Configuring Workspace Permission Sets
In data access permission management, permissions are usually classified into multiple levels of permissions, such as those for level-1, level-2, and level-3 departments. DataArts Security provides a top-down hierarchical mode for data permission management. You can configure the maximum permissions in the workspace through a workspace permission set. Then, you can split the workspace permission set into permission sets for refined permission management.
A workspace permission set contains all the permissions for users in a DataArts Studio workspace. This permission set is created by the DAYU Administrator, Tenant Administrator, or data security administrator. A permission set contains only part of the permissions in a workspace.
- A workspace permission set is a top-level permission set that has no parent permission set. Generally, you only need to create one workspace permission set for each workspace. However, a permission set must be associated with a parent permission set, which can be a workspace permission set or another permission set. You can create multiple permission sets to associate users with different permissions in different scenarios.
- A workspace permission set mainly determines the permissions of a workspace, while a permission set is mainly used to manage permissions. A workspace permission set does not require permission synchronization and cannot be associated with roles. A permission set supports permission synchronization, which can be used for permission management, though associating a permission set with roles for permission management is more recommended.
This section describes how to create and configure a workspace permission set to define the permissions for a workspace.
Prerequisites
- A DWS connection, DLI connection, MRS Hive connection, and MRS Ranger connection have been created in Management Center based on Creating a DataArts Studio Data Connection.
- Permissions have been configured for the dlg_agency based on Authorizing dlg_agency.
- User information has been synchronized from IAM to the data source based on Synchronizing IAM Users to the Data Source.
- Metadata of tables has been collected in DataArts Catalog through a metadata collection task if you want to view the metadata of databases, tables, and fields in data connections during permission configuration.
Constraints
- Only the DAYU Administrator, Tenant Administrator, or security administrator can create, modify, or synchronize workspace permission sets. The permission set administrator can synchronize workspace permission sets. Other common users cannot perform these operations.
- Workspace permission sets can only be used to define permissions for DLI, MRS Hive, DWS and MRS HetuEngine.
- You are advised to configure either Hetu permissions or Hetu permission synchronization. Do not use the two permission management modes for the same Hetu catalog. If the Hetu permissions in the permission set are inconsistent with those in Hetu permission synchronization, the permissions will overwrite each other.
- After a workspace permission set is configured, permission management does not take effect immediately. Instead, you need to synchronize the workspace permission set to the data source for permission management to take effect.
Because workspace permission sets are mainly used to determine the permissions of workspaces rather than manage permissions, generally workspace permission sets do not need to be synchronized. You are advised to configure roles based on Configuring Roles to manage permissions. To synchronize workspace permission sets, pay attention to the following restrictions:
- During authorization, the name of the object to be authorized (database, table, or column name) can contain only digits, letters, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and wildcards (*).
- DWS permission sets are used only to determine the permission scope. Only role permissions can be synchronized. Permissions of user groups and users cannot be synchronized. To make DWS permissions take effect, you must configure roles. For details, see Configuring Roles.
- DWS permission sets can be used to grant permissions of a specified database or schema. The asterisk (*) cannot be used as a wildcard character. Wildcard characters are supported for tables or columns. For example, if you want to grant permissions to all tables in a schema, enter * for the data tables.
- If a DWS permission set is used to grant a user the permissions of all tables in a schema of the DWS data source (that is, the data tables are set to *), the user has permissions on all tables in the schema. Due to the restrictions of DWS permissions, these permissions are applicable only to the current table. This user has no permissions on the tables (future tables) created after permission synchronization. In this case, the administrator must manually synchronize permissions of the role or permission set so that the user has permissions on future tables.
To avoid manually synchronizing the permissions on future tables, you can configure the users for creating future tables in a specified schema. When these users create future tables in the specified schema, all the users that have full table permissions on the schema in the current instance automatically obtain the permissions on the created future tables.
- During DLI permission set synchronization, the custom policies created in IAM are associated with users or user groups. A maximum of 200 custom policies can be created in IAM. Before synchronization, ensure that the quotas are sufficient.
- During permission synchronization, you need to configure required permissions for the dlg_agency. For details, see Authorizing dlg_agency.
- The current data permission control uses the allowlist mechanism, which adds operation conditions to the users to be authorized without affecting the permissions the users already have. If you only want to make the permissions granted by the data permission control take effect, you need to revoke the original permissions of the users to be authorized. For details, see Data Permission Management.
-
Deleted workspace permission sets are moved to the recycle bin. You can restore them within 30 days. After 30 days, they will be deleted permanently. For details, see Managing the Recycle Bin.
- During script execution and job testing in DataArts Factory, the MRS or DWS data source uses the account of the data connection for authentication by default. Therefore, permission management still does not take effect during data development. You need to enable fine-grained authentication so that the current user is used for authentication during script execution and job testing in DataArts Factory. In this way, different users have different data permissions, and permission management for roles and permission sets takes effect.
Creating a Workspace Permission Set
- On the DataArts Studio console, locate a workspace and click DataArts Security.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Access Permission Management > Workspace Permission Sets.
- On the displayed page, click Create.
Figure 1 Creating a workspace permission set

- Configure parameters based on Table 1 and click OK.
Table 1 Parameters for creating a workspace permission set Parameter
Description
*Name
Permission set name, which is unique in the instance.
You should include the meaning of the permission set and avoid meaningless descriptions in the name so that the permission set can be quickly identified.
*Administrator
Select up to five administrators of the user or user group type.
The administrators are the owners of the permission set and can configure the permissions in the permission set. The administrators can perform the following operations:- Permission configuration: Assign data source permissions to the workspace permission set.
- User configuration: Assign permissions in the workspace permission set to users, user groups, or workspace roles.
- Permission set creation: Create permission sets and roles based on the workspace permission set. The created permission sets do not contain more permissions than the workspace permission set.
Description
Information to make the workspace permission set easier to be identified
Figure 2 Creating a workspace permission set
Configuring the Workspace Permission Set
- On the DataArts Studio console, locate a workspace and click DataArts Security.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Access Permission Management > Workspace Permission Sets.
- Locate a workspace permission set and click its name to go to the details page.
- In the Basic Information area, you can view the name, ID, and administrator of the workspace permission set. For details, see Figure 3.
- On the Permission Configuration tab page, By data is selected by default. You can select By permissions. The configured permissions are the same for By data and By permissions, and the only difference lies in how the permissions are displayed. You are advised to select By permissions for batch authorization.
- By data: The system allows you to configure permissions for data. Currently, only MRS data sources are supported. The configured permissions will be automatically synchronized.
Figure 4 Configuring permissions on the By data page

When configuring permissions, you can select Entire DB, Entire table, or Entire column, and select the corresponding levels in the data source information to perform a batch authorization. You can also click Authorization in the Operation column of a data record in the expanded navigation pane to authorize access to the data.
Fast mode and Show data this role has no permission to are supported. If Fast mode is enabled, metadata of databases, tables, and columns is obtained from DataArts Catalog. Otherwise, metadata is obtained from the data source. If metadata has been collected, you are advised to enable Fast mode.
- Note that the permissions of databases, tables, and columns are managed by layer. For example, a user who has been granted database permissions does not have the permissions of tables and columns. Table and column permissions must be granted separately.
For example, if you enter a table name or an asterisk (*) as a wildcard during database authorization, you are authorizing the table. If you enter a column name or an asterisk (*) as a wildcard character, you are authorizing the column.
- During authorization, the name of the object to be authorized (database, table, or column name) can contain only digits, letters, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and wildcards (*).
Figure 5 Authorization on the By data page
- Note that the permissions of databases, tables, and columns are managed by layer. For example, a user who has been granted database permissions does not have the permissions of tables and columns. Table and column permissions must be granted separately.
- By permissions: The system allows you to configure permissions.
To configure permissions, click Add and select data levels in sequence. You cannot select multiple objects at the same level (such as the database, table, and column) for batch authorization. Permission Type cannot be set to DENY. During permission configuration, you can select Automatic Permissions Synchronization. If you select it, the configured permissions will be automatically synchronized. You do not need to synchronize them manually.

- Note that the permissions of databases, tables, and columns are managed by layer. For example, a user who has been granted database permissions does not have the permissions of tables and columns. Table and column permissions must be granted separately.
For example, if you enter a table name or an asterisk (*) as a wildcard during database authorization, you are authorizing the table. If you enter a column name or an asterisk (*) as a wildcard character, you are authorizing the column.
- During authorization, the name of the object to be authorized (database, table, or column name) can contain only digits, letters, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and wildcards (*).
- When you select HIVE for Data Source Type, you can change Database to URL to grant permissions to an OBS path in decoupled storage and compute. In this case, the following URL permissions are required for using Hive:
- write: creating a database
- read: creating a table, writing data, and deleting a table
- When you select DWS for Data Source Type, you can change Database to Logical Clusters to authorize logical DWS clusters. In this case, the following logical cluster permissions are required for using DWS:
- create: allows the creation of tables in sub-clusters.
- usage: allows access to tables in sub-clusters.
- compute: allows users with compute permissions to perform elastic computing in sub-clusters.
- When you select MRS HetuEngine for Data Source Type, the fast mode is not supported. Before using Hetu, you must enable Ranger authentication in MRS. To assign Hetu permissions to a user in the permission set, you must add the user to the hetuuser user group in MRS. Otherwise, the user cannot execute Hetu SQL statements.
After configuring permissions, you can edit, synchronize, or delete them.Figure 6 Configuring permissions on the By permissions page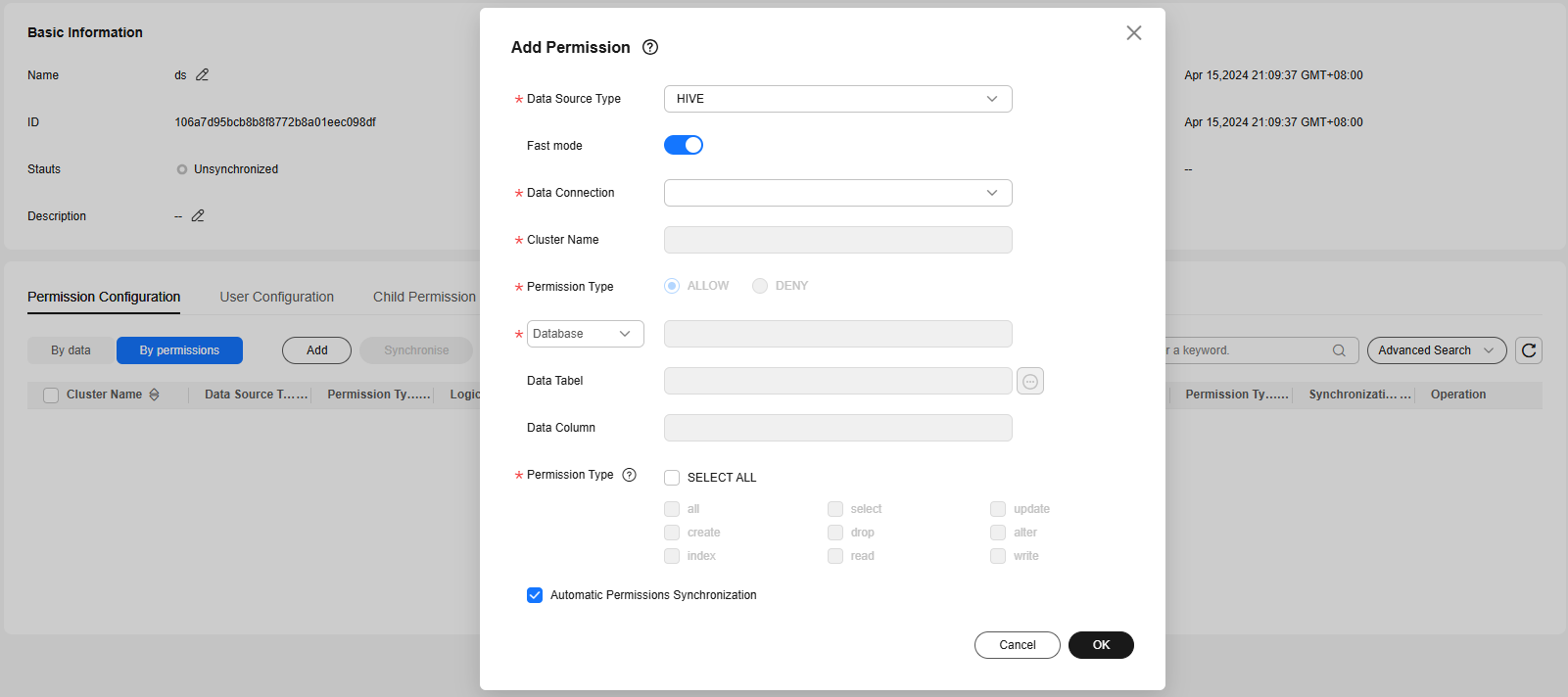
- Note that the permissions of databases, tables, and columns are managed by layer. For example, a user who has been granted database permissions does not have the permissions of tables and columns. Table and column permissions must be granted separately.
- By data: The system allows you to configure permissions for data. Currently, only MRS data sources are supported. The configured permissions will be automatically synchronized.
- User Configuration: On the permission set details page, click the User Configuration tab.
On this page, you can associate the permissions configured on the Permission Configuration page with users. Click Add and select User or User group (Workspace role is unavailable currently) to add users to the permission set. You can select users or user groups that have been added to the workspace.

When adding users or user groups based on the data source user type, you need to select target users from all users and user groups of the selected MRS cluster. After MRS users and user groups are configured, their permissions will be synchronized to all clusters in the current permission set. Therefore, ensure that the data source users exist in all clusters in the current permission set. Otherwise, the user permissions synchronization will fail.
Figure 7 User Configuration
- Child Permission Sets: On the permission set details page, click the Child Permission Sets tab.
On this page, you can view the child permission sets of the current permission set.Figure 8 View child permission sets

- Log: On the permission set details page, click the Log tab.
On this page, you can view the log details if permission synchronization fails. The system deletes logs generated 30 days ago at 00:00 every day.Figure 9 Viewing logs

- After the permission set is configured, permission management does not take effect immediately. You need to manually synchronize permissions to the data source for permission management to take effect. For details, see Synchronizing Permission Sets.
Because workspace permission sets are mainly used to determine the permissions of workspaces rather than manage permissions, generally workspace permission sets do not need to be synchronized. You are advised to configure roles based on Configuring Roles to manage permissions.
Related Operations
- Synchronizing workspace permission sets: Workspace permission sets take effect only after they are manually synchronized to the data source. Because workspace permission sets are mainly used to determine the permissions of workspaces rather than manage permissions, generally workspace permission sets do not need to be synchronized. You are advised to configure roles based on Configuring Roles to manage permissions.
To synchronize a workspace permission set, click Synchronize in the Operation column of the permission set on the Workspace Permission Sets page. To synchronize multiple permission sets, select them and click Synchronize above the list.
- Editing a workspace permission set: On the Workspace Permission Sets page, click Edit in the Operation column of a permission set. You can change the name, administrator, and description of the permission set.
- Deleting workspace permission sets: On the Workspace Permission Sets page, click Delete in the Operation column of a permission set. In the displayed dialog box, confirm the permission set to delete and click Yes. To delete multiple permission sets, select them and click Delete above the list.
Workspace permission sets for which permissions, users, or child permission sets have been configured cannot be deleted. To delete such workspace permission sets, delete the configurations first.

Deleted workspace permission sets are moved to the recycle bin. You can restore them within 30 days. After 30 days, they will be deleted permanently. For details, see Managing the Recycle Bin.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






