Inserting Data
Function
This statement is used to insert the SELECT query result or a certain data record into a table.
Notes and Constraints
- The insert overwrite syntax does not apply to self-read and self-write scenarios within the same table (including both partitioned and non-partitioned tables). Directly executing insert overwrite on the original table may lead to risks of data loss or inconsistency.
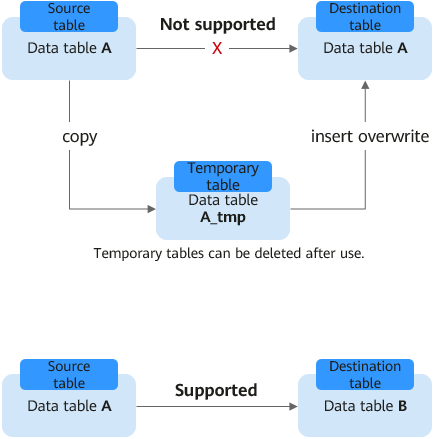
To implement data operations in self-read and self-write scenarios, you are advised to use a temporary table to handle the data. See Figure 1.
Self-read and self-write means that the destination table and the data source table are the same table. For example, suppose you want to extract information of students with class_no = 1 from the student table and overwrite the original table, the following statements represent typical operations in self-read and self-write scenarios:
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE student SELECT name FROM student WHERE class_no = 1;
- When using Hive and Datasource tables (excluding Hudi), executing data modification commands (such as insert into and load data) may result in data duplication or inconsistency if the data source does not support transactions and there is a system failure or queue restart.
To avoid this situation, you are advised to prioritize data sources that support transactions, such as Hudi data sources. This type of data source has Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability (ACID) capabilities, which helps ensure data consistency and accuracy.
To learn more, refer to How Do I Handle Duplicate Records After Executing the INSERT INTO Statement?
Syntax
- Insert the SELECT query result into a table.
1 2
INSERT INTO [TABLE] [db_name.]table_name [PARTITION part_spec] select_statement;
1 2
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE [db_name.]table_name [PARTITION part_spec] select_statement;
part_spec: : (part_col_name1=val1 [, part_col_name2=val2, ...])
- Insert a data record into a table.
1 2
INSERT INTO [TABLE] [db_name.]table_name [PARTITION part_spec] VALUES values_row [, values_row ...];
1 2
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE [db_name.]table_name [PARTITION part_spec] VALUES values_row [, values_row ...];
values_row: : (val1 [, val2, ...])
Keywords
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
db_name |
Name of the database where the target table resides. |
|
table_name |
Name of the target table. |
|
part_spec |
Detailed partition information. If there are multiple partition fields, all fields must be contained, but the corresponding values are optional. The system matches the corresponding partition. A maximum of 100,000 partitions can be created in a single table. |
|
select_statement |
SELECT query on the source table (DLI and OBS tables). |
|
values_row |
Value to be inserted to a table. Use commas (,) to separate columns. |
Precautions
- The target DLI table must exist.
- If no partition needs to be specified for dynamic partitioning, place part_spec in the SELECT statement as a common field.
- During creation of the target OBS table, only the folder path can be specified.
- The source table and the target table must have the same data types and column field quantity. Otherwise, data insertion fails.
- You are not advised to insert data concurrently into the same table as it may result in abnormal data insertion due to concurrency conflicts.
- The INSERT INTO statement is used to add the query result to the target table.
- The INSERT OVERWRITE statement is used to overwrite existing data in the source table.
- The INSERT INTO statement can be batch executed, but the INSERT OVERWRITE statement can be batch executed only when data of different partitioned tables is inserted to different static partitions.
- The INSERT INTO and INSERT OVERWRITE statements can be executed at the same time. However, the result is unknown.
- When you insert data of the source table to the target table, you cannot import or update data of the source table.
- The dynamic INSERT OVERWRITE statement of Hive partitioned tables can overwrite the involved partition data but cannot overwrite the entire table data.
- To overwrite data in a specified partition of the datasource table, set dli.sql.dynamicPartitionOverwrite.enabled to true and run the insert overwrite statement. The default value of dli.sql.dynamicPartitionOverwrite.enabled is false, indicating that data in the entire table is overwritten. The following is an example:
1insert overwrite table tb1 partition(part1='v1', part2='v2') select * from ...

On the DLI management console, click SQL Editor. In the upper right corner of the editing window, click Settings to configure parameters.
- You can configure the spark.sql.shuffle.partitions parameter to set the number of files to be inserted into the OBS bucket in the non-DLI table. In addition, to avoid data skew, you can add distribute by rand() to the end of the INSERT statement to increase the number of concurrent jobs. The following is an example:
insert into table table_target select * from table_source distribute by cast(rand() * N as int);
Example

Before importing data, you must create a table. For details, see Creating an OBS Table or Creating a DLI Table.
- Example 1: Insert the SELECT query result into a table.
- Use the DataSource syntax to create a parquet partitioned table.
CREATE TABLE data_source_tab1 (col1 INT, p1 INT, p2 INT) USING PARQUET PARTITIONED BY (p1, p2);
- Insert the query result to the partition (p1 = 3, p2 = 4).
INSERT INTO data_source_tab1 PARTITION (p1 = 3, p2 = 4) SELECT id FROM RANGE(1, 3);
- Insert the new query result to the partition (p1 = 3, p2 = 4).
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE data_source_tab1 PARTITION (p1 = 3, p2 = 4) SELECT id FROM RANGE(3, 5);
- Use the DataSource syntax to create a parquet partitioned table.
- Example 2: Insert a piece of data into a table.
- Create a Parquet partitioned table with Hive format
CREATE TABLE hive_serde_tab1 (col1 INT, p1 INT, p2 INT) USING HIVE OPTIONS(fileFormat 'PARQUET') PARTITIONED BY (p1, p2);
- Insert two data records into the partition (p1 = 3, p2 = 4).
INSERT INTO hive_serde_tab1 PARTITION (p1 = 3, p2 = 4) VALUES (1), (2);
- Insert new data to the partition (p1 = 3, p2 = 4).
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE hive_serde_tab1 PARTITION (p1 = 3, p2 = 4) VALUES (3), (4);
- Create a Parquet partitioned table with Hive format
How Do I Handle Duplicate Records After Executing the INSERT INTO Statement?
- Symptom
When using Hive and Datasource tables (excluding Hudi), executing data modification commands (such as insert into and load data) may result in data duplication or inconsistency if the data source does not support transactions and there is a system failure or queue restart.
- Possible causes
If queue resources are restarted in the data commit phase, data may have been restored to a formal directory. If an insert into statement is executed and a retry is triggered after a resource restart, there is a possibility that data will be repeatedly written.
- Solution
- Hudi data sources that support ACID properties are recommended.
- Use idempotent syntax such as insert overwrite instead of non-idempotent syntax such as insert into to insert data.
- If it is strictly required that data cannot be duplicated, you are advised to perform deduplication on the table data after executing the insert into statement to prevent duplicate data.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot