SQL Execution Control
Scenarios
- All requests whose execution duration exceeds n seconds need to be killed.
- Requests from an IP address for a specific client need to be killed.
- All requests for full table scan need to be killed.
Precautions
- All nodes of the selected node type must have at least 4 vCPUs.
- This function is available for replica set instances and cluster instances of version 3.4 or later.
- A maximum of 10 rules can be created for a DB instance.
- For an ultra-large cluster with more than 32 shards, creating and enabling rules whose Node Type is shard or dds mongos_shard will fail. You are advised to create rules whose Node Type is dds mongos.
- For a cluster with more than 10 shards, you are advised to select one rule at a time when enabling or disabling rules.
Creating a Rule
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service. - On the Instances page, locate the target DB instance and click its name.
- In the navigation tree on the left, click SQL Execution Control.
Figure 1 SQL Execution Control

- Click Create Rule.
Figure 2 Create Rule

- On the Create Rule page, set parameters as required. For details, see Table 1.
Figure 3 Parameters for creating a rule
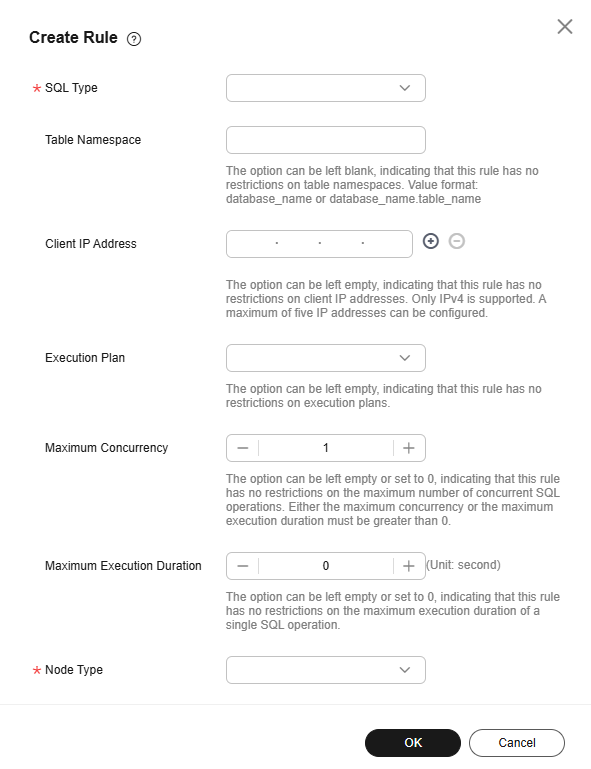
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
SQL Type
You can specify one or more SQL statement types.
The value can be:- query: operation for querying data.
- update: operation for updating data.
- insert: operation for inserting data.
- remove: operation for deleting data.
- command: command operation.
- getmore: operation for obtaining more data.
Table Namespace
- If this parameter is left blank, this rule applies to operations on all databases and tables in the DB instance.
- If this parameter is set to a database name, this rule applies to operations on all collections in the database. For example, the value can be db1.
- If this parameter is set to a value in the format of database_name.collection_name, this rule only applies to operations on the collection. For example, the value can be db1.coll1.
Client IP Address
If an ECS on Huawei Cloud is used, the value is the private IP address of the ECS.
NOTE:- This parameter does not take effect for cluster DB instances of version 3.4.
Execution Plan
- By default, this parameter is left blank, indicating that this rule applies to all execution plans.
- The value COLLSCAN indicates that the operation for full table scan will be killed.
Maximum Concurrency
- The value 0 indicates that this parameter does not take effect.
- For example, if this parameter is set to 100, a maximum of 100 operations that meet the conditions can be performed.
NOTE:
If there are 110 currentOp operations that meet the conditions, 10 operations will be randomly killed.
- Either this parameter or Maximum Execution Duration must be greater than 0.
Maximum Execution Duration
- The value 0 indicates that this parameter does not take effect.
- For example, if this parameter is set to 5, currentOp operations executed for more than 5s will be killed. The value must be no less than 2.
- Either this parameter or Maximum Concurrency must be greater than 0.
Node Type
- dds mongos indicates that this rule only applies to mongos nodes in a DDS instance.
- shard indicates that this rule only applies to shard nodes.
- dds mongos_shard indicates that this rule applies to both mongos and shard nodes in a DDS instance.
- replica indicates that this rule applies to replica sets.
- Click OK.
Enabling a Rule
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service. - On the Instances page, locate the target DB instance and click its name.
- In the navigation tree on the left, click SQL Execution Control.
Figure 4 SQL Execution Control

- Locate the target rule and click Enable in the Operation column.
Figure 5 Enable

- Click Yes.
Figure 6 Enable Rule

- View the rule status on the SQL Execution Control page.
Figure 7 Status

Disabling a Rule
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service. - On the Instances page, locate the target DB instance and click its name.
- In the navigation tree on the left, click SQL Execution Control.
Figure 8 SQL Execution Control
- Locate the target rule and click Disable in the Operation column.
Figure 9 Disable

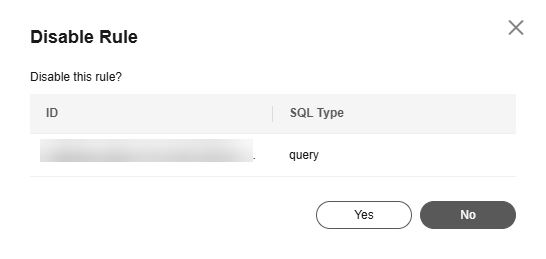
- Click Yes.
Figure 10 Disable Rule
- View the rule status on the SQL Execution Control page.
Figure 11 Status

Deleting a Rule

An enabled rule cannot be deleted. To delete a rule, you must disable the rule by referring to Disabling a Rule.
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service. - On the Instances page, locate the target DB instance and click its name.
- In the navigation tree on the left, click SQL Execution Control.
Figure 12 SQL Execution Control
- Locate the target rule and click Delete in the Operation column.
Figure 13 Delete

- Click Yes.
Figure 14 Delete Rule

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





