Submitting a SQL Job to Query RDS for MySQL Data Using DLI
Scenario
DLI can query data stored in RDS. This section describes how to use DLI to submit a SQL job to query RDS for MySQL data.
In this example, we will create an RDS for MySQL DB instance, create a database and table, create a DLI elastic resource pool and add a queue to it, create an enhanced datasource connection to connect the DLI elastic resource pool and the RDS for MySQL DB instance, and submit a SQL job to access the data in the RDS table.
Procedure
Table 1 shows the process for submitting a SQL job to query RDS for MySQL data.
Complete the preparations in Preparations before performing the following operations.
|
Procedure |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create an RDS for MySQL instance for the example scenario. |
|
|
Log in to the RDS for MySQL DB instance and create a database and a table. |
|
|
Step 3: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Add Queues to the Pool |
Create compute resources required for submitting jobs. |
|
Create an enhanced datasource connection to connect the DLI elastic resource pool and the RDS for MySQL DB instance. |
|
|
Create a datasource authentication to store the access credentials required by DLI to read from and write to RDS for MySQL data. |
|
|
Use standard SQL statements to query and analyze data. |
Preparations
- Register a Huawei ID and enable Huawei Cloud services. Make sure your account is not in arrears or frozen.
- Configure an agency for DLI.
To use DLI, you need to access services such as Object Storage Service (OBS), Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and Simple Message Notification (SMN). If it is your first time using DLI, you will need to configure an agency to allow access to these dependent services.
- Log in to the DLI management console using your account. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Global Configuration > Service Authorization.
- On the agency settings page, select the agency permissions under Basic Usage, Datasource, and O&M and click Update.
- View and understand the notes for updating the agency and click OK. The DLI agency permissions are updated.
Figure 1 Configuring an agency for DLI

- Once configured, you can check the agency dli_management_agency in the agency list on the IAM console.
- Configure a DLI job bucket.
Before using DLI to submit jobs, you need to configure a DLI job bucket. The bucket is used to store temporary data generated during DLI job running, such as job logs and results.
Configure a DLI job bucket on the Global Configuration > Project page of the DLI management console by referring to Configuring a DLI Job Bucket.
Step 1: Create an RDS MySQL Instance
In this example, assuming the job name is JobSample, RDS is used as the data source to create an RDS for MySQL DB instance.
For details, see Buying an RDS for MySQL Instance.
- Log in to the RDS management console.
- Select a region and a project in the upper left corner.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Instances. On the displayed page, click Buy DB Instance in the upper right corner.
- On the Buy DB Instance page, select a billing mode, set instance parameters, and click Buy.
Set the parameters listed below based on your service planning.
For how to set RDS for MySQL DB instance parameters, see Buying an RDS for MySQL Instance.
Table 2 RDS for MySQL instance parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Billing Mode
Billing mode of the RDS for MySQL DB instance
- Yearly/monthly is a prepaid billing. You pay in advance for a subscription term, and in exchange, you get a discounted rate. The longer the subscription, the bigger the discount. This mode is a good option for long-term, stable services.
- Pay-per-use: A postpaid billing mode. You pay as you go and just pay for what you use. The DB instance usage is calculated by the second but billed every hour. This mode allows you to flexibly adjust resource usage. You do not need to provision resources in advance, or have excessive or insufficient resources preset.
Pay-per-use
Region
Region where you want to create the instance
Products in different regions cannot communicate with each other through a private network. After a DB instance is created, the region cannot be changed. Exercise caution when selecting a region.
CN East-Shanghai2
DB Instance Name
Instance name
The name can contain 4 to 64 characters and must start with a letter. Only letters (case-sensitive), digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed.
If you intend to create multiple DB instances and read replicas at a time, the allowed length for each instance name will change.
rds-demo
DB Engine
MySQL
MySQL
DB Engine Version
If you select MySQL for DB Engine, select an engine version that best suits your service needs. You are advised to select the latest available version for more stable performance, higher security, and greater reliability.
8.0
DB Instance Type
Primary/standby mode of the instance
- Primary/Standby: An HA architecture. In a primary/standby pair, each instance has the same instance class. When a primary instance is being created, a standby instance is provisioned along with it to provide data redundancy. The standby instance is invisible to you after being created.
- Single: A single-node architecture is less expensive than a primary/standby DB pair. It is recommended for development and testing of microsites, and small- and medium-sized enterprises, or for learning about RDS.
Single
Storage Type
Determines the instance read/write speed. The higher the maximum throughput, the faster the read and write speeds.
Cloud SSD
AZ
For a single DB instance, you only need to select a single AZ.
-
Time Zone
Select a time zone based on the region you selected. You can change it after the DB instance is created.
Retain the default value.
Instance Class
vCPUs and memory. These instance classes support varying number of connections and maximum IOPS.
2 vCPUs | 4 GB
Storage Space
If the storage type is cloud SSD or extreme SSD, you can enable storage autoscaling. If the available storage drops to a specified threshold, autoscaling is triggered.
40 GB
Disk Encryption
Determine whether to enable disk encryption.
- Deselected: Encryption is not enabled.
- Selected: Selecting it enhances data security but may slightly impact database read and write performance.
For more details, see Buying an RDS for MySQL DB Instance.
Disable
VPC
Select an existing VPC.
For how to recreate a VPC and subnet, refer to .
NOTE:In datasource scenarios, the CIDR block of the data source cannot overlap that of the elastic resource pool.
-
Database Port
The default port is 3306. You can change it after the DB instance is created.
For RDS for MySQL instances, the value ranges from 1024 to 65535, excluding 12017, 33071, and 33062, which are reserved for RDS system use.
3306
Security Group
Enhances security by providing rules that control access to RDS from other services.
The security group where the data source is must allow access from the CIDR block of the DLI elastic resource pool.
-
Password
Set a password for logging in to the DB instance.
-
Administrator
DB administrator. The default username is root.
root
Administrator Password
Administrator password
The password must consist of 8 to 32 characters and contain at least three types of the following characters: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and the following special characters: ~!@#$%^*-_=+?,()&.| Enter a strong password and change it regularly to enhance security and prevent risks like brute-force attacks.
If the password you provide is considered weak by the system, you will be prompted to provide a stronger password.
Keep this password secure. The system cannot retrieve it.
-
Parameter Template
A template of parameters for creating an instance. The template contains engine configuration values that are applied to one or more instances.
Default-MySQL-5.7
Table Name
Determines whether the table name is case-insensitive.
Case insensitive
Enterprise Project
If the instance has been associated with an enterprise project, select the target project from the Enterprise Project drop-down list.
default
Quantity
Number of instances to buy
1
- Click Next. The confirmation page is displayed.
- Click Submit.
- To view and manage the DB instance, go to the Instance Management page.
During the creation process, the DB instance status is Creating. When the creation process is complete, the instance status will change to Available. You can view the detailed progress and result of the task on the Task Center page.
Step 2: Create an RDS Database Table
- Log in to the RDS management console.
- In the upper left corner of the management console, select the target region and project.
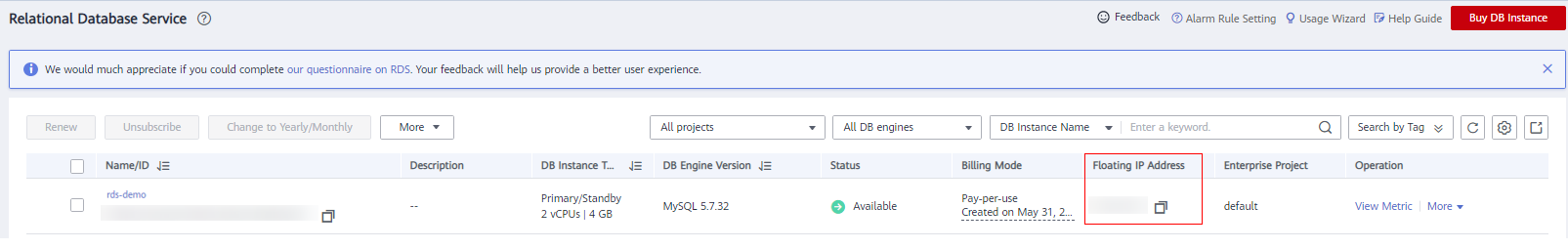
- On the Instances page, locate the DB instance you just created and record its floating IP address.
Figure 2 Viewing the floating IP address
- Locate the RDS for MySQL DB instance you created, click More in the Operation column, and select Log In. On the displayed page, enter the username and password for logging in to the instance and click Test Connection. After Connection is successful is displayed, click Log In.
Figure 3 RDS console
 Figure 4 Logging in to an instance
Figure 4 Logging in to an instance
- Click Create Database. In the displayed dialog box, enter database name dli_demo. Then, click OK.
- Click SQL Query and run the following SQL statement to create a table:
CREATE TABLE `dli_demo`.`tabletest` ( `id` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL, `name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4;
Step 3: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Add Queues to the Pool
To execute SQL jobs in datasource scenarios, you must use your own SQL queue as the existing default queue cannot be used. In this example, create an elastic resource pool named dli_resource_pool and a queue named dli_queue_01.
- Log in to the DLI management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- On the displayed page, click Buy Resource Pool in the upper right corner.
- On the displayed page, set the parameters.
In this example, we will buy the resource pool in the CN East-Shanghai2 region. Table 3 describes the parameters.
Table 3 Parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Region
Select a region where you want to buy the elastic resource pool.
CN East-Shanghai2
Project
Project uniquely preset by the system for each region
Default
Name
Name of the elastic resource pool
dli_resource_pool
Specifications
Specifications of the elastic resource pool
Standard
CU Range
The maximum and minimum CUs allowed for the elastic resource pool
64-64
CIDR Block
CIDR block the elastic resource pool belongs to. If you use an enhanced datasource connection, this CIDR block cannot overlap that of the data source. Once set, this CIDR block cannot be changed.
172.16.0.0/19
Enterprise Project
Select an enterprise project for the elastic resource pool.
default
- Click Buy.
- Click Submit.
- In the elastic resource pool list, locate the pool you just created and click Add Queue in the Operation column.
- Set the basic parameters listed below.
Table 4 Basic parameters for adding a queue Parameter
Description
Example Value
Name
Name of the queue to add
dli_queue_01
Type
Type of the queue
- To execute SQL jobs, select For SQL.
- To execute Flink or Spark jobs, select For general purpose.
For SQL jobs, select For SQL.
For other scenarios, select For general purpose.
Engine
SQL queue engine. The options are Spark and HetuEngine.
Spark
Enterprise Project
Select an enterprise project.
default
- Click Next and configure scaling policies for the queue.
Click Create to add a scaling policy with varying priority, period, minimum CUs, and maximum CUs.
Figure 5 shows the scaling policy configured in this example.Table 5 Scaling policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Priority
Priority of the scaling policy in the current elastic resource pool. A larger value indicates a higher priority. In this example, only one scaling policy is configured, so its priority is set to 1 by default.
1
Period
The first scaling policy is the default policy, and its Period parameter configuration cannot be deleted or modified.
The period for the scaling policy is from 00 to 24.
00–24
Min CU
Minimum number of CUs allowed by the scaling policy
16
Max CU
Maximum number of CUs allowed by the scaling policy
64
- Click OK.
Step 4: Create an Enhanced Datasource Connection
- Create a rule on the security group of the RDS DB instance to allow access from the CIDR block of the DLI queue.
- Go to the RDS management console and choose Instances in the navigation pane on the left. In the instance list, click the name of the RDS for MySQL DB instance you created to access its basic information page.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Connectivity & Security. In the Security Group Rules area, find the Inbound Rules tab and click Add Inbound Rule.
For example, if the CIDR block of the queue is 172.16.0.0/19, add the rule as follows:
- Set Priority to 1 and Action to Allow.
- Type: Select IPv4.
- Protocol & Port: Select Protocols/TCP (Custom) as the protocol and leave the port number blank.
- Source: Select IP Address and enter 172.16.0.0/19.
Click OK. The security group rule is added.
- Create an enhanced datasource connection between RDS for MySQL and DLI.
For how to create an enhanced datasource connection, see Creating an Enhanced Datasource Connection.

The CIDR block of the elastic resource pool bound to a datasource connection cannot overlap that of the data source.
- Go to the DLI management console and choose Datasource Connections in the navigation pane on the left.
- On the displayed Enhanced tab, click Create. Set the following parameters:
- Connection Name: dlirds
- Resource Pool: Select the elastic resource pool created in Step 3: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Add Queues to the Pool.
- VPC: Select the VPC where the RDS for MySQL DB instance is, that is, the VPC selected in Step 2: Create an RDS Database Table.
- Subnet: Select the subnet where the RDS for MySQL DB instance is, that is, the subnet selected in Step 2: Create an RDS Database Table.
To check the subnet information, go to the RDS console, choose Instances in the navigation pane on the left, click the name of the RDS for MySQL DB instance you created, and find Subnet in the Connection Information area on the displayed page.
- Click OK.
- In the Enhanced tab, click the created connection dlirds to view its VPC Peering ID and Connection Status. If the connection status is Active, the connection is successful.
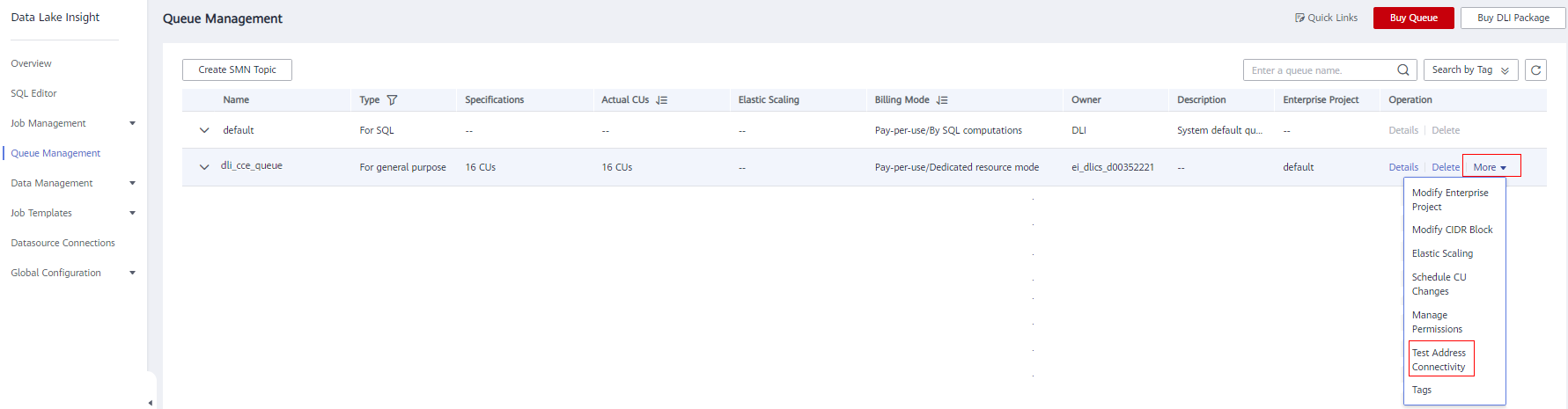
- Test if the queue can connect to the RDS for MySQL DB instance.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Queue Management. On the displayed page, locate the queue added in Step 3: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Add Queues to the Pool, click More in the Operation column, and select Test Address Connectivity.
Figure 6 Testing address connectivity
- Enter the floating IP address of the RDS for MySQL DB instance recorded in Step 2: Create an RDS Database Table.

On the Instance Management page, click the target DB instance. On the displayed page, choose Connection Information > Floating IP Address to obtain the floating IP address.
- If the IP address is reachable, the DLI queue can connect to the RDS for MySQL DB instance through the created enhanced datasource connection.
Figure 7 Testing address connectivity

- If the IP address is unreachable, rectify the fault by referring to Why Is a Datasource Connection Successfully Created But the Network Connectivity Test Fails?
Once the fault is rectified, retest the network connectivity.
- If the IP address is reachable, the DLI queue can connect to the RDS for MySQL DB instance through the created enhanced datasource connection.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Queue Management. On the displayed page, locate the queue added in Step 3: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Add Queues to the Pool, click More in the Operation column, and select Test Address Connectivity.
Step 5: Create a Datasource Authentication
When analyzing across multiple sources, you are advised not to configure authentication information directly in a job as it can lead to password leakage. Instead, you are advised to use datasource authentication provided by DLI to securely store data source authentication information.
To connect a Spark SQL job to an RDS for MySQL data source, you can create a password-type datasource authentication.
- Log in to the DLI management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Datasource Connections. On the displayed page, click Datasource Authentication.
- Click Create.
Set authentication parameters based on Table 6.
Table 6 Datasource authentication parameters Parameter
Description
Type
Select Password.
Authentication Certificate
Name of the datasource authentication to create
- Only numbers, letters, and underscores (_) are allowed. The name cannot contain only numbers or start with an underscore (_).
- The value can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
Username
Username for logging in to the RDS for MySQL DB instance
Password
Password for logging in to the RDS for MySQL DB instance
Figure 8 Creating a Password-type datasource authentication
Step 6: Submit a SQL Job
In this example, a SQL job accesses an RDS table using a datasource connection.
- On the DLI management console, choose SQL Editor in the navigation pane on the left.
- In the editing window on the right of the SQL Editor page, enter the following SQL statement to create database db1 and click Execute.
create database db1;
- On the top of the editing window, choose the dli_queue_01 queue and the db1 database. Enter the following SQL statements to create a table, insert data to the table, and query the data. Click Execute.
View the query result to verify that the query is successful and the datasource connection works.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS rds_test USING JDBC OPTIONS ( 'url' = 'jdbc:mysql://{{ip}}:{{port}}', // Private IP address and port of RDS 'driver' = 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver', 'dbtable' = 'dli_demo.tabletest', // Name of the created DB instance and table name 'encryption' = 'true', 'passwdauth'="xxxxx" // Name of the datasource authentication of the password type created on DLI. If datasource authentication is used, you do not need to set the username and password for the job. ) insert into rds_test VALUES ('123','abc'); SELECT * from rds_test;
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






