Configuring RabbitMQ Persistence
By default, messages produced by RabbitMQ producers are stored in the memory. When a node breaks down or restarts, messages are lost. RabbitMQ can persist data during such events for exchanges, queues, and messages.
Persistence means writing messages in the memory to the disk to prevent them from being lost due to exceptions. However, if message persistence is enabled, RabbitMQ performance deteriorates because read and write operations are much slower in disks than in memory. Different from the lazy queue mechanism, a persisted message is stored in both the disk and memory. It is deleted from the memory only when the memory is insufficient.
Notes and Constraints
- Non-persistent queues and exchanges are lost after a restart.
- Non-persistent messages are lost after a restart. (Messages that are sent to persistent queues or exchanges will not automatically become persistent.)
- A message will be lost if the server restarts before the message persistence is complete.
- RabbitMQ AMQP-0-9-1 exchanges, queues, and messages support persistence.
Configuring Exchange Persistence
Exchange persistence can be configured on the management UI or RabbitMQ console.
- Log in to the RabbitMQ management UI.
- Click the Exchanges tab.
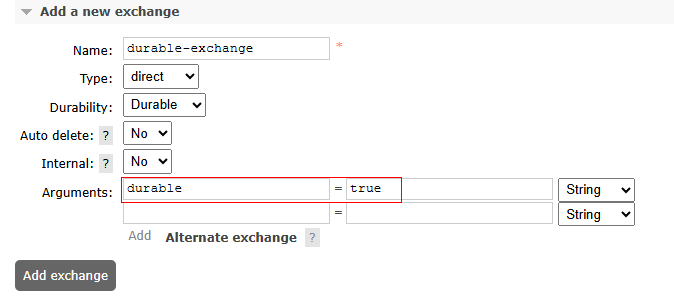
- Create an exchange and set durable to true, as shown in Figure 1.
Table 1 Exchange creation parameters Parameter
Description
Name
Exchange name, which is user-defined.
Type
Exchange type.
Select a value from the drop-down list.
- direct: Exchanges route messages to matching queues based on the routing keys.
- fanout: Exchanges route messages to all bound queues.
- topic: Exchanges route messages to queues based on routing key wildcard matching.
- headers: Exchanges are related to the message headers. Routing keys are not used. Exchanges route messages based on matching between key-value pairs in the message headers and the binding (a key-value pair).
Durability
Whether to enable persistence.
- Durable: The exchange survives server restart.
- Transient: The exchange will be deleted after server restarts and needs to be recreated.
Auto delete
Whether to enable automatic deletion.
- Yes: This exchange will be automatically deleted when the last bound queue unbound from the exchange.
- No: This exchange will not be deleted when the last bound queue unbound from the exchange.
Internal
Indicates whether exchanges are for internal use.
- Yes: This exchange can only bind another exchange instead of a queue.
- No: This exchange can bind other exchanges and queues.
Arguments
Set durable=true to configure exchange persistence.
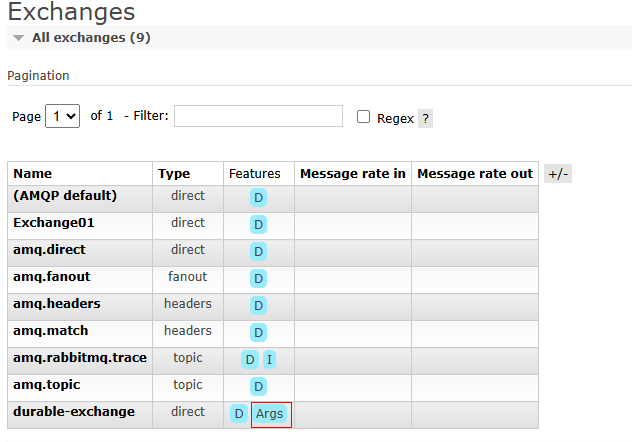
- In the exchange list, move the cursor to Args of the new exchange, as shown in Figure 2. If durable: true is displayed in the floating window, the exchange persistence is configured successfully.
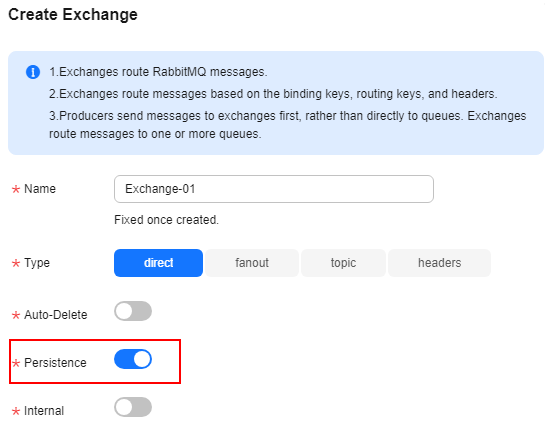
- Create an exchange by referring to Creating a RabbitMQ Exchange and configure exchange persistence, as shown in Figure 3.
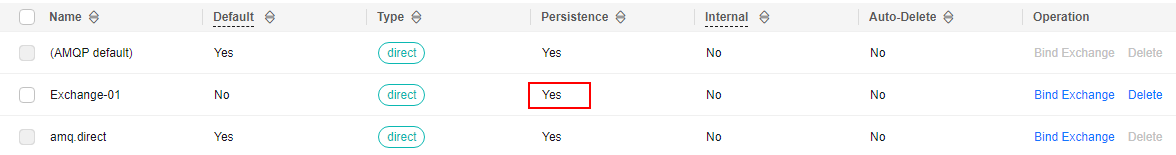
- In the exchange list, check whether persistence is enabled for the new exchange. If Yes is displayed in the Persistence column, persistence is enabled, as shown in Figure 4.
Configuring Queue Persistence
Queue persistence can be configured on the management UI or RabbitMQ console.
- Log in to the RabbitMQ management UI.
- Click the Queues tab.
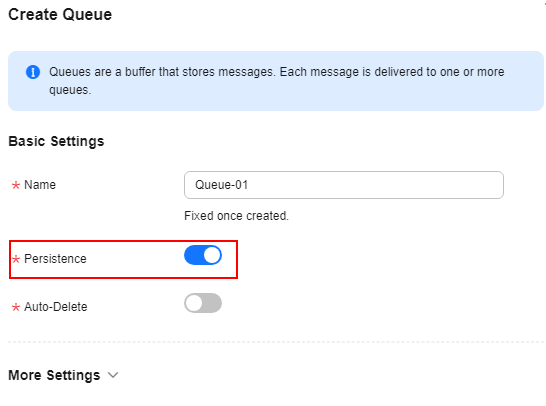
- Create a queue and set Durability to Durable.
Figure 5 Creating queues
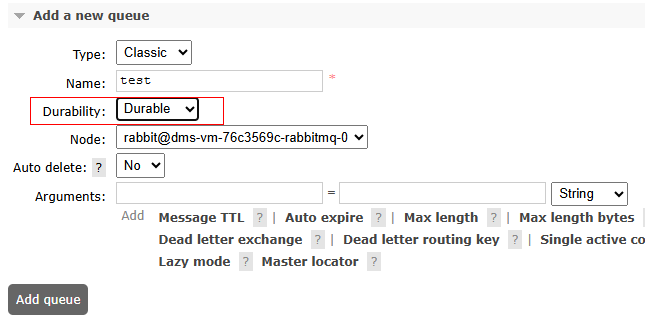
Table 2 Queue parameters Parameter
Description
Type
Queue type.
Name
Name of the single active consumer queue, which is user-defined.
Durability
Whether to enable persistence. Set Durability to Durable.
- Durable: This queue survives after server restart.
- Transient: This queue will be deleted after server restart and needs to be recreated.
Node
Node where a single active consumer queue is deployed.
Auto delete
Whether to enable automatic deletion.
- Yes: This queue will be automatically deleted when the last consumer unsubscribes from the queue.
- No: This queue will not be deleted when the last consumer unsubscribes from the queue.
(Optional) Arguments
Queue attribute. You do not need to set it.
- Click Add queue.
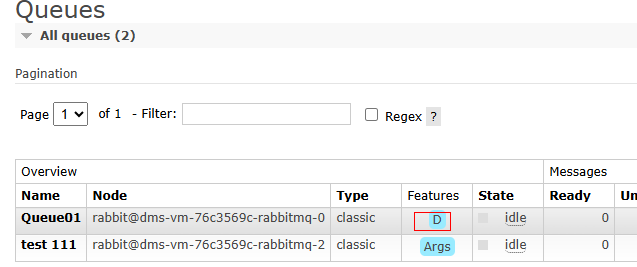
- On the Queues page, check whether the new queue is a persistent queue. If Features is D, the queue is a persistent queue.
Figure 6 Viewing queue attributes
- Create a queue by referring to Creating a RabbitMQ Queue and set the queue persistence, as shown in Figure 7.
- In the queue list, check whether persistence is enabled for the new queue. If Yes is displayed in the Persistence column, as shown in Figure 8, persistence is enabled.
Configuring Message Persistence
After configuring queue persistence, set MessageProperties to PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN on the client to send persistent messages to the queue.
The following example shows how to configure message persistence on a Java client.
import com.rabbitmq.client.MessageProperties;
channel.basicPublish("", "my_queue",MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN, message.getBytes());
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot