Cross-Region Replication Across Accounts Using OMS
Scenarios
Cross-region replication across accounts is to replicate data from a source bucket in one region of an account to a destination bucket in a different region of another account.
This section describes how to replicate data between buckets across different accounts and regions using the OMS console, OMS APIs, or obsutil.
Replication scope: files, folders, object lists, objects with specified prefix, or specified URL lists
Replication content: object content, metadata (object name, size, last modification time, creator, version number, and user-defined metadata), ACL (supported by obsutil), and storage class
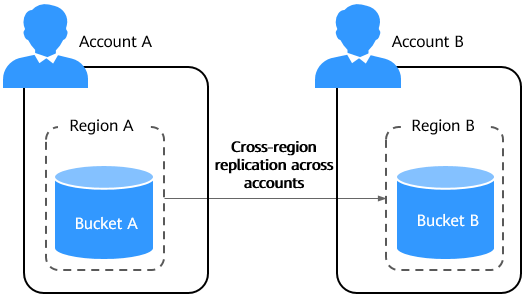
You can use cross-region replication across accounts to meet the following requirements:
- Regulatory compliance
By default, OBS stores data across AZs that are relatively far apart from each other. However, regulatory compliance may require data to be stored at even greater distances. In such cases, you can use cross-region replication to meet compliance requirements.
- Low latency
The same OBS resources may need to be accessed from different locations. To minimize the access latency, you can use cross-region replication to create object copies in the nearest region.
- Data replication
You want to migrate data stored in OBS to the data center in another region.
- Data backup and disaster recovery
For security and availability purposes, you want to create explicit backups for all data written to OBS in the data center of another region to ensure data remains available if there is any damage.
- Easy maintenance
You have compute clusters used to analyze the same group of objects in two different OBS regions and may need to maintain object copies in these two regions.

OBS helps you replicate your service data stored in OBS to a specified region. However, Huawei Cloud does not have visibility into your data and is not responsible for ensuring the legal compliance of your use of OBS. If your replication involves cross-border transfer, ensure that your use complies with relevant laws and regulations.
Constraints
The following table describes the constraints on using Object Storage Migration Service (OMS) to migrate data.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Objects with multiple versions |
By default, OMS migrates only the latest version of objects in source buckets. |
|
Destination storage class |
The destination storage class can be Standard, Infrequent Access, Archive, or Deep Archive. |
|
Migration network |
Migrations can be performed over the Internet or intranet. Migrations cannot be performed over private lines. |
|
Metadata migration |
Only Chinese characters, English characters, digits, and hyphens (-) can be migrated. Any other characters cannot be migrated.
Chinese punctuation marks cannot be URL-encoded during the migration. If metadata contains Chinese punctuation marks, migrating the metadata and the corresponding object will fail.
|
|
Migration scope |
A single migration task or migration task group can only migrate data of one bucket. If data of multiple buckets needs to be migrated, you need to create multiple tasks or task groups. |
|
Symbolic links |
Symbolic link files cannot be migrated. Symbolic link files will be recorded as failed, and the migration task will also be marked as failed. Other files can be migrated normally. If the source contains symbolic links, enter the actual file paths. |
|
Migration of object ACLs |
OMS cannot migrate object ACLs. |
|
Migration speed |
Generally, OMS can migrate 10 TB to 20 TB of data per day. For higher migration efficiency, you are advised to use storage migration workflows on MgC. MgC allows you to migrate data using dedicated, scalable migration clusters and up to 20 Gbit/s of bandwidth. However, the speed depends on the number and size of source objects, bandwidth, and transmission distance over the Internet between the source and destination buckets. You are advised to create a migration task to test the migration speed. The maximum migration speed is five times the average speed of a single task because up to five tasks can be executed concurrently in a region by default. If you need to define a higher number of concurrent tasks, you can create a storage migration workflow on MgC. |
|
Archived data |
You need to restore archived data before the migration. Note that when there is archived data to be migrated, you need to:
|
|
Migration tasks |
A maximum of five concurrent migration tasks is allowed for your account per region.
NOTE:
If your destination regions are CN North-Beijing1 and CN South-Guangzhou, you can run up to 10 migration tasks concurrently. |
|
A maximum of 1,000,000 migration tasks can be created in a region within 24 hours. |
|
|
Migration Task Groups |
A maximum of five concurrent migration task groups is allowed for your account per region.
NOTE:
If your destination regions are CN North-Beijing1 and CN South-Guangzhou, you can run up to 10 migration task groups concurrently. |
|
Synchronization tasks |
Synchronization tasks share quotas with migration tasks and migration task groups, but enjoy a higher priority. A maximum of five concurrent synchronization tasks is allowed. |
|
Object list files |
|
|
URL list files |
|
|
Failed object list files |
A maximum of 100,000 failed objects can be recorded in a list file.
NOTE:
If more than 100,000 objects fail to be migrated in a migration task, you are advised to rectify the fault based on the existing failed object list and perform the migration again. |
Billing for Cross-Region Replication Across Accounts
- When you use the OMS console or APIs to migrate data, OBS APIs of both the source and destination ends are invoked to handle data upload and download. You will be billed for the API requests and data download traffic. For details, see OMS Billing. In addition, you will be billed for storing the objects in the destination bucket. For details, see Storage Costs.
- When you use obsutil to replicate data across regions, you will be billed for requests, traffic, and storage. For details, see Table 2.
Table 2 Billing for data replication across regions Action
Billing Item
Description
Billing Mode
Replicate data across regions
Requests
You are billed for the number of successfully replicated objects. Successfully replicating one object creates a copy request. For details, see Copying Objects.
- For non-multipart objects, replicating an object creates a GET request to the source bucket and a PUT request to the destination bucket; deleting an object from the source bucket creates a DELETE request to the destination bucket.
- For multipart objects, replicating each part creates a GET request to the source bucket and a PUT request to the destination bucket.
For details about how requests are billed, see Requests.
Pay-per-use
Data transfer
Traffic generated when you replicate data from the source bucket to the destination bucket in another region. Billing only applies to the data transferred out of the source bucket.
If objects are encrypted using server-side encryption, the cost of their cross-region replication traffic is calculated based on the length of the plaintext for SSE-KMS and SSE-OBS.
Pay-per-use
Storage space
Space occupied by the replicated objects in the destination bucket
If you have specified another storage class for object copies in the destination bucket, these copies are billed based on the new storage class.
If objects are encrypted using server-side encryption, their storage cost is calculated based on the length of the ciphertext.
Pay-per-use
Resource packages
Synchronize existing objects
Requests
You are billed for the number of existing objects that are successfully replicated to the destination bucket.
Billing applies to the number of objects that are successfully replicated. You are also billed for listing the existing objects.
Pay-per-use
Data transfer
Traffic generated when OBS replicates existing objects to the destination bucket in another region. Billing only applies to the data transferred out of the source bucket.
If historical objects are encrypted using server-side encryption, the cost of their cross-region replication traffic is calculated based on the length of the plaintext for SSE-KMS and SSE-OBS.
Pay-per-use
Storage space
Space occupied by the replicated objects in the destination bucket
If you have specified another storage class for object copies in the destination bucket, these copies are billed based on the new storage class.
If historical objects are encrypted using server-side encryption, their storage cost is calculated based on the length of the ciphertext.
Pay-per-use
Resource packages
Prerequisites
- There is a source bucket in a region of an account.
- There is a destination bucket in a different region of another account. To create a bucket, see Creating a Bucket.
- When obsutil is used to replicate objects across accounts and regions, the version of the source bucket is 3.0 or later, and the source bucket region supports cross-region replication.
Cross-Region Replication Across Accounts
You can use the OMS console or APIs to migrate data across accounts and regions or use obsutil to replicate data across accounts and regions.

OMS does not automatically migrate data. This means that data changes in a source bucket will not be automatically synchronized to the destination bucket. To synchronize the data changes, you must execute a migration task.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






