Viewing CTS Traces in the Trace List
Scenarios
Cloud Trace Service (CTS) records operations performed on cloud service resources. A record contains information such as the user who performed the operation, IP address, operation content, and returned response message. These records facilitate security auditing, issue tracking, and resource locating. They also help you plan and use resources, and identify high-risk or non-compliant operations.
What Is a Trace?
A trace is an operation log for a cloud service resource, tracked and stored by CTS. Traces record operations such as adding, modifying, or deleting cloud service resources. You can view them to identify who performed operations and when for detailed tracking.
What Is a Management Tracker and Data Tracker?
A management tracker identifies and associates with all your cloud services, recording all user operations. It records management traces, which are operations performed by users on cloud service resources, such as their creation, modification, and deletion.
A data tracker records details of user operations on data in OBS buckets. It records data traces reported by OBS, detailing user operations on data in OBS buckets, including uploads and downloads.
Constraints
- Before the organization function is enabled, you can query the traces of a single account on the CTS console. After the organization function is enabled, you can only view multi-account traces on the Trace List page of each account, or in the OBS bucket or the CTS/system log stream configured for the management tracker with the organization function enabled. For details about organization trackers, see Organization Trackers.
- You can only query operation records of the last seven days on the CTS console. They are automatically deleted upon expiration and cannot be manually deleted. To store them for longer than seven days, configure transfer to Object Storage Service (OBS) or Log Tank Service (LTS) so that you can view them in OBS buckets or LTS log groups.
- After creating, modifying, or deleting a cloud service resource, you can query management traces on the CTS console 1 minute later and query data traces 5 minutes later.
- Data traces are not displayed in the trace list of the new version. To view them, you need to go to the old version.
Prerequisites
- Register with Huawei Cloud and complete real-name authentication.
If you already have a Huawei Cloud account, skip this step. If you do not have one, do as follows:
- Log in to the Huawei Cloud official website, and click Sign Up in the upper right corner.
- Complete the registration as prompted. For details, see Registering with Huawei Cloud.
Your personal information page is displayed after the registration completes.
- Complete individual or enterprise real-name authentication by referring to Real-Name Authentication.
- Grant permissions for users.
If you log in to the console using a Huawei Cloud account, skip this step.
If you log in to the console as an IAM user, first contact your CTS administrator (account owner or a user in the admin user group) to obtain the CTS FullAccess permissions. For details, see Assigning Permissions to an IAM User.
Viewing Traces
After you enable CTS and the management tracker is created, CTS starts recording operations on cloud resources. After a data tracker is created, CTS starts recording user operations on data in OBS buckets. CTS retains operation records of the latest seven days.
This section describes how to query and export operation records of the last seven days on the CTS console.
Viewing Real-Time Traces in the Trace List of the New Edition
- Log in to the CTS console.
- Log in to the management console, click
 in the upper left corner, and choose Management & Deployment > Cloud Trace Service.
in the upper left corner, and choose Management & Deployment > Cloud Trace Service. - In the navigation pane, choose Trace List.
- In the time range drop-down list above the trace list, select a desired query time range: Last 1 hour, Last 1 day, or Last 1 week. You can also select Custom to specify a custom time range within the last seven days.
- The search box above the trace list supports advanced queries. Combine one or more filters to refine your search.
Table 1 Trace filtering parameters Parameter
Description
Trace Name
Name of a trace.
The entered value is case-sensitive and requires an exact match. Fuzzy matching is not supported.
For details about the operations that can be audited for each cloud service, see Supported Services and Operationssection "Supported Services and Operations" in the Cloud Trace Service User Guide.
Example: updateAlarm
Trace Source
Cloud service name abbreviation.
The entered value is case-sensitive and requires an exact match. Fuzzy matching is not supported.
Example: IAM
Resource Name
Name of a cloud resource involved in a trace.
The entered value is case-sensitive and requires an exact match. Fuzzy matching is not supported.
If the cloud resource involved in the trace does not have a resource name or the corresponding API operation does not involve the resource name parameter, leave this field empty.
Example: ecs-name
Resource ID
ID of a cloud resource involved in a trace.
The entered value is case-sensitive and requires an exact match. Fuzzy matching is not supported.
Leave this field empty if the resource has no resource ID or if resource creation failed.
Example: {VM ID}
Trace ID
Value of the trace_id parameter for a trace reported to CTS.
The entered value requires an exact match. Fuzzy matching is not supported.
Example: 01d18a1b-56ee-11f0-ac81-******1e229
Resource Type
Type of a resource involved in a trace.
The entered value is case-sensitive and requires an exact match. Fuzzy matching is not supported.
For details about the resource types of each cloud service, see Supported Services and Operationssection "Supported Services and Operations" in the Cloud Trace Service User Guide.
Example: user
Operator
User who triggers a trace.
Select one or more operators from the drop-down list.
If the value of trace_type in a trace is SystemAction, the operation is triggered by the service and the trace's operator may be empty.
For details about the relationship between IAM identities and operators and the operator username format, see Relationship Between IAM Identities and Operators.
Trace Status
Select one of the following options from the drop-down list:
- normal: The operation succeeded.
- warning: The operation failed.
- incident: The operation caused a fault that is more serious than a normal failure, for example, causing other faults.
Enterprise Project ID
ID of the enterprise project to which a resource belongs.
To check enterprise project IDs, go to the Enterprise Project Management Service (EPS) console and choose Project Management in the navigation pane.
Example: b305ea24-c930-4922-b4b9-******1eb2
Access Key
Temporary or permanent access key ID.
To check access key IDs, hover over your username in the upper right corner of the console and select My Credentials from the pop-up list. On the displayed page, choose Access Keys in the navigation pane.
Example: HSTAB47V9V*******TLN9
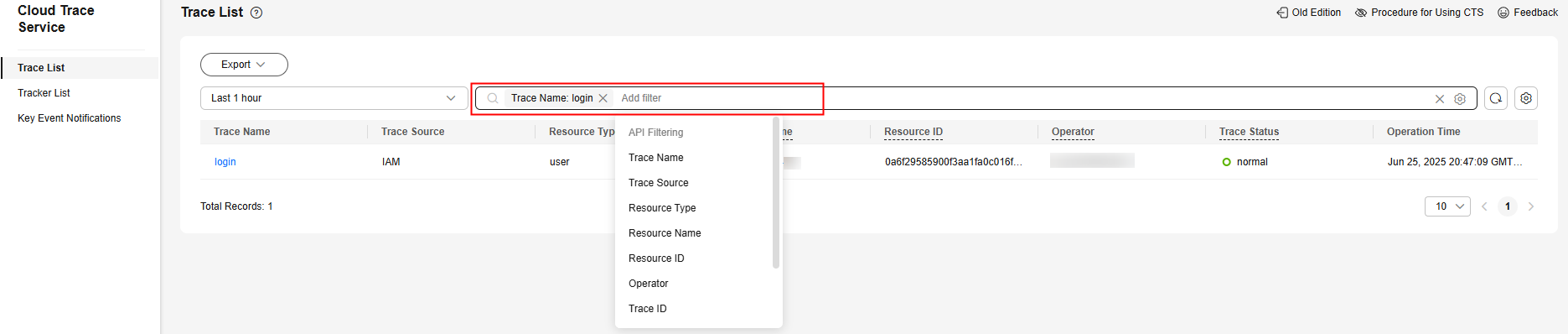
- On the Trace List page, you can also export and refresh the trace list, and customize columns to display.
- Enter any keyword in the search box and press Enter to filter desired traces.
- Click Export to export all traces in the query result as an .xlsx file. The file can contain up to 5,000 records.
- Click
 to view the latest information about traces.
to view the latest information about traces. - Click
 to customize the information to be displayed in the trace list. If Auto wrapping is enabled (
to customize the information to be displayed in the trace list. If Auto wrapping is enabled ( ), excess text will move down to the next line; otherwise, the text will be truncated. By default, this function is disabled.
), excess text will move down to the next line; otherwise, the text will be truncated. By default, this function is disabled.
- (Optional) On the Trace List page of the new edition, click Old Edition in the upper right corner to switch to the Trace List page of the old edition.
Viewing Traces in the Trace List of the Old Edition
- Log in to the CTS console.
- Log in to the management console, click
 in the upper left corner, and choose Management & Deployment > Cloud Trace Service.
in the upper left corner, and choose Management & Deployment > Cloud Trace Service. - In the navigation pane, choose Trace List.
- Each time you log in to the CTS console, the new edition is displayed by default. Click Old Edition in the upper right corner to switch to the trace list of the old edition.
- In the upper right corner of the page, set a desired query time range: Last 1 hour, Last 1 day, or Last 1 week. You can also click Customize to specify a custom time range within the last seven days.
- Set filters to search for your desired traces.
Table 2 Trace filtering parameters Parameter
Description
Trace Type
Select Management or Data.
- Management traces record operations performed by users on cloud service resources, including creation, modification, and deletion.
- Data traces are reported by OBS and record operations performed on data in OBS buckets, including uploads and downloads.
Trace Source
Select the name of the cloud service that triggers a trace from the drop-down list.
Resource type
Select the type of the resource involved in a trace from the drop-down list.
For details about the resource types of each cloud service, see Supported Services and Operationssection "Supported Services and Operations" in the Cloud Trace Service User Guide.
Search By
Select one of the following options:
- Resource ID: ID of the cloud resource involved in a trace.
Leave this field empty if the resource has no resource ID or if resource creation failed.
- Trace name: name of a trace.
For details about the operations that can be audited for each cloud service, see Supported Services and Operationssection "Supported Services and Operations" in the Cloud Trace Service User Guide.
- Resource name: name of the cloud resource involved in a trace.
If the cloud resource involved in the trace does not have a resource name or the corresponding API operation does not involve the resource name parameter, leave this field empty.
Operator
User who triggers a trace.
Select one or more operators from the drop-down list.
If the value of trace_type in a trace is SystemAction, the operation is triggered by the service and the trace's operator may be empty.
For details about the relationship between IAM identities and operators and the operator username format, see Relationship Between IAM Identities and Operators.
Trace Status
Select one of the following options:
- Normal: The operation succeeded.
- Warning: The operation failed.
- Incident: The operation caused a fault that is more serious than a normal failure, for example, causing other faults.
- Click Query.
- On the Trace List page, you can also export and refresh the trace list.
- Click Export to export all traces in the query result as a CSV file. The file can contain up to 5,000 records.
- Click
 to view the latest information about traces.
to view the latest information about traces.
- In the Tampered or Not column of a trace, check whether the trace is tampered with.
- If no, No is displayed.
- If yes, Yes is displayed.
- Click
 on the left of a trace to expand its details.
on the left of a trace to expand its details.
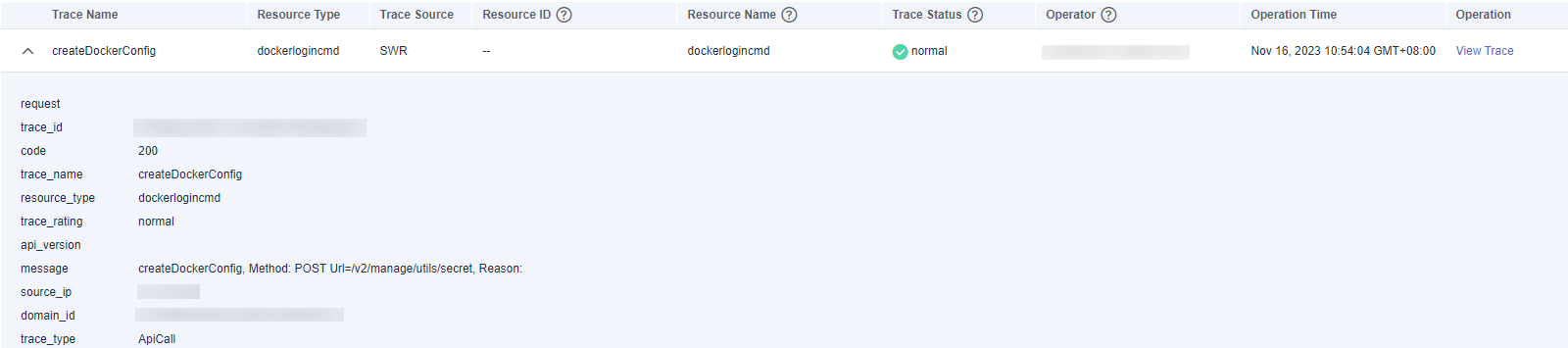
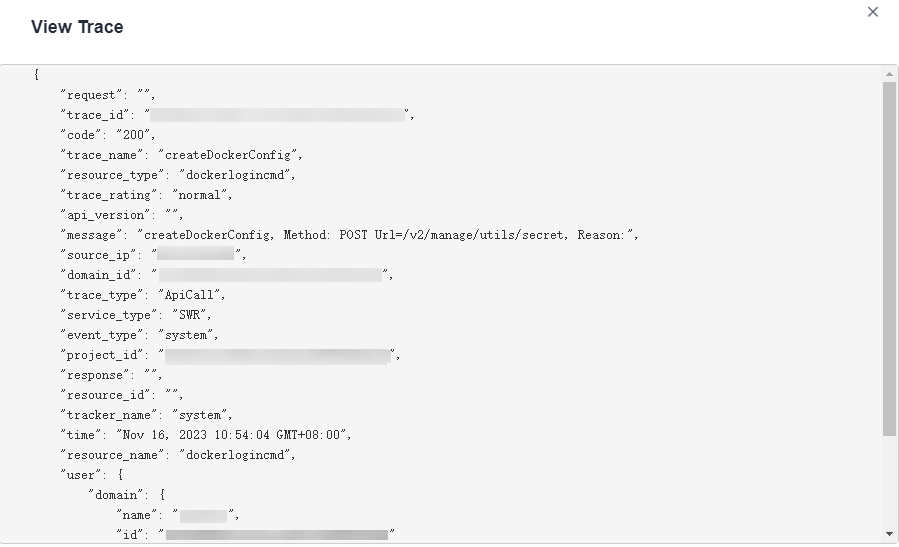
- Click View Trace in the Operation column. The trace details are displayed.
- (Optional) On the Trace List page of the old edition, click New Edition in the upper right corner to switch to the Trace List page of the new edition.
Helpful Links
- For details about the key fields in the trace structure, see Trace Structuresection "Trace References" > "Trace Structure" in the Cloud Trace Service User Guide and Example Tracessection "Trace References" > "Example Traces" in the Cloud Trace Service User Guide.
- You can use the following examples to learn how to query a specific trace:
- Use CTS to audit Elastic Volume Service (EVS) creation and deletion operations from the last two weeks. For details, see Security Auditing.
- Use CTS to locate a fault or creation failure for an Elastic Cloud Server (ECS). For details, see Fault Locating.
- Use CTS to check all operation records for an ECS. For details, see Resource Tracking.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





