هذه الصفحة غير متوفرة حاليًا بلغتك المحلية. نحن نعمل جاهدين على إضافة المزيد من اللغات. شاكرين تفهمك ودعمك المستمر لنا.
- What's New
- Function Overview
- Service Overview
-
Billing
- Billing Overview
- Billing Modes
- Billing Items
- Billing Examples
- Changing the Billing Mode
- Renewing Your Subscription
- Bills
- Arrears
- Billing Termination
- Cost Management
-
Billing FAQs
- How Is SecMaster Billed?
- Can I Use SecMaster for Free?
- How Do I Change or Disable Auto Renewal for SecMaster?
- Will SecMaster Be Billed After It Expires?
- How Do I Renew SecMaster When It Is About to Expire?
- Where Can I Unsubscribe from SecMaster?
- Where Can I View the Remaining Quotas of Security Data Collection and Security Data Packages?
- Getting Started
-
User Guide
- Buying SecMaster
- Authorizing SecMaster
- Checking Security Overview
- Workspaces
- Viewing Purchased Resources
-
Security Governance
- Security Governance Overview
- Security Compliance Pack Description
- Authorizing SecMaster to Access Cloud Service Resources
- Subscribing to or Unsubscribing from a Compliance Pack
- Starting a Self-Assessment
- Viewing Security Compliance Overview
- Viewing Evaluation Results
- Viewing Policy Scanning Results
- Downloading a Compliance Report
- Security Situation
- Resource Manager
- Risk Prevention
- Threat Operations
- Security Orchestration
-
Playbook Overview
- Ransomware Incident Response Solution
- Attack Link Analysis Alert Notification
- HSS Isolation and Killing of Malware
- Automatic Renaming of Alert Names
- Auto High-Risk Vulnerability Notification
- Automatic Notification of High-Risk Alerts
- Auto Blocking for High-risk Alerts
- Real-time Notification of Critical Organization and Management Operations
-
Settings
- Data Integration
-
Log Data Collection
- Data Collection Overview
- Adding a Node
- Configuring a Component
- Adding a Connection
- Creating and Editing a Parser
- Adding and Editing a Collection Channel
- Managing Connections
- Managing Parsers
- Managing Collection Channels
- Managing Collection Nodes
- Viewing Collection Nodes
- Partitioning a Disk
- Logstash Configuration Description
- Connector Rules
- Parser Rules
- Upgrading the Component Controller
- Customizing Directories
- Permissions Management
- Key Operations Recorded by CTS
-
Best Practices
-
Log Access and Transfer Operation Guide
- Solution Overview
- Resource Planning
- Process Flow
-
Procedure
- (Optional) Step 1: Buy an ECS
- (Optional) Step 2: Buy a Data Disk
- (Optional) Step 3: Attach a Data Disk
- Step 4: Create a Non-administrator IAM User
- Step 5: Configure Network Connection
- Step 6: Install the Component Controller (isap-agent)
- Step 7: Install the Log Collection Component (Logstash)
- (Optional) Step 8: Creating a Log Storage Pipeline
- Step 9: Configure a Connector
- (Optional) Step 10: Configure a Log Parser
- Step 11: Configure a Log Collection Channel
- Step 12: Verify Log Access and Transfer
- Credential Leakage Response Solution
-
Log Access and Transfer Operation Guide
-
API Reference
- Before You Start
- API Overview
- Calling APIs
-
API
- Alert Management
- Incident Management
- Indicator Management
- Playbook Management
- Alert Rule Management
- Playbook Version Management
- Playbook Rule Management
- Playbook Instance Management
- Playbook Approval Management
- Playbook Action Management
- Incident Relationship Management
- Data Class Management
- Workflow Management
- Data Space Management
- Pipelines
- Workspace Management
- Metering and Billing
- Metric Query
- Baseline Inspection
- Appendix
- FAQs
-
More Documents
-
User Guide (ME-Abu Dhabi Region)
- Service Overview
- Permissions Management
- Buying SecMaster
- Authorizing SecMaster
- Security Overview
- Workspaces
- Viewing Purchased Resources
- Security Situation
- Resource Manager
- Risk Prevention
-
Threat Operations
- Incident Management
- Alert Management
- Indicator Management
- Intelligent Modeling
-
Security Analysis
- Security Analysis Overview
- How to Use Security Analysis
- Configuring Indexes
- Querying and Analyzing Data
- Downloading Logs
-
Query and Analysis Statements - SQL Syntax
- Basic Syntax
- Limitations and Constraints
- Query Statements
- Syntax of Analysis Statements
- Analysis Statements - SELECT
- Analysis Statements - GROUP BY
- Analysis Statements - HAVING
- Analysis Statements - ORDER BY
- Analysis Statements - LIMIT
- Analysis Statements - Functions
- Analysis Statements - Aggregate Functions
- Quick Query
- Quickly Adding a Log Alarm Model
- Charts
- Managing Data Spaces
- Managing Pipelines
- Data Consumption
- Data Delivery
- Data Monitoring
-
Security Orchestration
- Security Orchestration Overview
- Built-in Playbooks and Workflows
- Security Orchestration Process
- (Optional) Configuring and Enabling a Workflow
- Configuring and Enabling a Playbook
- Operation Object Management
- Playbook Orchestration Management
- Layout Management
- Plug-in Management
- Settings
-
FAQs
-
Product Consulting
- Why Is There No Attack Data or Only A Small Amount of Attack Data?
- Where Does SecMaster Obtain Its Data From?
- What Are the Dependencies and Differences Between SecMaster and Other Security Services?
- What Are the Differences Between SecMaster and HSS?
- How Do I Update My Security Score?
- How Do I Handle a Brute-force Attack?
- Data Synchronization and Consistency
- How Do I Grant Permissions to an IAM User?
- Purchase Consulting
- Troubleshooting
-
Product Consulting
- Change History
-
User Guide (Kuala Lumpur Region)
- Service Overview
- Authorizing SecMaster
- Security Overview
- Workspaces
- Viewing Purchased Resources
- Security Situation
- Resource Manager
-
Risk Prevention
-
Baseline Inspection
- Baseline Inspection Overview
- Creating a Custom Check Plan
- Starting an Immediate Baseline Check
- Viewing Check Results
- Handling Check Results
- Viewing Compliance Packs
- Creating a Custom Compliance Pack
- Importing and Exporting a Compliance Pack
- Viewing Check Items
- Creating a Custom Check Item
- Importing and Exporting Check Items
- Vulnerability Management
- Policy Management
-
Baseline Inspection
-
Threat Operations
- Incident Management
- Alert Management
- Indicator Management
- Intelligent Modeling
- Security Analysis
- Data Delivery
-
Security Orchestration
- Security Orchestration Overview
- Built-in Playbooks
- Security Orchestration Process
- (Optional) Configuring and Enabling a Workflow
- Configuring and Enabling a Playbook
- Operation Object Management
- Playbook Orchestration Management
- Layout Management
- Plug-in Management
- Settings
-
FAQs
-
Product Consulting
- Why Is There No Attack Data or Only A Small Amount of Attack Data?
- Where Does SecMaster Obtain Its Data From?
- What Are the Dependencies and Differences Between SecMaster and Other Security Services?
- What Are the Differences Between SecMaster and HSS?
- How Do I Update My Security Score?
- How Do I Handle a Brute-force Attack?
- Issues About Data Synchronization and Data Consistency
- About Data Collection Faults
-
Product Consulting
- Change History
-
User Guide (ME-Abu Dhabi Region)
- General Reference
Show all
Copied.
Creating a Pipeline
Scenario
A data transfer message topic and a storage index form a pipeline.
To use the security analysis, data analysis, and intelligent modeling functions provided by SecMaster, you need to create pipelines.
This section describes how to create a pipeline.
Prerequisites
- A workspace has been created. For details, see Creating a Workspace.
- A data space has been added. For details, see Creating a Data Space.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper part of the page and choose Security > SecMaster.
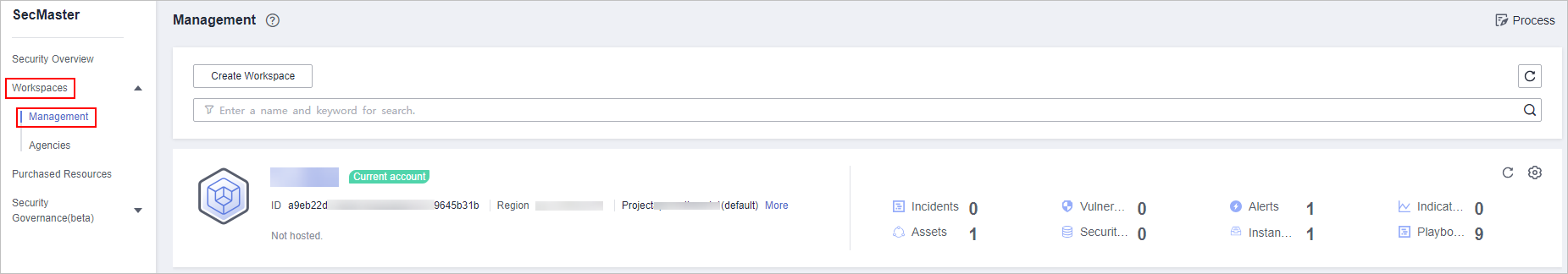
in the upper part of the page and choose Security > SecMaster. - In the navigation pane on the left, choose Workspaces > Management. In the workspace list, click the name of the target workspace.
Figure 1 Workspace management page
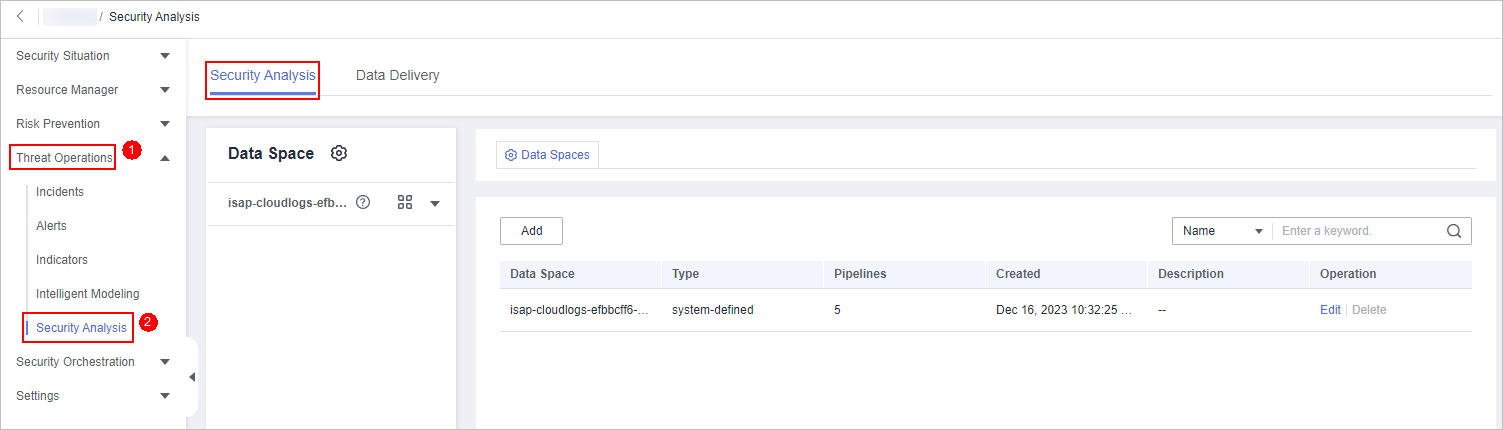
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Threat Operations > Security Analysis. The security analysis page is displayed.
Figure 2 Accessing the Security Analysis tab page
- In the data space navigation pane on the left, click
 on the right of the data space name and select Create Pipeline from the drop-down list box. The Create Pipeline page is displayed on the right.
Figure 3 Creating a pipeline
on the right of the data space name and select Create Pipeline from the drop-down list box. The Create Pipeline page is displayed on the right.
Figure 3 Creating a pipeline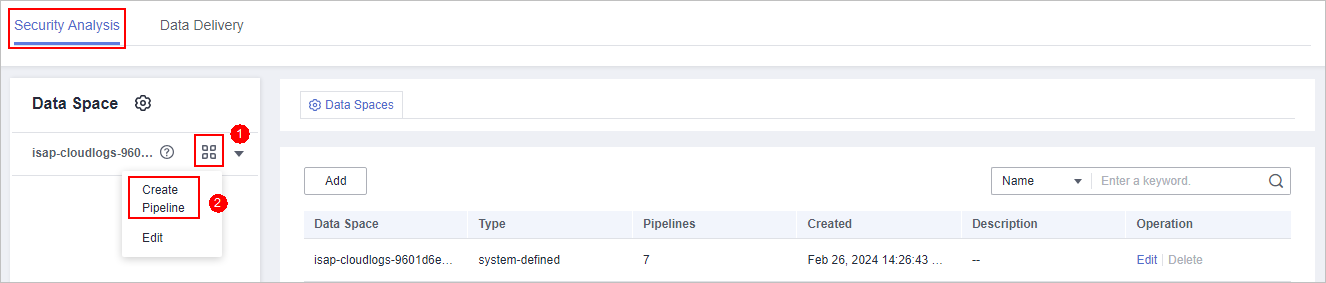
- On the Create Pipeline page, configure pipeline parameters. For details about the parameters, see Table 1.
Table 1 Creating a pipeline Parameter
Description
Data Spaces
Data space to which the pipeline belongs, which is generated by the system by default.
Pipeline Name
Name of the pipeline. It must meet the following requirements:
- The name contains 5 to 63 characters.
- The value can contain letters, numbers, and hyphens (-). The hyphen (-) cannot be used at the beginning or end, or used consecutively.
- The name must be unique in the data space.
Shards
The number of shards of the pipeline. The value range is 1 to 64.
An index can potentially store a large amount of data that exceeds the hardware limits of a single node. To solve this problem, Elasticsearch subdivides your index into multiple pieces called shards. When creating an index, you can specify the number of shards as required. Each shard is in itself a fully-functional and independent "index" that can be hosted on any node in the cluster.
Lifecycle
Life cycle of data in the pipeline. Value range: 7-180
Description
Remarks on the pipeline. This parameter is optional.
- Click OK.
After the pipeline is created, you can click the data space name or
 next to the data space to view the created pipeline.
next to the data space to view the created pipeline.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





