Using IAM Roles or Policies to Grant Access to DLI
The role/policy-based authorization model provided by Identity and Access Management (IAM) lets you control access to DLI resources. With IAM, you can:
- Based on the organizational structure of your enterprise, create IAM users in you master account for employees from different departments within the company. This ensures that each employee has unique security credentials and can use DLI resources.
- Grant users the minimum permissions required to perform specific tasks based on their job responsibilities.
- Entrust an account or cloud service to perform professional, efficient O&M on your DLI resources.
If your account does not need individual IAM users, you may skip over this section.
Process Flow shows the process flow of role/policy-based authorization.
Prerequisites
Before granting permissions to a user group, familiarize yourself with the DLI permissions that can be added to the user group and select them accordingly based on actual needs.
For details about the system permissions supported by DLI, see Role/Policy-based Permission Management.
For details about the system permissions of other services, see System-defined Permissions.
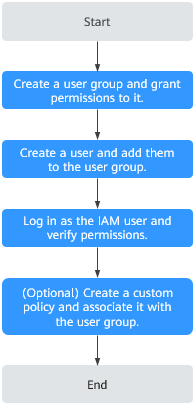
Process Flow
|
No. |
Step |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Create a user group on the IAM console and grant the DLI ReadOnlyAccess permission to it. |
|
|
2 |
Create a user on the IAM console and add them to the created user group. |
|
|
3 |
Log in to the console using the newly created user, switch to the authorized region, and verify permissions.
|
|
|
4 |
Create a custom policy and associate it with the user group. |
If the predefined DLI permissions in the system do not meet your authorization requirements, you can create custom policies. For details about how to create a custom policy, see Creating a Custom Policy. |
Creating a Custom DLI Policy
If the predefined DLI permissions in the system do not meet your authorization requirements, you can create custom policies. For the actions that can be added to custom policies, refer to .
You can create custom policies in either of the following two ways:
- Visual editor: Select cloud services, actions, resources, and request conditions. This does not require knowledge of policy syntax.
- JSON: Create a JSON policy or edit an existing one.
For details, see Creating a Custom Policy.
Policy Fields
In the following example, an IAM user is granted the permission to create tables across all databases in all regions.
{
"Version": "1.1",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dli:database:createTable"
],
"Resource": [
"dli:*:*:database:*"
]
}
]
}
- Version
Version: 1.1. Policy: A fine-grained authorization strategy that defines the permissions required to perform actions on a specific cloud resource under certain conditions.
- Effect
Function. The value can be Allow and Deny. If both Allow and Deny are found in statements, the Deny overrides the Allow.
- Action
Specific action on a resource. A maximum of 100 actions are allowed.
Figure 2 DLI actions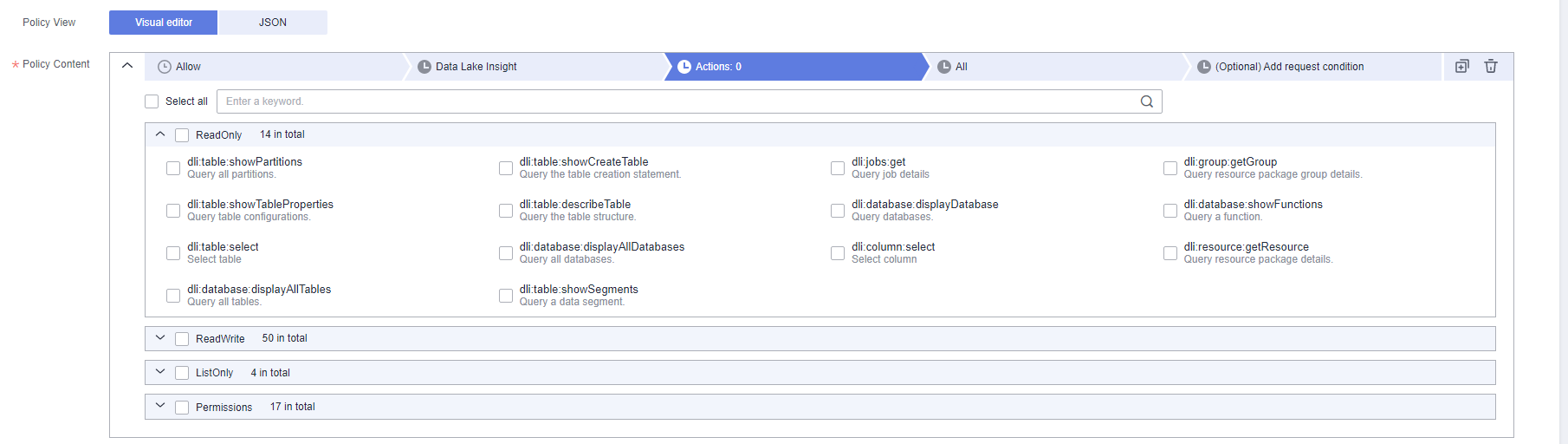
- The format is Service name:Resource type:Action, for example, dli:queue:submit_job.
- Service name: product name, such as dli, evs, or vpc. Only lowercase letters are allowed. Resource types and actions are not case-sensitive. You can use an asterisk (*) to represent all actions.
- Resource type: For details, see Table 5.
- Action: action registered with IAM.
- Condition
Determines when a policy is in effect. A condition consists of a condition key and a condition operator.
A key in the Condition element of a statement. There are global and service-specific condition keys.
- Global-level condition key: The prefix is g:, which applies to all actions. For details, see the condition key description in Policy Syntax.
- Service-level condition key: applies only to actions of the specific service.
An operator must be used together with a condition key to form a complete condition statement. For details, see Table 2.
IAM provides a set of DLI predefined condition keys. The following table lists the DLI predefined condition keys.
Table 2 DLI request conditions Condition Key
Type
Operator
Description
g:CurrentTime
Global
Date and time
Time when an authentication request is received
NOTE:The time is expressed in the format defined by ISO 8601, for example, 2012-11-11T23:59:59Z.
g:MFAPresent
Global
Boolean
Whether multi-factor authentication is used during user login
g:UserId
Global
String
ID of the current login user
g:UserName
Global
String
Current login username
g:ProjectName
Global
String
Project that you have logged in to
g:DomainName
Global
String
Domain that you have logged in to
g:ResourceTag
Global
StringEquals
Resource tag value
- Resource
The format is Service name:Region:Domain ID:Resource type:Resource path. The wildcard (*) indicates all options. For details about the resource types and path, see Table 5.
Example:
dli:*:*:queue:* indicates all queues.
Creating a Custom Policy
You can set actions and resources at varying levels based on scenarios.
- Define an action.
The format is Service name:Resource type:Action. You can use wildcards *. Example:
Table 3 Action Action
Description
dli:queue:submit_job
Submission operations on a DLI queue
dli:queue:*
All operations on a DLI queue
dli:*:*
All operations on all DLI resource types
For details about the actions supported by system-defined permissions, see Common Operations Supported by DLI System Policy.
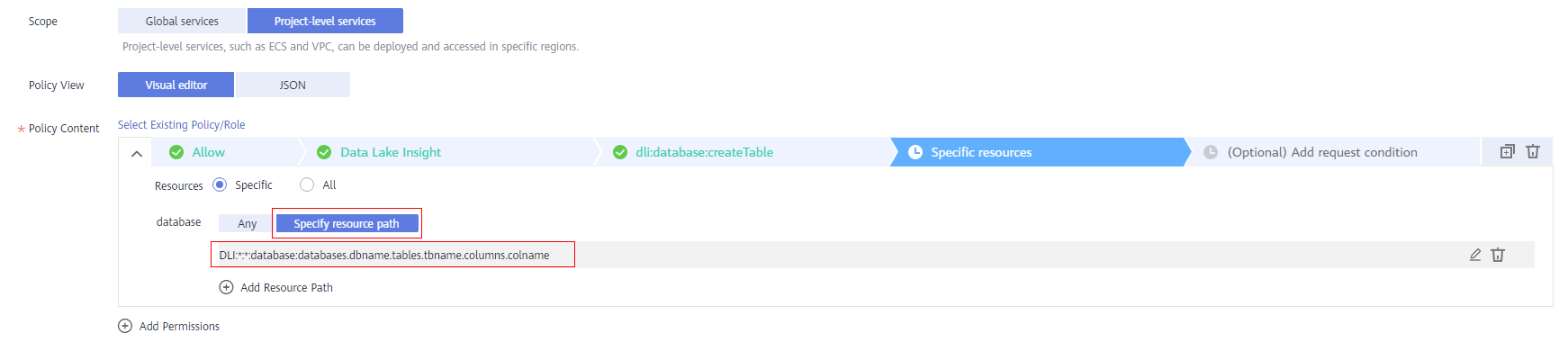
- Define a resource.
The format is Service name:Region:Domain ID:Resource type:Resource path. The wildcard (*) indicates all resources. You can flexibly set these five fields. The Resource path field can be set with varying levels of access control based on the specific scenario. If you need to set permissions for all resources under this service, you can leave this field unspecified.
For details about how to define a resource, see Table 4.
For details about the resource types and resource paths, see Table 5.
Table 4 Resource Resource
Description
DLI:*:*:table:databases.dbname.tables.*
DLI, any region, any account ID, all table resources of database dbname
DLI:*:*:database:databases.dbname
DLI, any region, any account ID, resource of database dbname
DLI:*:*:queue:queues.*
DLI, any region, any account ID, any queue resource
DLI:*:*:jobs:jobs.flink.1
DLI, any region, any account ID, Flink job whose ID is 1
Table 5 DLI resources and their paths Type
Resource
Path
elasticresourcepool
DLI elastic resource pool
elasticresourcepools.name
queue
DLI queue
queues.queuename
database
DLI database
databases.dbname
table
DLI table
databases.dbname.tables.tbname
column
DLI column
databases.dbname.tables.tbname.columns.colname
jobs
DLI Flink job
jobs.flink.jobid
resource
DLI package
resources.resourcename
group
DLI package group
groups.groupname
datasourceauth
DLI datasource authentication information
datasourceauth.name
edsconnections
Enhanced datasource connection
edsconnections.Connection ID
variable
DLI global variable
variables.name
sqldefendrule
SQL inspection rule
sqldefendes.*
catalog
DLI data catalog
catalogs.name
- Specific resources:
Figure 3 Specific resources
- All resources: all resources of the service
Figure 4 All resources
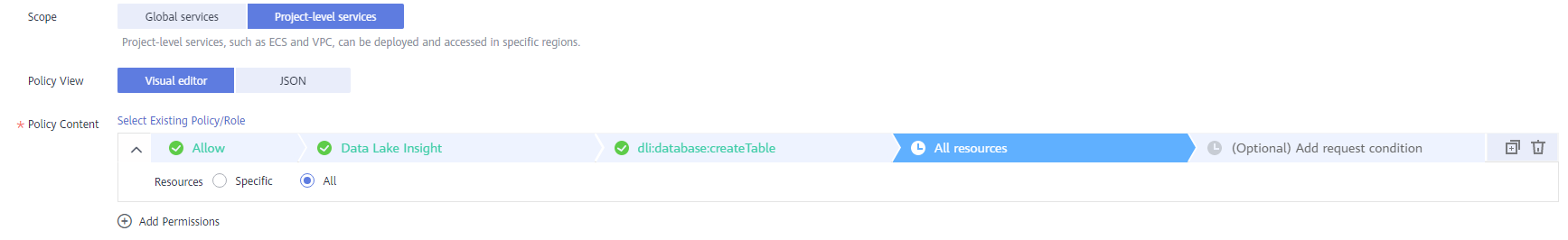
- Specific resources:
- Combine all of the preceding fields into a JSON string to create a complete policy. You can set multiple actions and resources, and you also have the option to create policies through the IAM console. For example:
Create a policy that grants users the permission to create and delete databases, submit jobs for any queue, and delete tables under any account ID in any region of DLI.
{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": " Allow", "Action": [ "dli:database:createDatabase", "dli:database:dropDatabase", "dli:queue:submitJob", "dli:table:dropTable" ], "Resource": [ "dli:*:*:database:*", "dli:*:*:queue:*", "dli:*:*:table:*" ] } ] }
Example Custom Policies
- Example 1: Allow policies
- Allow users to create tables across all databases in all regions.
{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "dli:database:createTable" ], "Resource": [ "dli:*:*:database:*" ] } ] } - Allow users to query column col in the table tb of the database db in the region where the user is.
{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "dli:column:select" ], "Resource": [ "dli:xxx:*:column:databases.db.tables.tb.columns.col" ] } ] }
- Allow users to create tables across all databases in all regions.
- Example 2: Deny policies
A deny policy must be used together with other policies. Users need to be granted some operation permission policies first before a deny policy can be set within those permissions. Otherwise, if the user has no permissions at all, the deny policy has no practical effect.
In the policies granted to a user, if an action has both Allow and Deny, the Deny takes precedence.
- Deny users to create or delete databases, submit jobs (except the default queue), or delete tables.
{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Deny", "Action": [ "dli:database:createDatabase", "dli:database:dropDatabase", "dli:queue:submitJob", "dli:table:dropTable" ], "Resource": [ "dli:*:*:database:*", "dli:*:*:queue:*", "dli:*:*:table:*" ] } ] } - Deny users to submit jobs on the demo queue.
{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Deny", "Action": [ "dli:queue:submitJob" ], "Resource": [ "dli:*:*:queue:queues.demo" ] } ] }
- Deny users to create or delete databases, submit jobs (except the default queue), or delete tables.
- Example 3: Tag-based authorization. You need to associate an action with a condition and define the key and value of the g:ResourceTag.
The g:ResourceTag condition indicates resources that have the specified tag key=value. Only resource operations included in the policy actions are allowed.
The key is case insensitive. Fuzzy match for values is currently not supported.{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "dli:database:dropDatabase", "dli:table:select", "dli:database:createTable", "dli:table:dropTable" ], "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "g:ResourceTag/key": [ "value" ] } } } ] }
DLI Resources
Resources are objects that exist within a service. In DLI, resources include the following, and you can select specific resources when creating custom policies by specifying the resource path.
|
Type |
Resource |
Path |
|---|---|---|
|
elasticresourcepool |
DLI elastic resource pool |
elasticresourcepools.name |
|
queue |
DLI queue |
queues.queuename |
|
database |
DLI database |
databases.dbname |
|
table |
DLI table |
databases.dbname.tables.tbname |
|
column |
DLI column |
databases.dbname.tables.tbname.columns.colname |
|
jobs |
DLI Flink job |
jobs.flink.jobid |
|
resource |
DLI package |
resources.resourcename |
|
group |
DLI package group |
groups.groupname |
|
datasourceauth |
DLI datasource authentication information |
datasourceauth.name |
|
edsconnections |
Enhanced datasource connection |
edsconnections.Connection ID |
|
variable |
DLI global variable |
variables.name |
|
sqldefendrule |
SQL inspection rule |
sqldefendes.* |
|
catalog |
DLI data catalog |
catalogs.name |
DLI Request Condition
Request conditions are useful in determining when a custom policy is in effect. A request condition consists of condition keys and operators. Condition keys are either global or service-level and are used in the Condition element of a policy statement. Global condition keys (starting with g:) are available for operations of all services, while service-level condition keys (starting with a service name such as dli) are available only for operations of a specific service. An operator must be used together with a condition key to form a complete condition statement.
IAM provides a set of DLI predefined condition keys. The following table lists the DLI predefined condition keys.
|
Condition Key |
Type |
Operator |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
g:CurrentTime |
Global |
Date and time |
Time when an authentication request is received
NOTE:
The time is expressed in the format defined by ISO 8601, for example, 2012-11-11T23:59:59Z. |
|
g:MFAPresent |
Global |
Boolean |
Whether multi-factor authentication is used during user login |
|
g:UserId |
Global |
String |
ID of the current login user |
|
g:UserName |
Global |
String |
Current login username |
|
g:ProjectName |
Global |
String |
Project that you have logged in to |
|
g:DomainName |
Global |
String |
Domain that you have logged in to |
|
g:ResourceTag |
Global |
StringEquals |
Resource tag value |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





