Application Scenarios
RabbitMQ is popular message-oriented middleware that features highly reliable, asynchronous message delivery. It can be used for transmitting data between different systems in the enterprise application, payment, telecommunications, e-commerce, social networking, instant messaging, video, Internet of Things, and Internet of Vehicle industries.
For synchronization links that require real-time results, Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is recommended.
Asynchronous Communication
Non-core or less important messages are sent asynchronously to receiving systems, so that the main service process is not kept waiting for the results of other systems, allowing for faster responses.
For example, RabbitMQ can be used to send a notification email and SMS message after a user has registered with a website, providing fast responses throughout the registration process.


Traffic Control
In e-commerce systems or large-scale websites, there is a processing capability gap between upstream and downstream systems. Traffic bursts from upstream systems with high processing capabilities may have a large impact on downstream systems with lower processing capabilities. For example, online sales promotions involve a huge amount of traffic flooding into e-commerce systems. RabbitMQ provides a three-day buffer by default for hundreds of millions of messages, such as orders and other information. In this way, message consumption systems can process the messages during off-peak periods.
In addition, flash sale traffic bursts originating from frontend systems can be handled with RabbitMQ, keeping the backend systems from crashing.

System Decoupling
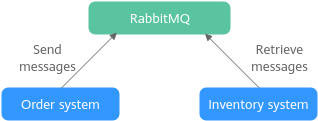
Take e-commerce flash sales as an example. Traditionally, an order processing system sends order requests to the inventory system and waits for responses. If the inventory system goes down, the order processing system will not be able to get the data it wants, and the order will fail to be submitted. This means that the order processing system and the inventory system are closely coupled.

With RabbitMQ, order submission data will be stored in queues. Then, a response will be returned indicating that the order has been submitted.
The inventory system consumes the order submission message it has subscribed to. In this way, order submission will not be interrupted even if the inventory system breaks down.
High Availability
Normally, there is only one broker. If the broker fails, queues on it will become unavailable.
Queue mirroring is available since RabbitMQ 2.6.0. In a RabbitMQ cluster, queues can be mirrored across brokers. In the event of a broker failure, services are still available because the mirrors will take over.
Quorum queues are available since RabbitMQ 3.8. Quorum queues can be used to replicate queue data, ensuring that queues can still run if a broker breaks down.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





