Fault Locating
Scenarios
If a resource or action encounters a fault, you can quickly locate and analyze it. Just query the traces for that resource at the time of the fault and check the related actions and responses.
This section provides examples demonstrating how to use CTS to locate an ECS fault or an ECS creation failure.
Prerequisites
You have enabled CTS and trackers are running properly. For details about how to enable CTS, see Overview.
Viewing Real-Time Traces in the Trace List of the New Edition
The following shows how to locate an ECS fault which occurred in a morning.
- Log in to the management console as a CTS administrator.
- Click
 in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed.
in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed. - Choose Trace List in the navigation pane.
- Set the time range to 06:00 to 12:00 of the certain day and set the filters as follows:
Select Trace Source: ECS and Resource Type: ecs, then select Resource ID and enter {ID of the faulty VM}. You can also directly enter {ID of the faulty VM}.
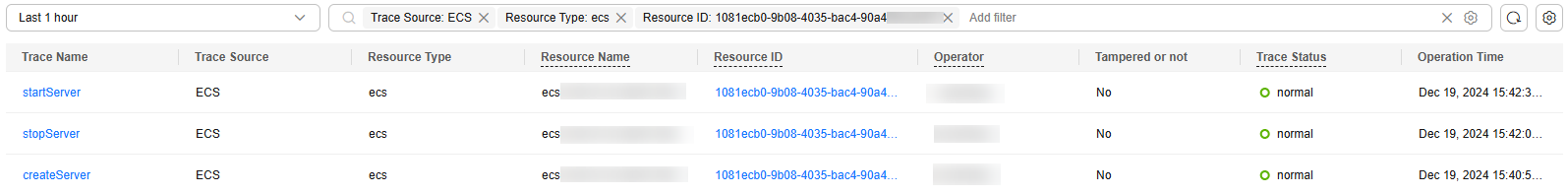
- Check the returned traces, especially the request type and response of each trace. Pay attention to traces whose status is warning or incident, and traces whose response indicates a failure.
The following shows how to locate a fault after an ECS server failed to be created.
- Log in to the management console as a CTS administrator.
- Click
 in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed.
in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed. - Choose Trace List in the navigation pane.
- Set filters as follows:
Select Trace Source: ECS, Resource Type: ecs, and Trace Status: warning.

- In the filtering result, locate the trace named createServer. Based on its error code or message, identify and analyze the fault.
Viewing Real-Time Traces in the Trace List of the Old Edition
The following shows how to locate an ECS fault which occurred in a morning.
- Log in to the management console as a CTS administrator.
- Click
 in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed.
in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed. - Choose Trace List in the navigation pane.
- In the time range setting area in the upper right corner, set the time to 06:00 to 12:00 on the certain day.
- Set filters above the trace list. Set Trace Type to Management, Trace Source to ECS, Resource Type to ecs, and Filter By to Resource ID. Enter {ID of the faulty VM} in the Resource ID text box.
- Click Query.
- Check the returned traces, especially the request type and response of each trace. Pay attention to traces whose status is warning or incident, and traces whose response indicates a failure.
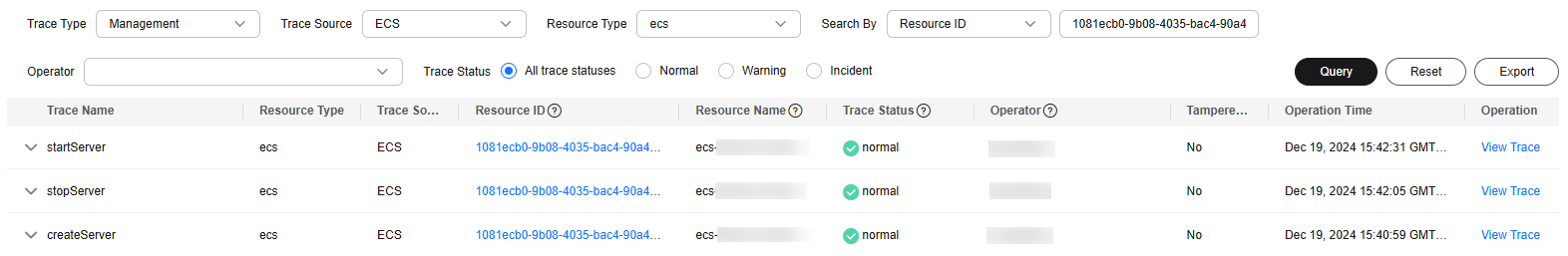
The following shows how to locate a fault after an ECS server failed to be created.
- Log in to the management console as a CTS administrator.
- Click
 in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner to select the desired region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed.
in the upper left corner and choose Management & Governance > Cloud Trace Service. The CTS console is displayed. - Choose Trace List in the navigation pane.
- Set filters as follows: Set Management for Trace Type, ECS for Trace Source, ecs for Resource Type, and Warning for Trace Status.
- Click Query.
- In the filtering result, locate the trace named createServer. Based on its error code or message, identify and analyze the fault.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





