How Do I Perform Local Development and Testing?
The local development tool provides you with service discovery, registration, and query functions during development, commissioning, and testing.
Concept
This section describes how to locally develop and commission consumer and provider applications. Both service providers and consumers need to connect to a remote service center. This section describes how to start the local service center for local microservice commissioning.
The service center is an important component in the microservice framework. It is used to manage, register, and discover service metadata and service instance metadata. The following figure shows the logical relationship between the service center and microservice provider/consumer.
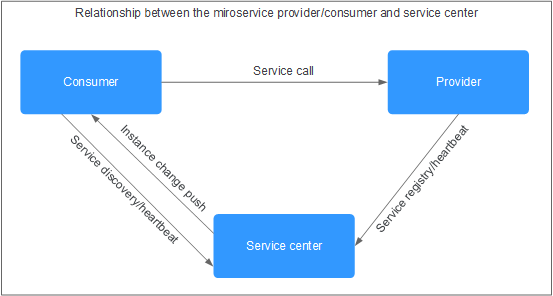
Prerequisites
- Starting the local service center will occupy ports 30100, 30110, and 30103 of the server, which indicate the backend service port of the service center and the backend and frontend service ports of the configuration center. Ensure that these ports are not in use.
- Before using the local service center, ensure that the environment meets the following requirements:
- Operating system: Linux/Unix, Windows 64-bit
- CPU architecture: x86/Arm
- Browser: Chrome, Safari, Edge
Starting the Local Service Center
- Download the local development tool package of the required version to the local PC based on the operating system and CPU architecture, and decompress the package to the installation directory. For details, see Local Development Tool.
- Start CSE.
- On Linux or Unix, go to the root installation directory and run the following command:
nohup sh start.sh >/dev/null 2>&1 &
- On Windows, go to the root installation directory and double-click cse.exe.
- On Linux or Unix, go to the root installation directory and run the following command:
- Stop CSE.
- On Linux or Unix, go to the root installation directory and run the following command:
sh stop.sh
- On Windows, close the command-line interface.
- On Linux or Unix, go to the root installation directory and run the following command:
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





