Audit Log Policy Management
Scenarios
An audit log records operations performed on your databases and collections. The generated log files are stored in OBS. Auditing logs can enhance your database security and help you analyze the cause of failed operations.
Precautions
- The audit policy of a DDS DB instance is disabled by default. You can enable it based on your service requirements. After the function is enabled, the system records audit information about read and write operations. The impacts on database performance vary depending on the service model. If the database encounters a performance bottleneck after this function is enabled, you need to temporarily disable the function or upgrade the specifications.
- You will be charged for enabling SQL audit log. For details, see Service Pricing.
- DDS checks generated audit logs. If the retention period of logs exceeds the period you set, DDS will delete the logs. It is recommended that audit logs be stored for more than 180 days for tracing and problem analysis.
- After the audit policy is modified, DDS audits logs according to the new policy and the retention period of the original audit logs is subject to the modified retention period.
- You are not advised to delete audit logs. To delete audit logs, ensure that this operation meets external and internal security compliance requirements, and download audit logs and back them up locally. Audit logs cannot be restored after being deleted. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- You can view, download, and delete DDS instance audit logs on the DDS console. For details, see Viewing Audit Logs on the DDS Console. By enabling log reporting in Log Reporting, you can also view details about audit logs of DDS DB instances on the LTS console, including searching for logs, monitoring logs, downloading logs, and viewing real-time logs. For details, see Viewing Audit Logs on the LTS Console.
- By default, audit logs are generated every hour. If the size of an audit log exceeds 20 MB, a new audit log is generated.
- Your data must be encoded in UTF-8 format. For data in other format, the auditing result of the corresponding statement may be missing or contain garbled characters.
- Audit log files stored on OBS are invisible to you. They are only visible in the DDS backend management system.
Example Traces
The following is an example of querying the replica set status. For details about the fields, see Table 1.
{
"atype": "query",
"ts": {
"$date": "2025-02-27T12:35:40.512+0000"
},
"local": {
"ip": "192.168.30.90",
"port": 8635
},
"remote": {
"ip": "192.168.26.20",
"port": 43818
},
"users": [
{
"user": "rwuser",
"db": "admin"
}
],
"roles": [
{
"role": "root",
"db": "admin"
}
],
"param": {
"command": "query",
"ns": "test.a",
"args": {
"find": "a",
"filter": {
},
"lsid": {
"id": {
"$binary": "7kwKmFh9TxGStjtn5Urt2w==",
"$type": "04"
}
},
"$clusterTime": {
"clusterTime": {
"$timestamp": {
"t": 1740659738,
"i": 2
}
},
"signature": {
"hash": {
"$binary": "t2eFI3gB9ZruNYf5Y0FIgAZRCr4=",
"$type": "00"
},
"keyId": {
"$numberLong": "7472645695153897501"
}
}
},
"$db": "test"
}
},
"result": 0
"sessionId": "1641365",
"username": "rwuser",
"clientname": "MongoDB Shell",
"affectRows": "0",
"startTime": "1740659740512716",
"endTime": "1740659740513937",
"docsExamined": "0",
"keysExamined": "0",
"returnNum": "0",
"success": true
}
New fields have been added to audit logs in versions later than 250130. You can download the original logs to view the new fields. The audit log fields displayed on the console remain unchanged.
|
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
atype |
stringData |
Operation type of the event. |
|
ts |
Date_t |
Timestamp when the event is generated. |
|
local(ip) |
BSONObj (ip + port) |
Local IP address. |
|
remote(ip) |
BSONObj (ip + port) |
Remote IP address. |
|
users |
BSONArray |
User group. |
|
roles |
BSONArray |
Role group. |
|
param |
BSONObj |
Parameters involved in the command. |
|
result |
ErrorCodes::Error |
Permission authentication result (not the command execution result). |
|
sessionId |
stringData |
Session ID, which uniquely identifies a connection. |
|
username |
stringData |
User who runs the command. |
|
clientname |
stringData |
Information about the client that runs the command. |
|
affectRows |
long long |
Number of rows in the document that is affected by the command execution. |
|
startTime |
timestamp |
Time when the command starts to be executed. |
|
endTime |
timestamp |
Time when the command ends to be executed. |
|
docsExamined |
long long |
Number of documents read during command execution. |
|
keysExamined |
long long |
Number of indexes read during command execution. |
|
returnNum |
long long |
Number of documents in the command execution result. |
|
success |
bool |
Whether the command execution status is normal. |
Configuring the Audit Policy
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Document Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Audit Logs.
- On the Audit Logs page, click Set Audit Policy.
- On the displayed page, click
 .
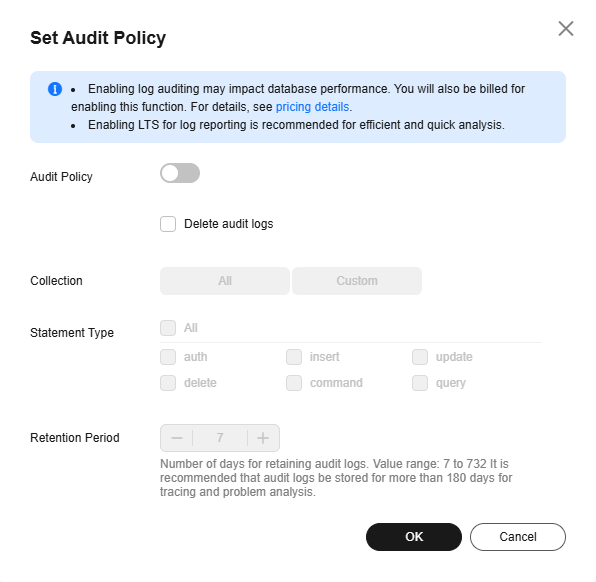
. - Configure required parameters and click OK to enable the audit policy.
Figure 1 Enabling audit policy
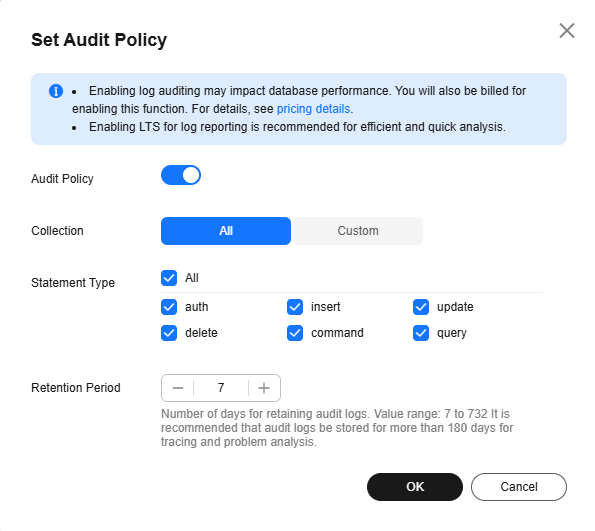
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Description
All
Audit all collections in the instance.
Custom
Audit specified databases or collections in the instance.
The database or collection name cannot contain spaces or the following special characters: /\' : "[]{}() The dollar sign ($) can be used only as an escape character.
The database name can contain a maximum of 64 characters.
If you enter a combined database and collection name, the total name length is 120 characters with the database name length of no more than 64 characters and the collection name cannot be blank, contain null, or use system. in prefix.
Statement Type
You can query audit logs of specified statements in a collection, including auth, insert, update, delete, command and query statements.
Retention Days
The number of days to retain audit logs. Range: 7 to 732
- After the audit policy is enabled, you can modify it as required. After the modification, logs are generated according to the new policy and the retention period of the original logs is subject to the modified retention period.
To modify the audit policy, click Set Audit Policy. In the dialog box that is displayed, modify the audit policy.
Figure 2 Modifying the audit policy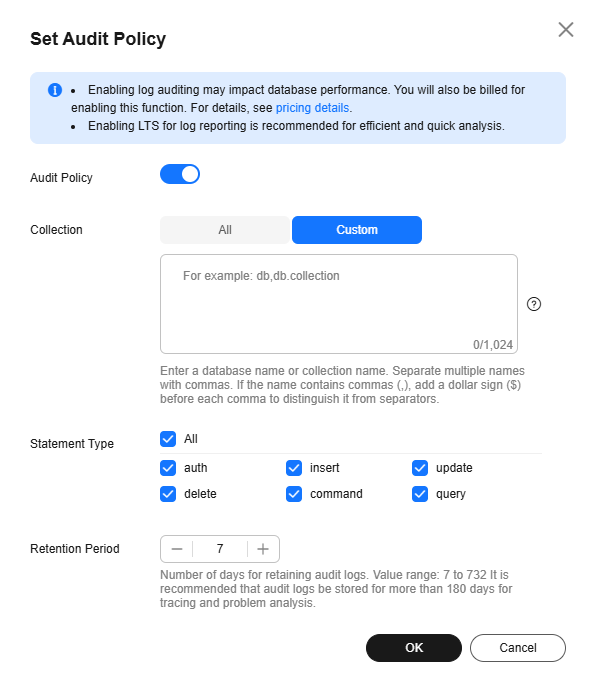
- Disable the audit policy.
After the audit policy is disabled, no audit log is generated.
To disable the audit policy, click
 . Figure 3 shows the dialog box for setting the backup policy.
. Figure 3 shows the dialog box for setting the backup policy.You can determine whether to delete all audit logs:
- If you do not select Delete audit logs, all audit logs within the retention period will be retained. You can manually delete them later.
- If you select Delete audit logs, all audit logs within the retention period will be deleted.
Click OK.
- After the audit policy is enabled, you can modify it as required. After the modification, logs are generated according to the new policy and the retention period of the original logs is subject to the modified retention period.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot