard for custom metrics on AOM.
Why Is Resource Information Not Displayed in the Node List for 1 to 2 Minutes After a prometheus-server Pod Is Restarted When the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on Is Deployed with Local Data Storage Enabled?
After a prometheus-server pod is restarted, the UID label values of its metrics change. During the rolling restart of the prometheus-server pod, metrics overlap because data is stored locally. This means the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on reports metrics from both the old and new prometheus-server pods to AOM. As a result, the resource information in the node list is incorrect. For this reason, when the metrics overlap, the resource information is not displayed in the node list. If there is no special scenario, disable local data storage when you use the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on.
Why There Are Two Sets of Data After a kube-state-metrics Pod Is Restarted When the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on Is Deployed with Local Data Storage Enabled?
The instance label value in the metrics collected by kube-state-metrics is the node IP address. When the kube-state-metrics pod is scheduled to a new node, the node IP address changes. As a result, the instance label value changes. During the rolling restart of the kube-state-metrics pod, metrics overlap because data is stored locally. This means the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on reports metrics from both the old and new kube-state-metrics pods. The instance label values are different, so the two sets of metrics are considered valid. As a result, there are two data records for the numbers of nodes, workloads, pods, namespaces, and control plane components on the Clusters tab (Monitoring Center > Clusters). If there is no special scenario, disable local data storage when you use the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on.
Why Does the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on with Local Data Storage Enabled Fail to Report Metrics?
Go to the Add-ons page, select the prometheus-server-x pod, and view its log.

- If the log contains "no space left on device", the disk space for this add-on pod is insufficient. As a result, metrics cannot be written.
- Solution 1: Connect the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on to the AOM instance, with local data storage disabled. If AOM is used to host metrics, storage management is not required.
- Solution 2: In the navigation pane, choose Storage. On the displayed page, switch to the monitoring namespace, select the pvc-prometheus-server-0 disk, and click More > Scale-out in the Operation column. Then, go to the StatefulSets tab and restart the prometheus-server pod.
Figure 6 Expanding the PVC capacity


Insufficient disk space will prevent the metrics of this add-on pod from being written. As a result, data cannot be collected. This means that any monitoring data generated before the pod restart will be lost.
- If there are no error logs and a large number of "WAL segment loaded" logs are generated, the startup fails.
The possible causes are as follows:
- Possible cause 1: prometheus-server has a large number of events indicating that the startup probe check fails. There are a large number of non-persistent metrics, and these events last longer than the startup probe delay.
- Solution 1: Connect the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on to the AOM instance, with local data storage disabled. If AOM is used to host metrics, storage management is not required.
- Solution 2: Access the cluster using kubectl and run the following command:
kubectl edit Prometheus -n monitoring server
Modify the startup probe settings. The default startup probe check lasts 3 minutes, but the recommended setting is 30 minutes. Set failureThreshold to 30 and periodSeconds to 60. This allows the probe to retry up to 30 times every 60 seconds. You can modify the settings based on the actual startup time.

After the add-on is upgraded, you need to change the values.
- Possible cause 2: There is always an OOM error for prometheus-server. When Prometheus is started, it loads the metrics that are not persistently stored in the PVC. The metrics occupy a large amount of memory.
- Solution 1: Connect the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on to the AOM instance, with local data storage disabled. If AOM is used to host metrics, storage management is not required.
- Solution 2: Go to the Add-ons page, edit the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on, and increase the memory limit of prometheus-server to prevent OOM.
- Possible cause 1: prometheus-server has a large number of events indicating that the startup probe check fails. There are a large number of non-persistent metrics, and these events last longer than the startup probe delay.
Why Does the Workload/Node CPU Usage Displayed in Monitoring Center Exceed 100%?
The workload CPU usage is calculated using container_cpu_usage_seconds_total. The system periodically updates the used CPU and the time point at which the used CPU is collected. By default, Prometheus collects metrics at the collection time point instead of the time point specified by container_cpu_usage_seconds_total. As a result, the time point at which the used CPU is collected is inaccurate, and there is a short latency.
Assume that the system updates the used CPU every 6 seconds, and the collection period is 15 seconds, Prometheus collected data at 18:30:14 for the first time and at 18:30:29 for the second time. However, the time point specified by container_cpu_usage_seconds_total is 18:30:10 for the first and 18:30:28 for the second time.
|
Used CPU |
Time Point |
|---|---|
|
100,000 |
18:30:10 |
|
150,000 |
18:30:16 |
|
200,000 |
18:30:22 |
|
250,000 |
18:30:28 |
|
300,000 |
18:30:34 |
- Actual used CPU per second: (150000-100000)/(18:30:16-18:30:10) = 8333.33
- Used CPU per second collected by Prometheus: (250000-100000)/(18:30:29-18:30:14) = 10000

The preceding data values are manually amplified and are only examples. The actual difference is small.
Solution
To avoid this problem, you can configure honorTimestamps to use the time point specified by container_cpu_usage_seconds_total. Weigh the pros and cons before deciding whether to configure honorTimestamps.
|
Configure honorTimestamps |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
No (default behavior of Prometheus) |
|
Metrics such as the CPU usage may be slightly distorted. |
|
Yes |
The time points at which metrics are collected are consistent with the actual time points. In scenarios such as pressure tests, the calculated results are more authentic. |
|
To configure honorTimestamps, take the following steps:

Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring 3.11.0 or later has been installed in the cluster, and the preset collection function has been enabled.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose ConfigMaps and Secrets. Then, select the monitoring namespace. On the ConfigMaps tab, locate persistent-user-config.
- Click Edit YAML, search for kubelet-cadvisor, and add honorTimestamps: true.
... - customBlacklist: [] customWhitelist: [] destNamespace: kube-system name: kubelet-cadvisor namespace: monitoring scrapeAllMetrics: false honorTimestamps: true scrapeInterval: "" status: "on" type: ServiceMonitor ... - Click OK to save the configuration. The configuration takes effect in about 1 minute.
Why Is 403 Displayed in Collection Endpoint Access? How Do I Handle It?
Root Cause
Authentication has been configured for collection tasks in the ServiceMonitor or PodMonitor format corresponding to your collection endpoint. For security purposes, the endpoint to be authenticated cannot be accessed by default.
Solution: You can configure to allow access to endpoints with authentication.

If you allow access to endpoints with authentication, the endpoints to be authenticated can be directly accessed by accessing the prometheus-lightweight service in the cluster. For this reason, do not expose the prometheus-lightweight service port outside the cluster.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose ConfigMaps and Secrets. Then, select All namespaces for Namespace. On the ConfigMaps tab, locate persistent-user-config.
- Click Update to edit lightweight-user-config.yaml and add - --target-response-auto-auth=true under operatorConfigOverride.
customSettings: operatorEnvOverride: [] operatorConfigOverride: - --target-response-auto-auth=true promAdapterConfigOverride: []
- Click OK to save the configuration. The configuration takes effect in about 1 minute.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





