What Is DSS?
Dedicated Distributed Storage Service (DSS) provides you with dedicated storage pools which are physically isolated from other pools to ensure high security. With data redundancy and cache acceleration technologies, DSS delivers highly reliable, durable, low-latency, and stable storage resources. By flexibly interconnecting with various compute services, such as Dedicated Computing Cluster (DCC), Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) and Bare Metal Server (BMS), DSS is suitable for different scenarios, including high performance computing (HPC), online analytical processing (OLAP), and mixed loads.
Advantages
- A variety of specifications
- High I/O: Suitable for scenarios that require high performance, high read/write speed, and real-time data storage.
- Ultra-high I/O: Excellent for read/write-intensive scenarios that require extremely high performance and read/write speed, and low latency.
- Elastic scalability
- On-demand capacity improves resource utilization.
- Linear performance increase can be achieved with capacity expansion.
- Security and reliability
- Distributed storage with three data replicas ensures 99.9999999% durability.
- System disks and data disks support data encryption with zero application awareness.
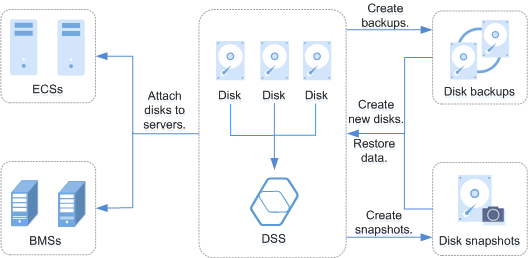
- Backup and restoration
- Backups can be created for a DSS disk, and the backup data can be used to restore the disk data, maximizing data security and correctness and ensuring service security.
Differences Between DSS and EVS

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





