Property Delivery
Introduction
Property delivery is used for property query or modification. An application or the platform can obtain device property information or modify the properties, and synchronize the modification result to the device. After receiving a message, the device needs to return the property execution result to the platform in a timely manner. If the device does not respond, the platform considers that the property delivery times out.
Scenarios
- The platform proactively obtains or modifies device properties.
- The platform standardizes, parses, and filters the data.
Constraints
- Max. size of a single message: 64 KB.
- Product models are required.
Property Delivery
Property delivery is used for property modification or query. The following uses property modification as an example.
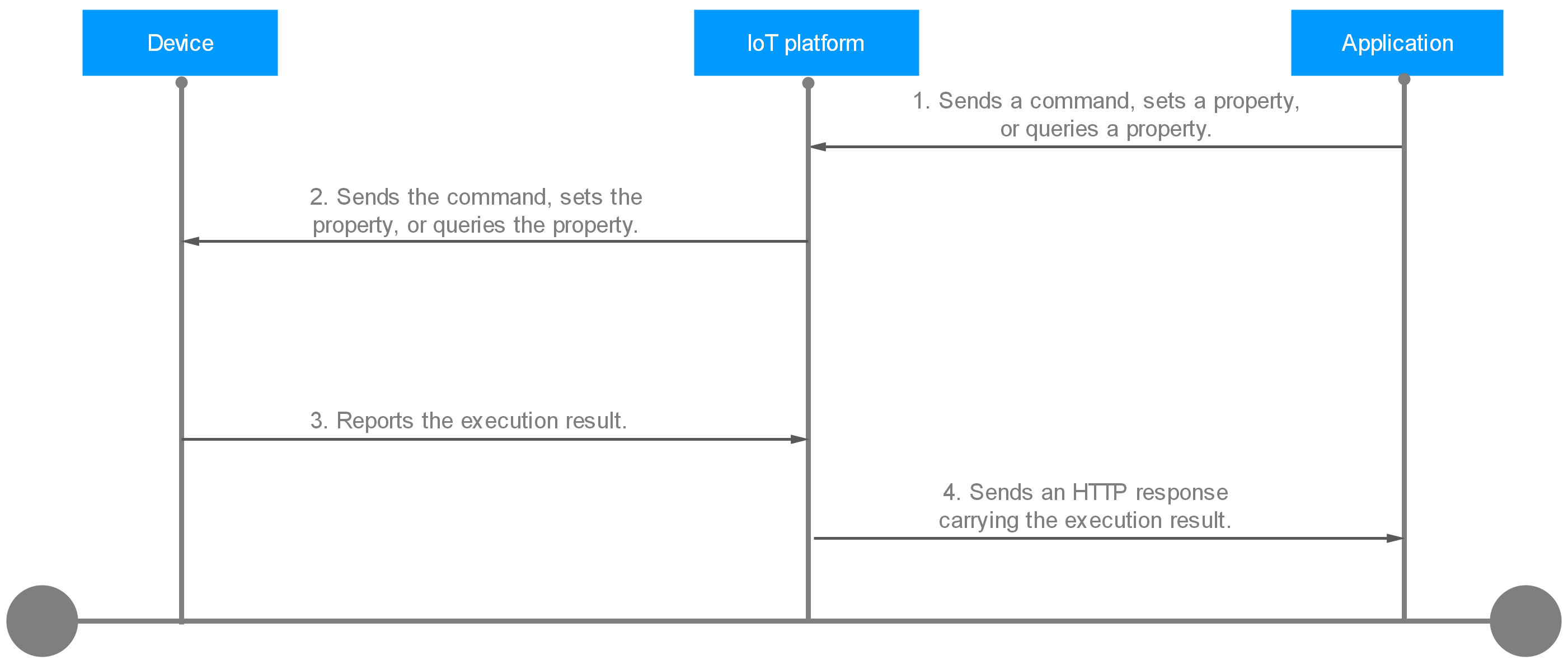
- An application calls the API for modifying device properties to deliver a request to the platform. Example message:
PUT https://{endpoint}/v5/iot/{project_id}/devices/{device_id}/properties { "services" : [ { "service_id" : "Temperature", "properties" : { "value" : 57 } }, { "service_id" : "Battery", "properties" : { "level" : 80 } } ] } - The platform sends the property to the device according to the protocol specifications. The following is an example of setting properties through the APIs for MQTT devices.
Topic: $oc/devices/{device_id}/sys/properties/set/request_id={request_id} Data format: { "object_device_id": "{object_device_id} ", "services": [ { "service_id": "Temperature", "properties": { "value": 57, "value2": 60 } }, { "service_id": "Battery", "properties": { "level": 80, "level2": 90 } } ] } - The device executes the command and returns the execution result. Example message:
Topic: $oc/devices/{device_id}/sys/properties/set/response/request_id={request_id} Data format: { "result_code": 0, "result_desc": "success" } - The platform synchronously sends a response to the HTTP command. Example message:
Status Code: 200 OK Content-Type: application/json { "response" : { "result_code" : 0, "result_desc" : "success" } }
Property Delivery with Java SDK
This section describes how to use the Java SDK for the development of property configuration. Download an SDK. JDK 1.8 or later is used.
Configure the SDK on the application side:
- Configure the Maven dependency.
<dependency> <groupId>com.huaweicloud.sdk</groupId> <artifactId>huaweicloud-sdk-core</artifactId> <version>[3.0.40-rc, 3.2.0)</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.huaweicloud.sdk</groupId> <artifactId>huaweicloud-sdk-iotda</artifactId> <version>[3.0.40-rc, 3.2.0)</version> </dependency> - Set the device properties on the application by referring to the following example.
public class AttributeDistributionSolution { // REGION_ID: If CN East-Shanghai1 is used, enter cn-east-3. If CN North-Beijing4 is used, enter cn-north-4. If CN South-Guangzhou is used, enter cn-south-4. private static final String REGION_ID = "<YOUR REGION ID>"; // ENDPOINT: On the console, choose Overview and click Access Addresses to view the HTTPS application access address. private static final String ENDPOINT = "<YOUR ENDPOINT>"; // For the standard or enterprise edition, create a region object. public static final Region REGION_CN_NORTH_4 = new Region(REGION_ID, ENDPOINT); public static void main(String[] args) { String ak = "<YOUR AK>"; String sk = "<YOUR SK>"; String projectId = "<YOUR PROJECTID>"; // Create a credential. ICredential auth = new BasicCredentials().withDerivedPredicate(AbstractCredentials.DEFAULT_DERIVED_PREDICATE) .withAk(ak) .withSk(sk) .withProjectId(projectId); // Create and initialize an IoTDAClient instance. IoTDAClient client = IoTDAClient.newBuilder().withCredential(auth) // For the basic edition, select the region object in IoTDARegion. //.withRegion(IoTDARegion.CN_NORTH_4) // For the standard or enterprise edition, create a region object. .withRegion(REGION_CN_NORTH_4).build(); // Instantiate a request object. UpdatePropertiesRequest request = new UpdatePropertiesRequest(); request.withDeviceId("<YOUR DEVICE_ID>"); DevicePropertiesRequest body = new DevicePropertiesRequest(); body.withServices("[{\"service_id\":\"smokeDetector\",\"properties\":{\"alarm\":\"hello\"," + "\"temperature\":10.323,\"humidity\":654.32,\"smokeConcentration\":342.4}}]"); request.withBody(body); try { UpdatePropertiesResponse response = client.updateProperties(request); System.out.println(response.toString()); } catch (ConnectionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (RequestTimeoutException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ServiceResponseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println(e.getHttpStatusCode()); System.out.println(e.getRequestId()); System.out.println(e.getErrorCode()); System.out.println(e.getErrorMsg()); } } }Table 1 Parameters Parameter
Description
ak
Access key ID (AK) of your Huawei Cloud account. You can create and check your AK/SK on the My Credentials > Access Keys page of the Huawei Cloud console. For details, see Access Keys.
sk
Secret access key (SK) of your Huawei Cloud account.
projectId
Project ID. For details on how to obtain a project ID, see Obtaining a Project ID.
IoTDARegion.CN_NORTH_4
Region where the platform to be accessed is located. The available regions of the platform have been defined in the SDK code IoTDARegion.java.
On the console, you can view the region name of the current service and the mapping between regions and endpoints. For details, see Platform Connection Information.
REGION_ID
If CN East-Shanghai1 is used, enter cn-east-3. If CN North-Beijing4 is used, enter cn-north-4. If CN South-Guangzhou is used, enter cn-south-4.
ENDPOINT
On the console, choose Overview and click Access Addresses to view the HTTPS application access address.
DEVICE_ID
Unique ID of the device that a message is delivered to. The value of this parameter is allocated by the platform during device registration. The value is a string of no more than 128 characters. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed.
Configure the SDK on the device side:
- Configure the Maven dependency of the SDK on devices.
<dependency> <groupId>com.huaweicloud</groupId> <artifactId>iot-device-sdk-java</artifactId> <version>1.1.4</version> </dependency>
- Configure the SDK and device connection parameters on devices.
// Load the CA certificate of the IoT platform. For details about how to obtain the certificate, visit https://support.huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/devg-iothub/iot_02_1004.html. URL resource = AttributeSample.class.getClassLoader().getResource("ca.jks"); File file = new File(resource.getPath()); // Format: ssl://Domain name:Port number // To obtain the domain name, log in to the Huawei Cloud IoTDA console. In the navigation pane, choose Overview and click Access Details in the Instance Information area. Select the access domain name corresponding to port 8883. String serverUrl = "ssl://localhost:8883"; // Device ID created on the platform String deviceId = "deviceId"; // Secret corresponding to the device ID String deviceSecret = "secret"; // Create a device. IoTDevice device = new IoTDevice(serverUrl, deviceId, deviceSecret, file); if (device.init() != 0) { return; }
- Define the property delivery callback function.
device.getClient().setPropertyListener(new PropertyListener() { // Process property writing. @Override public void onPropertiesSet(String requestId, List<ServiceProperty> services) { // Traverse services. for (ServiceProperty serviceProperty: services){ log.info("OnPropertiesSet, serviceId = " + serviceProperty.getServiceId()); // Traverse properties. for (String name :serviceProperty.getProperties().keySet()){ log.info("property name = "+ name); log.info("set property value = "+ serviceProperty.getProperties().get(name)); if (name.equals("alarm")){ // Change the local value. alarm = (Integer) serviceProperty.getProperties().get(name); } } } // Set property response. device.getClient().respondPropsSet(requestId, IotResult.SUCCESS); } // Process property reading. @Override public void onPropertiesGet(String requestId, String serviceId) { log.info("OnPropertiesGet " + serviceId); Map<String ,Object> json = new HashMap<>(); Random rand = new Random(); json.put("alarm", alarm); json.put("temperature", rand.nextFloat()*100.0f); json.put("humidity", rand.nextFloat()*100.0f); json.put("smokeConcentration", rand.nextFloat() * 100.0f); ServiceProperty serviceProperty = new ServiceProperty(); serviceProperty.setProperties(json); serviceProperty.setServiceId("smokeDetector"); // Report the property reading response. device.getClient().respondPropsGet(requestId, Arrays.asList(serviceProperty)); } });
Verify the setting:
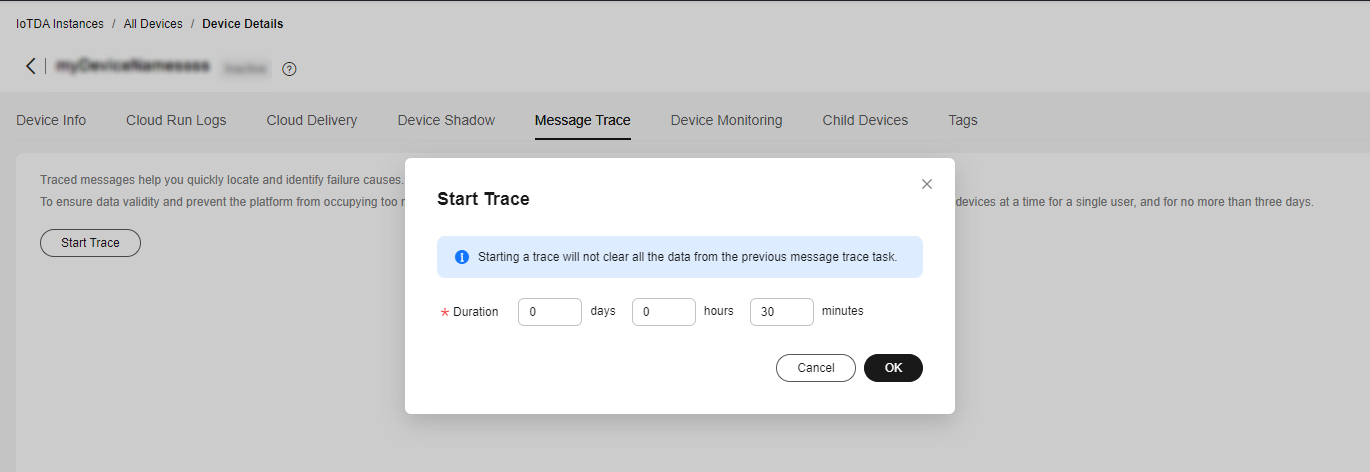
- On the IoTDA console, click the target instance card. In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices. On the displayed page, locate the target device, and click View in the Operation column to access its details page. Click the Message Trace tab, and click Start Trace.
Figure 2 Message tracing - Starting message tracing
- Run the SDK code on the device to bring the device online.
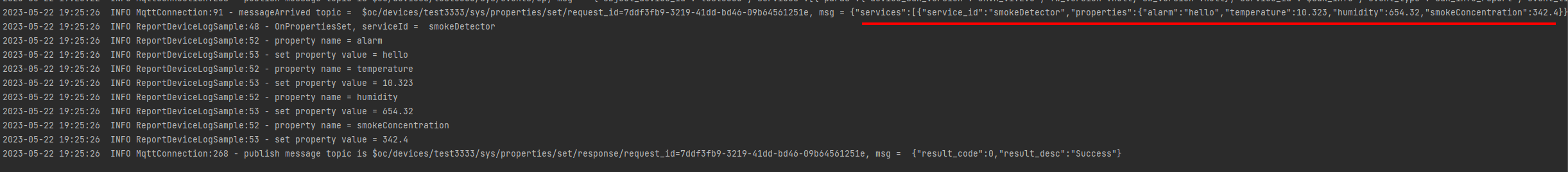
- Run the SDK code on the application and call the API for modifying device properties to send a request to the device. The following provides the result received by the device.
Figure 3 Property modification result on the device
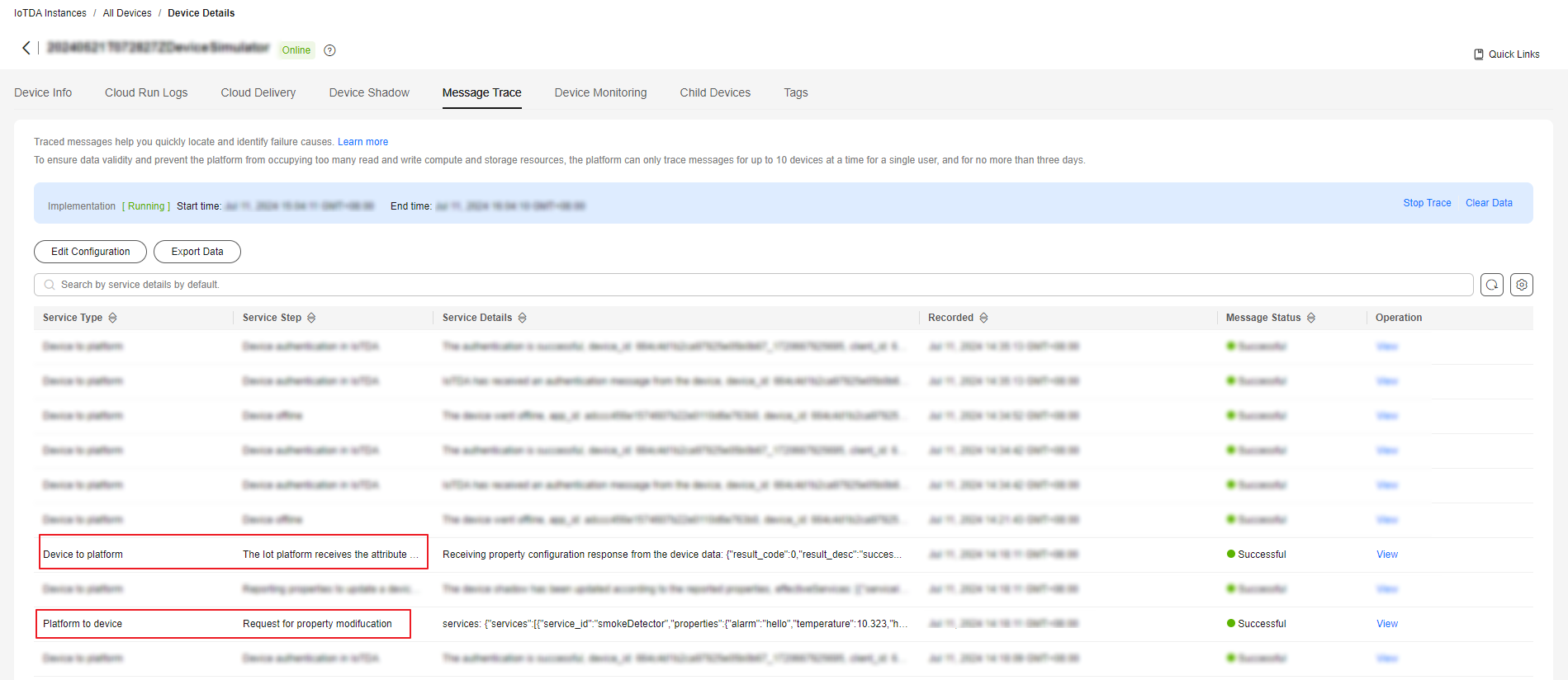
- Check the result on the Message Trace tab page.
Figure 4 Message tracing - Delivering properties
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





