What Is CloudPond?
Background Information
5th generation mobile networks (5G) and artificial intelligence (AI) make innovative services, such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), interactive live streaming, automated driving, and smart manufacturing, a reality for the world. These services demand for low latency and high bandwidth. Centralized cloud computing is generally far away from devices and has the following disadvantages:
- High network latency: Centralized cloud computing cannot process and analyze data in a timely manner, resulting in slow application response and poor user experience.
- High bandwidth cost: Data generated by applications needs to be transmitted to the cloud, which consumes large bandwidth. As a result, service providers need to spend a large amount of money on bandwidth.
- Data compliance: Data generated by applications is stored on the cloud, whereas enterprises want sensitive data to be stored on premises to meet the requirement for data compliance.
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to where they are needed to improve response speed, save bandwidth, and ensure data compliance.
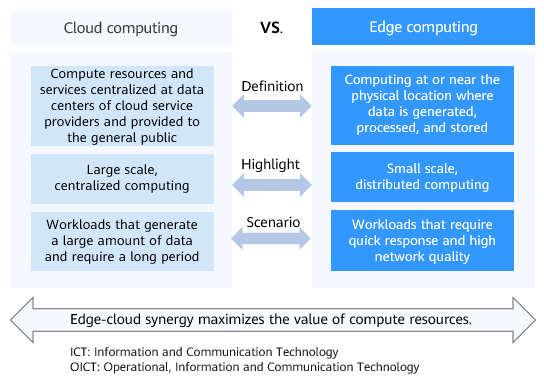
Figure 1 shows the differences between cloud computing and edge computing.
Edge computing extends cloud computing to the edge, and the two are mutually complementary. To fit into the requirements in different scenarios, you need to leverage both cloud computing and edge computing to form an edge-cloud synergy.
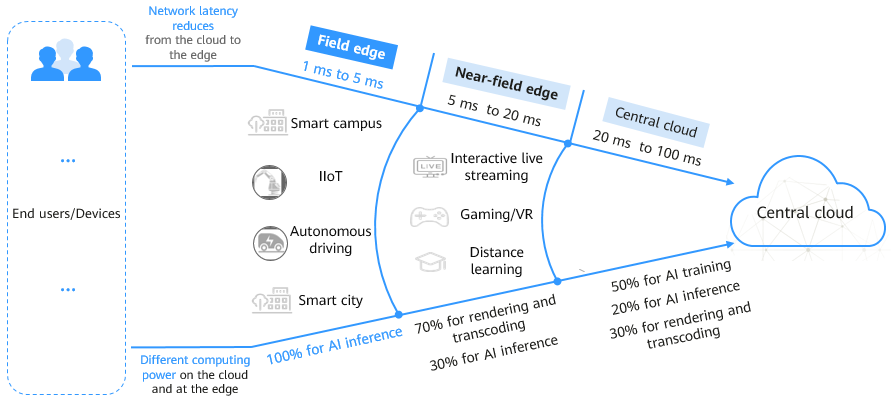
Figure 2 illustrates the scope of edge computing.
There are three rough categories of network latency, each defined by their distance from end users. From closest to farthest, these ranges are the field edge, the near-field edge, and the cloud.
- Field edge: The network latency ranges from 1 ms to 5 ms, and computing power is primarily used for AI inference. Real-time services, such as autonomous driving and industrial Internet perform well at the field edge.
- Near-field edge: The network latency ranges from 5 ms to 20 ms. The computing power is mainly used for rendering, and the rest for AI inference. Video services are positioned to run at the near-field edge.
- Public cloud (or central cloud): The network latency is between 20 ms and 100 ms, and workloads that are not delegated to the edge, such as massive data storage, data mining, and training, are generally deployed on the central cloud.
For the field edge scenarios, CloudPond is a good choice that provides integrated hardware and software on your premises.
What Is CloudPond?
CloudPond extends the cloud infrastructure and cloud services to your on-premises facility to allow you to enjoy ultra-low latency and faster access to applications on the cloud. It is suitable for scenarios that have high requirements for network latency, local data storage, and interaction with the on-premises system.
For more information, see How Is CloudPond Related to Huawei Cloud?
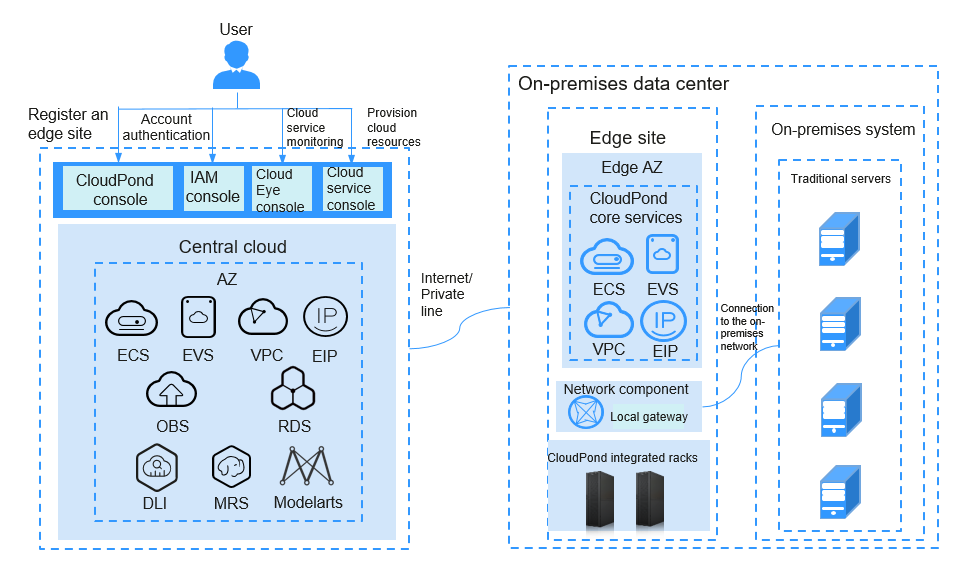
Figure 3 shows the CloudPond product architecture. You are advised to familiarize yourself with the product concepts.
- Pre-integrated racks are delivered to your on-premises data center, allowing you to use cloud services locally.
- An edge site is deployed in an edge AZ and is fully managed by Huawei Cloud. You can enjoy the same experience as in central AZs. Edge sites, edge AZs, and cloud resources used by the edge sites are dedicated for your exclusive use. For more information about edge AZs and regions, see What Are the Relationships Between Edge Sites, Regions, and AZs?
You can deploy multiple edge sites in one on-premises data center or an edge site in each data center, depending on your requirements.
- The CloudPond console is deployed on the central cloud. You can view edge site information and cloud service resource usage on the console.
- CloudPond allows you to run core cloud services on premises, including Elastic Cloud Server (ECS), Elastic Volume Service (EVS), Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and Elastic IP. In addition to core cloud services, you can deploy additional cloud services as required. For details about cloud services supported by CloudPond, see Cloud Services Interacting with CloudPond. You can also use Identity and Access Management (IAM) to authenticate accounts and Cloud Eye to monitor cloud resources used by edge site.
- An edge site can connect to both your on-premises network and the cloud.
- You can connect the edge site to your on-premises system. In this way, the edge site can communicate with the on-premises over a private network.
- The edge AZ where the edge site resides shares the same VPC with the central AZ on the cloud, so that the edge site can access other cloud services on the cloud over a private network.
For more information, see Network Connectivity and Networking Requirements.
Why CloudPond?
Considering the difficulties of building IT systems, such as long deployment period, difficult O&M, and high operation costs, many enterprises choose to migrate their workloads to the cloud. Choosing an appropriate type of cloud computing depends on legacy systems of enterprises and their requirements for the cloud. There are three main types of cloud computing, including private clouds, public clouds, and hybrid clouds. Each type has their own strengths and shortcomings.
CloudPond provides a brand new form of cloud computing. It inherits the advantages of mainstream cloud computing and features low network latency, low cost, and data localization, addressing the pain points in some scenarios where only one type of cloud computing is used.
Table 1 lists the differences between CloudPond, private cloud, public cloud, and hybrid cloud.
|
Type |
CloudPond |
Private Cloud |
Public Cloud |
Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Outline |
A cloud service that extends the cloud infrastructure and provides compute and storage resources for the edge. |
A cloud computing environment that is dedicated to a single customer. The underlying IT infrastructure is dedicated to this customer with completely isolated access. |
A cloud computing environment that is typically created from the IT infrastructure owned by the cloud service provider and provides services to the general public over the Internet in pay-per-use or yearly/monthly mode. |
A blend of private clouds and public clouds. Customers keep confidential information secured on their private clouds, but make more general, customer-facing content on a public cloud. |
|
Installation and Maintenance |
Customers lease pre-integrated racks from Huawei Cloud, who is responsible for the installation and O&M of racks on premises. They only need to ensure the availability and stability of their equipment rooms. |
|
Customers can directly use cloud services provided by the cloud providers, who are responsible for the installation and O&M of the IT infrastructure. |
Customers lease or buy the IT infrastructure from both the private and public cloud providers and work with them to install and maintain the infrastructure. |
|
Exclusive Use of Cloud Resources |
Exclusive use |
Exclusive use |
Shared with other users |
Blend |
|
Data Localization |
Data is stored on customer premises, meeting data compliance requirements. |
Data is stored in customer's or cloud provider's data center. |
Data is stored in the cloud provider's data center. |
Partial data is stored locally, and partial data is stored in the cloud provider's data center, depending on customer requirements. |
|
Network Latency |
Low (workloads running on customer premises) |
Low (workloads running on customer premises or in the cloud provider's data center) |
High (workloads running on the public cloud) |
Depends on where workloads are running |
|
Cost |
Low. The cost mainly consists of the equipment room, energy, cloud services, service support, and personnel (for on-premises system O&M). |
High. The cost mainly consists of the equipment room, energy, devices, private cloud software, service support, and personnel (for on-premises system O&M and platform O&M). |
Low. The cost consists of cloud services, network, service support, and personnel costs (for on-premises system O&M). |
Medium. The cost depends on how much each cloud is used. |
For more details, see Product Advantages.
Access Methods
You can access CloudPond using the management console.
For details, see Getting Started.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot