Using IAM Roles or Policies to Grant Access to DMS for RabbitMQ
Roles/Policies provided by Identity and Access Management (IAM) let you control access to DMS for RabbitMQ. With IAM, you can:
- Create IAM users for personnel based on your enterprise's organizational structure. Each IAM user has their own identity credentials for accessing DMS for RabbitMQ resources.
- Grant users only the permissions required to perform a given task based on their job responsibilities.
- Entrust a HUAWEI ID or a cloud service to perform efficient O&M on your DMS for RabbitMQ resources.
If your HUAWEI ID meets your permissions requirements, you can skip this section.
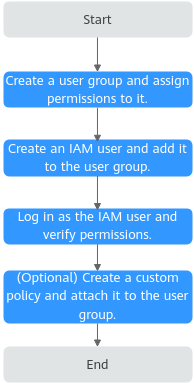
Figure 1 shows the process flow of role/policy-based authorization.
Prerequisites
Before assigning permissions to user groups, learn about system-defined permissions in role/policy-based authorization for DMS for RabbitMQ. To grant permissions for other services, learn about all system-defined permissions supported by IAM.
DMS for RabbitMQ permissions policies are based on DMS. Therefore, when assigning permissions for user groups, select DMS permissions policies.
Process Flow
- For the following example, create a user group on the IAM console, and assign the DMS ReadOnlyAccess policy to the group.
- Log in as the IAM user and verify permissions.
In the authorized region, perform the following operations:
- Choose Service List > Distributed Message Service (for RabbitMQ). Then click Buy Instance on the console of DMS for RabbitMQ. If a message appears indicating that you have insufficient permissions to perform the operation, the DMS ReadOnlyAccess policy is in effect.
- Choose Service List > Elastic Volume Service. If a message appears indicating that you have insufficient permissions to access the service, the DMS ReadOnlyAccess policy is in effect.
- Choose Service List > Distributed Message Service (for RabbitMQ). The RabbitMQ console is displayed. If a list of RabbitMQ instances are displayed, the DMS ReadOnlyAccess policy is in effect.
Example Custom Policies
You can create custom policies to supplement the system-defined policies of DMS for RabbitMQ. Add actions in custom policies as needed. For details about supported actions, see Actions Supported by Policy-based Authorization.
To create a custom policy, choose either visual editor or JSON.
- Visual editor: Select cloud services, actions, resources, and request conditions. This does not require knowledge of policy syntax.
- JSON: Create a JSON policy or edit an existing one.
For details, see Creating a Custom Policy. The following lists examples of common DMS for RabbitMQ custom policies.
- Example 1: Grant permission to create and delete instances.
{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "dms:instance:create", "dms:instance:delete" ] } ] } - Example 2: Grant permission to deny instance deletion.
A policy with only "Deny" permissions must be used together with other policies. If the permissions granted to an IAM user contain both "Allow" and "Deny", the "Deny" permissions take precedence over the "Allow" permissions.
For example, if you want to assign all of the permissions of the DMS FullAccess policy to a user, except for deleting instances, you can create a custom policy to deny only instance deletion. When you apply both the DMS FullAccess policy and the custom policy denying instance deletion, since "Deny" always takes precedence over "Allow", the "Deny" will be applied for that one conflicting permission. The user will then be able to perform all operations on instances except deleting instances. The following is an example of a deny policy:
{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Deny", "Action": [ "dms:instance:delete" ] } ] }
DMS for RabbitMQ Resources
A resource is an object that exists within a service. DMS for RabbitMQ resources include rabbitmq. To select these resources, specify their paths.
|
Resource |
Resource Name |
Path |
|---|---|---|
|
rabbitmq |
Instance |
[Format] DMS:*:*: rabbitmq: instance ID [Note] For instance resources, IAM automatically generates the prefix (DMS:*:*:rabbitmq:) of the resource path. For the path of a specific instance, add the instance ID to the end. You can also use an asterisk * to indicate any instance. For example: DMS:*:*:rabbitmq:* indicates any RabbitMQ instance. |
|
vhost |
Vhost |
[Format] DMS:*:*:vhost:instance ID/virtual host name [Note] For virtual host resources, IAM automatically generates the prefix (DMS:*:*:vhost:) of the resource path. For the path of a specific virtual host, add the instance ID/virtual host to the end. You can also use an asterisk * to indicate any virtual host. For example: DMS:*:*:vhost:* indicates any virtual host. |
|
amqpQueue |
Queue |
[Format] DMS:*:*:amqpQueue:instance ID/queue name [Note] For queue resources, IAM automatically generates the prefix (DMS:*:*:amqpQueue:) of the resource path. For the path of a specific queue, add the instance ID/queue name to the end. You can also use an asterisk * to indicate any queue. For example: DMS:*:*:amqpQueue:* indicates any queue. |
|
exchange |
Exchange |
[Format] DMS:*:*:exchange:instance ID/exchange name [Note] For exchange resources, IAM automatically generates the prefix (DMS:*:*:exchange:) of the resource path. For the path of a specific exchange, add the instance ID/exchange name to the end. You can also use an asterisk * to indicate any exchange. For example: DMS:*:*:exchange:* indicates any exchange. |
DMS for RabbitMQ Request Conditions
Request conditions are useful in determining when a custom policy is in effect. A request condition consists of condition keys and operators. Condition keys are either global or service-level and are used in the Condition element of a policy statement. Global condition keys (starting with g:) are available for operations of all services, while service-specific condition keys (starting with a service name such as dms:) are available only for operations of specific services. An operator must be used together with a condition key to form a complete condition statement.
DMS for RabbitMQ has a group of predefined condition keys that can be used in IAM. For example, to define an "Allow" permission, you can use the condition key dms:ssl to check whether SSL is enabled for a RabbitMQ instance. The following table lists the predefined condition keys of DMS for RabbitMQ.
|
Condition Key |
Operator |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
dms:publicIP |
Bool |
Whether public access is enabled |
|
dms:ssl |
Bool |
Whether SSL is enabled |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot