Before You Start
Cloud Service Engine (CSE) is a cloud middleware used for microservice applications. It supports ServiceComb engines contributed to Apache by Huawei Cloud and open-source enhanced Nacos engines. You can also use other cloud services to quickly build a cloud-native microservice system, implementing quick development and high-availability O&M of microservice applications.
This document describes how to use APIs to perform operations on microservice engines, such as dynamic configuration, engine management, and microservice governance. For details about all supported operations, see API Overview.
Before calling microservice engine APIs, ensure that you are familiar with microservice engine concepts. For details, see Service Overview.
Service Center Address
The service center address is the request address for calling APIs. Different microservice engine instances have different service center addresses. For details, see Obtaining the Service Center Address of a ServiceComb Engine.
Concepts
- Account
An account is created upon successful registration with the cloud platform. The account has full access permissions for all of its cloud services and resources. It can be used to reset user passwords and grant user permissions. The account is a payment entity and should not be used directly to perform routine management. For security purposes, create users and grant them permissions for routine management.
- User
An Identity and Access Management (IAM) user is created using an account to use cloud services. Each IAM user has its own identity credentials (password and access keys).
The account name, username, and password will be required for API authentication.
- Region
Regions are divided from the dimensions of geographical location and network latency. Public services, such as Elastic Cloud Server (ECS), Elastic Volume Service (EVS), Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Elastic IP (EIP), and Image Management Service (IMS), are shared within the same region. Regions are classified into universal and dedicated regions. A universal region provides universal cloud services for common tenants. A dedicated region provides specific services for specific tenants.
For details, see Region and AZ.
- Availability zone
An availability zone (AZ) comprises one or more physical data centers equipped with independent ventilation, fire, water, and electricity facilities. Compute, network, storage, and other resources in an AZ are logically divided into multiple clusters. AZs within a region are connected using high-speed optical fibers to support cross-AZ high-availability systems.
- Project
Projects group and isolate resources (including compute, storage, and network resources) across physical regions. A default project is provided for each region, and subprojects can be created under each default project. Users can be granted permissions to access all resources in a specific project. If you need more refined access control, create subprojects under a default project and create resources in subprojects. Then you can assign users the permissions required to access only the resources in the specific subprojects.
To view a project ID, go to the My Credentials page.
Figure 1 Project isolating model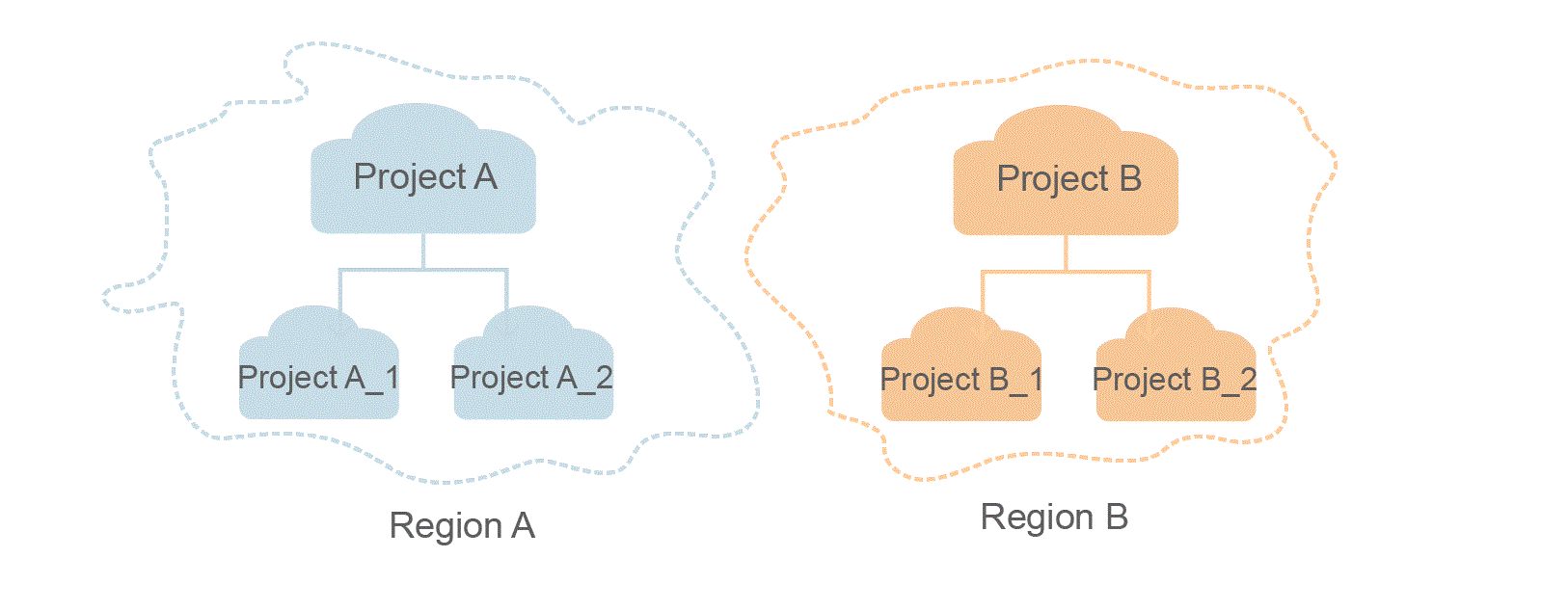
- Enterprise project
Enterprise projects group and manage resources across regions. Resources in enterprise projects are logically isolated. An enterprise project can contain resources of multiple regions, and resources can be added to or removed from enterprise projects.
For details about how to obtain the enterprise project ID and features, see Enterprise Management User Guide.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





