Copied.
Configuring a Storage Class
Scenarios
This section describes how to configure a storage class when you create a bucket or upload an object. If you want to change the storage class of an existing bucket or object, see Changing the Storage Class of a Bucket or Object.
Bucket and Object Storage Classes
When creating a bucket, you can specify a storage class for it. You can also change the storage class after the bucket has been created.
By default, an object inherits the storage class of the bucket where it is uploaded. You can specify a storage class for an object when uploading it, or you can change the object storage class after the object has been uploaded.
Changing the storage class of a bucket does not change the storage class of existing objects in the bucket. However, any new objects uploaded to the bucket will inherit the bucket's new storage class.
Configuring a Storage Class During Bucket Creation
You can use OBS Console, APIs, OBS SDKs, OBS Browser+, or obsutil to configure a storage class when creating a bucket.
Using OBS Console
- In the navigation pane of OBS Console, choose Object Storage.
- In the upper right corner, click Create Bucket.
- Configure parameters under General Configuration.

Table 1 Parameters under General Configuration Parameter
Description
Replicate Settings from Existing Bucket
Optional
To replicate settings from an existing bucket, do as follows:
Click Select Bucket. In the bucket list, select a source bucket. Then, on the Create Bucket page, you will see that the source bucket's settings have been replicated to the bucket you are creating. The settings that can be replicated include Region, Data Redundancy Policy, Storage Class, Block Public Access, Bucket Policy, Enterprise Project, Direct Reading, Server-Side Encryption, WORM, and Tag.
You can change some or all of the replicated settings later if necessary.
Region
The region where the bucket is created
- Once the bucket is created, its region cannot be changed.
- For lower latency and faster access, select the region nearest to where the data will be accessed.
- If your ECS needs to access the OBS bucket over an intranet, ensure that the bucket and the ECS are in the same region. For details, see Accessing OBS from an ECS over an Intranet.
- Configure parameters under Bucket Settings.


Table 2 Parameters under Bucket Settings Parameter
Description
Bucket Name
When creating a bucket, you need to set a proper bucket name.
Once a bucket is created, its name cannot be changed.
An OBS bucket name must comply with the globally applied DNS naming rules. A bucket name:
- Must be globally unique. It cannot be the same as the name of any existing bucket or parallel file system (including those created by others). You must wait at least 30 minutes before you can reuse the name of a deleted bucket or parallel file system.
- Must be 3 to 63 characters long.
- Can contain only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.). It cannot start or end with a hyphen (-) or period (.).
- Cannot contain two consecutive periods (..) or contain a period (.) and a hyphen (-) adjacent to each other.
- Cannot be formatted as an IP address.
NOTE:
When you use virtual-hosted-style URLs to access OBS over HTTPS, bucket names containing periods (.) will cause certificate verification to fail. To avoid this issue, we recommend that you do not use periods (.) in bucket names.
Data Redundancy Policy
You can choose to store data in a single AZ or multiple AZs within a region.
- Multi-AZ storage: Data in the bucket is stored in multiple AZs within a region. If an AZ is ever unavailable, the data can still be accessed in the other AZs.
- Single-AZ storage: Data in the bucket is stored in a single AZ, which is less expensive.
For details about their performance comparison, see Comparison of Storage Classes.
Multi-AZ storage is selected by default.
Once a bucket is created, its data redundancy policy cannot be changed.
If Multi-AZ storage is used, the Archive or Deep Archive storage class will become unavailable.
Storage Class
The storage class of the bucket
The storage classes can meet different performance and cost requirements.
- The Standard storage class is for storing a large number of hot files or small files that are frequently accessed (multiple times per month on average) and require fast access.
- The Infrequent Access storage class is for storing data that is less frequently accessed (less than 12 times per year on average), but when needed, the access has to be fast.
- The Archive storage class is for archiving data that is rarely accessed (once a year on average) and does not require fast access.
For more information, see Storage Class.
NOTE:The object you upload to the bucket later will inherit the bucket's storage class by default. You can also specify a different storage class for the object.
Block Public Access
Used to centrally set certain levels of public access to buckets. You can use this option to ignore the existing public access permissions or prevent new public access permissions from being created.
Enabling all settings prevents the creation of new ACLs or bucket policies that contain public access, and invalidates existing ones. Only the bucket owner can access the bucket and objects within.
The following four settings are supported:
- Prevent the creation of ACLs that allow public access.
- Prevent the creation of bucket policies that allow public access.
- Ignore ACLs that allow public access.
- Ignore bucket policies that allow public access.
To block public access, your account must have the PutBucketPublicAccessBlock permission.
If your services rely on public access to buckets or objects, blocking public access may interrupt their normal operation. Take care when blocking public access.
Enabling Block Public Access will make the public read and public read/write bucket policies unavailable.
For more information, see Block Public Access.
Bucket Policy
Controls read and write permissions for the bucket.
- Private: Only users granted permissions by the bucket ACL can access the bucket.
- Public Read: Anyone can read objects in the bucket.
- Public Read/Write: Anyone can read, write, or delete objects in the bucket.
If your account does not have permission to create a bucket policy, a private bucket will be created even if you select Public Read or Public Read/Write. To create a public bucket, your account must have the obs:bucket:PutBucketPolicy permission.
Enterprise Project
You can add the bucket to an enterprise project for unified management. To realize this, do as follows:
On the enterprise project management page, create an enterprise object. Then, create a user group, add users to the user group, and add the user group to the created enterprise project. By doing so, the users obtain the operation permissions for the buckets and objects in the enterprise project.
If you do not have any specific needs for enterprise project division and management, choose the default enterprise project.
- Only an enterprise account can configure enterprise projects.
- The OBS user group must have the OBS Buckets Viewer and OBS OperateAccess permissions for the enterprise project.
- Creating the first bucket in a new enterprise project will take about 10 minutes.
- Configure parameters under Properties.


Table 3 Parameters under Properties Parameter
Description
Direct Reading
After direct reading is enabled, you can access Archive objects (such as download or share an object or change an object's storage class) without having to restore them first.
Direct reading will incur retrieval costs according to the objects' size. For details, see Data Retrievals.
For more information, see Direct Reading.
Server-Side Encryption
After server-side encryption is enabled, new objects uploaded to the bucket will be encrypted.
With the encryption enabled, you can choose a required encryption method:
- SSE-KMS: The encryption key managed in Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) is used to encrypt objects in your bucket.
After choosing SSE-KMS, you need to specify an encryption key type:
- Default: The default key in the current region will be used to encrypt the objects uploaded to the bucket. If no default key is available, OBS will create one the first time you upload an object.
- Custom: Your custom key will be used to encrypt the objects uploaded to the bucket. If you do not have a custom key, click View KMS Keys to go to the Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) page and create one. Then, choose the created KMS key from the custom key drop-down list.
- Shared: A shared key will be used to encrypt the objects uploaded to the bucket. You need to enter the ID of the shared key. To obtain a shared key ID, see Viewing Key Details.
NOTE:
A shared key from a project or a subproject can be configured here. However, if a shared key from a subproject is specified, the owner of the shared key cannot access objects encrypted with that key, but the bucket owner can.
Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) APIs have traffic control limits (see DEW API Overview). After SSE-KMS is used, your service access may be affected by traffic control.
If SSE-KMS is used, you will be billed for what you use beyond the free quota given by KMS. For details, see DEW Billing Items.
- SSE-OBS: The key created and managed by OBS will be used to encrypt the objects uploaded to the bucket.
After you enable server-side encryption for the bucket, any object you upload to it will inherit the encryption settings from the bucket by default. You can also separately configure encryption for the object.
For more information, see Server-Side Encryption Overview.
WORM
You can enable write-once-read-many (WORM) to help prevent object versions from being deleted or overwritten within a specified period.
- WORM cannot be disabled once enabled. However, you can choose whether to configure a retention policy to control whether objects can be written or deleted.
- Enabling WORM automatically enables versioning, and versioning cannot be disabled later.
- A bucket with WORM enabled does not support cross-region replication, and any existing cross-region replication rules applied to the bucket will become invalid.
For more information, see Configuring WORM to Protect Objects from Being Overwritten or Deleted.
Tag
Optional. You can add tags to organize and manage buckets.
You can customize a tag or choose one predefined on TMS.
A tag is a key-value pair.
- Tags associated with a bucket must have unique tag keys. A tag key:
- Must contain 1 to 36 characters and be case sensitive.
- Cannot start or end with a space or contain the following characters: ,/|<>=*\
- Tag values can be duplicate and can be left blank. A tag value:
- Can contain 0 to 43 characters and must be case sensitive.
- Cannot contain the following characters: ,/|<>=*\
A bucket can have up to 10 tags. Each tag has only one key and one value.
For more information, see Adding Tags to a Bucket.
- SSE-KMS: The encryption key managed in Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) is used to encrypt objects in your bucket.
- Click Create Now.
Using APIs
Specifying a Storage Class During Bucket Creation (adding the x-obs-storage-class header)
Using the GUI Tool - OBS Browser+
- Log in to OBS Browser+.
- In the upper part of the page, click Create Bucket.
- In the displayed dialog box, configure bucket parameters, as shown in Figure 1.
Table 4 Bucket creation parameters Parameter
Description
Region
Enter the region where you want to create a bucket.
- Once the bucket is created, its region cannot be changed.
- For lower latency and faster access, create a bucket in the region nearest to you.
- If you want your bucket to be accessed from an ECS over the intranet, ensure that the bucket and the ECS are in the same region. For details, see Accessing OBS from an ECS over the Intranet.
Storage Class
Storage class of the bucket.
Different storage classes meet customers' needs for storage performance and costs.
- Standard: applicable to scenarios where a large number of hot files or small files need to be accessed frequently (multiple times per month on average) and require fast access response.
- Infrequent Access: ideal for storing data that is not frequently accessed (less than 12 times per year on average) but requires fast access response.
- Archive: suitable for archiving data that is rarely accessed (averagely once a year) and has no requirements for quick response.
NOTE:During the object upload, an object inherits its bucket's storage class by default, and you can also specify a different storage class for the object.
For more information, see Storage Class.
Bucket ACL
Controls read and write permissions on buckets.
- Private: Only users granted permissions by the ACL can access the bucket.
- Public Read: Anyone can read objects in the bucket.
- Public Read and Write: Anyone can read, write, or delete objects in the bucket.
Multi-AZ Mode
If multi-AZ storage is enabled, data in your bucket is stored in multiple AZs within a region.
After a bucket is created, its data redundancy policy cannot be changed.
Bucket Name
Name of the bucket you want to create, which must be globally unique.
A bucket name:
- Must be 3 to 63 characters long and start with a digit or letter. Only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.) are allowed.
- Cannot be formatted as an IP address.
- Cannot start or end with a hyphen (-) or period (.).
- Cannot contain two consecutive periods (..), for example, my..bucket.
- Cannot contain a period (.) and a hyphen (-) adjacent to each other, for example, my-.bucket or my.-bucket.
After a bucket is created, its name cannot be changed.
A user can create a maximum of 100 buckets in OBS.
NOTE:- You can click
 next to the Bucket Name text box to view the bucket naming rules.
next to the Bucket Name text box to view the bucket naming rules. - When a URL is used to access a bucket, the bucket name will become part of the URL. According to the DNS rule, URLs do not support uppercase letters and cannot recognize buckets whose name contains uppercase letters. Therefore, a bucket name can contain only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.). For example, if you attempt to access bucket MyBucket using a URL, the URL will parse MyBucket as mybucket. This results in an access error.
- DNS naming rules can standardize bucket names globally, facilitating the resolution during bucket access. With the DNS naming rules used, you can benefit from new functions and optimized features, and configure static website hosting for buckets.
- Click OK. If the bucket is successfully created, it is displayed in the bucket list. If the creation fails, an error message will be displayed.
Using the CLI Tool - obsutil
Command Line Structure
- In Windows
obsutil mb obs://bucket [-fs] [-az=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-location=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
- In Linux or macOS
./obsutil mb obs://bucket [-fs] [-az=xxx] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-location=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
Examples
- Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil mb obs://bucket-test command to create a bucket. The creation is successful.
obsutil mb obs://bucket-test Start at 2024-09-29 07:52:11.3769487 +0000 UTC Create bucket [bucket-test] successfully, request id [000001923CC401864018BA75753D2D5F]
- Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil mb obs://bucket001 command to create a bucket with the same name as the bucket of another account. The creation fails.
obsutil mb obs://bucket001 Start at 2024-09-30 07:03:50.1378331 +0000 UTC Create bucket [bucket001] failed, status [409], error code [BucketAlreadyExists], error message [The requested bucket name is not available. The bucket namespace is shared by all users of the system. Please select a different name and try again.], request id [0000019241BE18DB4019EDD66E135C56]
Parameter Description
|
Parameter |
Optional or Mandatory |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
bucket |
Mandatory |
The bucket name
A bucket name must comply with the following rules:
|
|
fs |
Optional (additional parameter) |
Creates a parallel file system. |
|
az |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The data redundancy policy that can be specified for a bucket to store data in a single AZ or multiple AZs in the same region The value is multi-az. If multi-az is used, a bucket with multi-AZ storage will be created. If this parameter is not included, a bucket with single-AZ storage will be created. |
|
acl |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The access control policy that can be specified when creating a bucket Possible values are:
|
|
sc |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The storage class of the bucket Different storage classes meet customers' needs for storage performance and costs. Possible values are:
|
|
location |
Mandatory unless the requested OBS region is the default one (additional parameter) |
The region where the bucket resides To view the currently valid regions, see Regions and Endpoints.
NOTE:
This parameter indicates the region where a bucket will be created. It is mandatory only when the endpoint belongs to any other regions than the default one CN North-Beijing1 (cn-north-1). |
|
config |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user-defined configuration file for executing the current command. For details about parameters that can be configured, see Configuration Parameters. |
|
e |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The endpoint |
|
i |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user's AK |
|
k |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user's SK |
|
t |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user's security token |
Configuring a Storage Class During Object Uploads
You can use OBS Console, APIs, OBS SDKs, OBS Browser+, or obsutil to configure a storage class when uploading an object.
Using OBS Console
- In the navigation pane of OBS Console, choose Object Storage.
- In the bucket list of OBS Console, click the desired bucket to go to the Objects page.
- On the object list page, click Upload Object.
You can also go to the folder where you want to upload the file and click Upload Object.

If the files that you want to upload to OBS are stored in Microsoft OneDrive, it is recommended that the names of these files contain a maximum of 32 characters to ensure compatibility.
- Configure basic parameters.
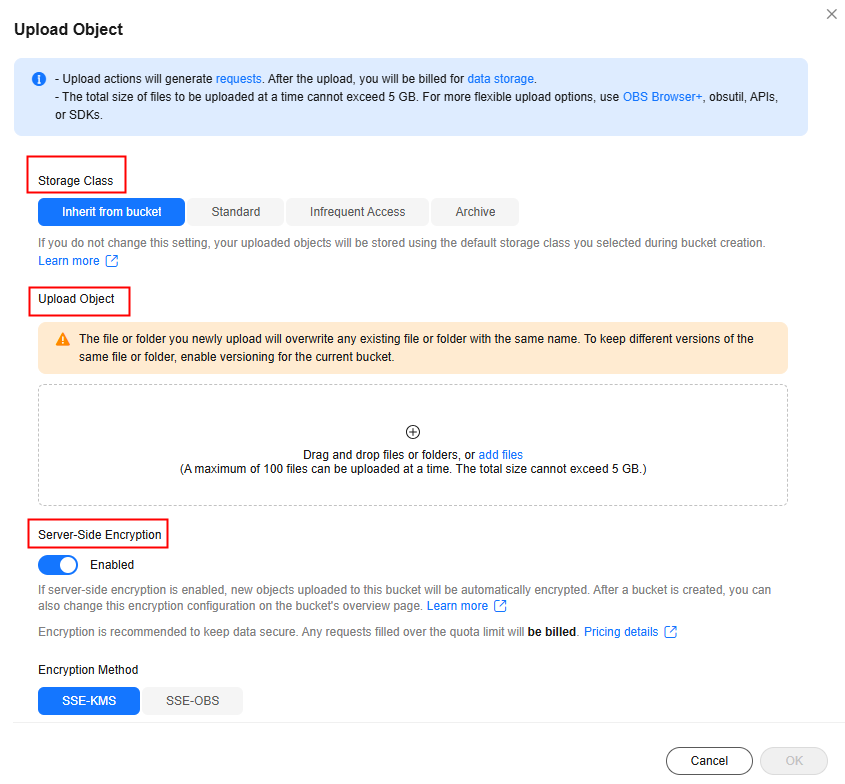
Table 5 Basic parameters Parameter
Description
Storage Class
The storage class of an object
You can choose a storage class that meets your needs for storage performance and costs.
- The Standard storage class is for storing a large number of hot files or small files that are frequently accessed (multiple times per month on average) and require fast access.
- The Infrequent Access storage class is for storing data that is less frequently accessed (less than 12 times per year on average), but when needed, the access has to be fast.
- The Archive storage class is for archiving data that is rarely accessed (once a year on average) and does not require fast access.
For more information, see Storage Class.
Upload Object
Choose a required file and upload it to the OBS bucket.
You can drag and drop the file or folder to the Upload Object area. Alternatively, click
 or add files and choose the file using the local file browser.
or add files and choose the file using the local file browser.- A maximum of 100 files (no more than 5 GB in total) can be uploaded at a time.
- If you upload only one file in a batch, this file cannot exceed 5 GB in size.
- To upload more than 5 GB of objects, see How Do I Upload Objects Larger Than 5 GB?
- Uploading objects incurs request costs. After objects are uploaded, there will be storage costs.
Server-Side Encryption
Optional
After server-side encryption is enabled, the uploaded objects will be encrypted.
If the bucket has server-side encryption enabled, server-side encryption is enabled for any object uploaded to the bucket by default and cannot be disabled.
With the encryption enabled, you can choose a required encryption method:
- Inherit from bucket: This option is only available when the bucket has Server-Side Encryption enabled. Using this option makes the object you uploaded inherit the encryption settings of the bucket.
- SSE-KMS: The encryption key managed in Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) is used to encrypt the object you uploaded.
After choosing SSE-KMS, you need to specify an encryption key type:
- Default: The default key in the current region will be used to encrypt the object you uploaded. If no default key is available, OBS will create one the first time you upload an object.
- Custom: Your custom key will be used to encrypt the object you uploaded. If you do not have a custom key, click View KMS Keys to go to the Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) page and create one. Then, choose the created KMS key from the custom key drop-down list.
- Shared: A shared key will be used to encrypt the object you uploaded. You need to enter the ID of the shared key. To obtain a shared key ID, see Viewing Key Details.
NOTE:
A shared key from a project or a subproject can be configured here. However, if a shared key from a subproject is specified, the owner of the shared key cannot access objects encrypted with that key, but the bucket owner can.
DEW APIs have traffic control limits (see DEW API Overview). After SSE-KMS is used, your service access may be affected by traffic control.
If SSE-KMS is used, you will be billed for what you use beyond the free quota given by KMS. For details, see DEW Billing Items.
- SSE-OBS: The key created and managed by OBS will be used to encrypt the object you uploaded.
For more information, see Server-Side Encryption Overview.
- (Optional) Configure advanced parameters.
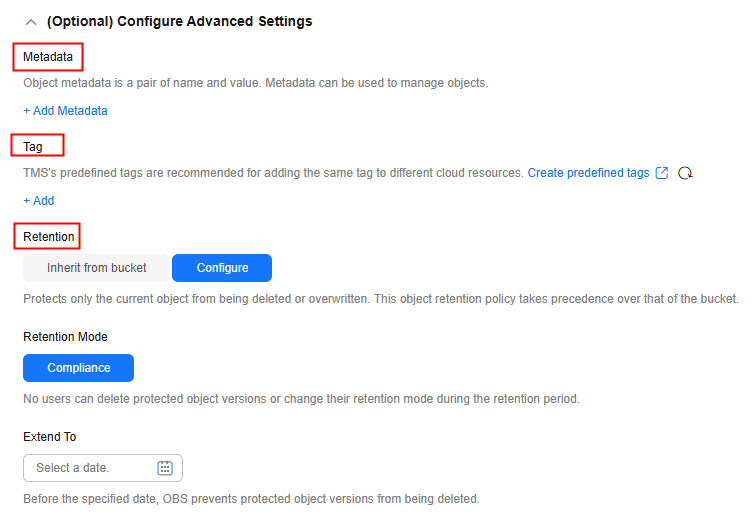
Table 6 Advanced parameters Parameter
Description
Metadata
Object metadata is a set of name-value pairs that describe an object and is used for object management.
To configure metadata, click Add Metadata.
You can add the following metadata: ContentDisposition, ContentLanguage, WebsiteRedirectLocation, ContentEncoding, and ContentType. For more information, see Configuring and Viewing Object Metadata.
The metadata key and value must be specified.
Tag
Add tags to the object you uploaded for categorization. You can customize a tag or choose one predefined on TMS.
To add a tag, click Add Tag and enter a tag key and value. Each object can have up to 10 tags.
A tag key:
- Must be unique if there are multiple tags specified for an object.
- Can be up to 36 characters long and cannot contain the following special characters: ,/|<>=*\. It must be case sensitive and unique and cannot start or end with a space. It cannot be left blank.
A tag value:
For more information about object tags, see Adding Tags to an Object.
Retention
WORM retention can be configured in the advanced settings during object upload only if WORM is enabled for the bucket.
An object retention policy protects only the current object from being deleted or overwritten. This policy takes precedence over that of the bucket.
- Inherit from bucket: The object inherits the default retention policy of its bucket. If no default retention is configured for the bucket, the object is not protected by WORM.
- Configure: Configure a retention policy for the current object.
- Retention Mode: Only Compliance is currently supported. In this mode, no users can delete protected object versions or change their retention mode during the specified retention period.
- Retention Period: Before the specified date, OBS prevents protected object versions from being deleted.
- Click Upload.
Using APIs
Specifying a Storage Class During Object Uploads with PUT (adding the x-obs-storage-class header)
Specifying a Storage Class During Object Uploads with POST (adding the x-obs-storage-class header)
Initiating a Multipart Upload (adding the x-obs-storage-class header during the initiation process if a multipart upload is used)
Using the GUI Tool - OBS Browser+
- Log in to OBS Browser+.
- Click the bucket where you want to upload files or folders.
- Click Upload. The Upload Object dialog box is displayed.
Figure 2 Uploading a file or folder
- Set object parameters, including the object permission and storage class.
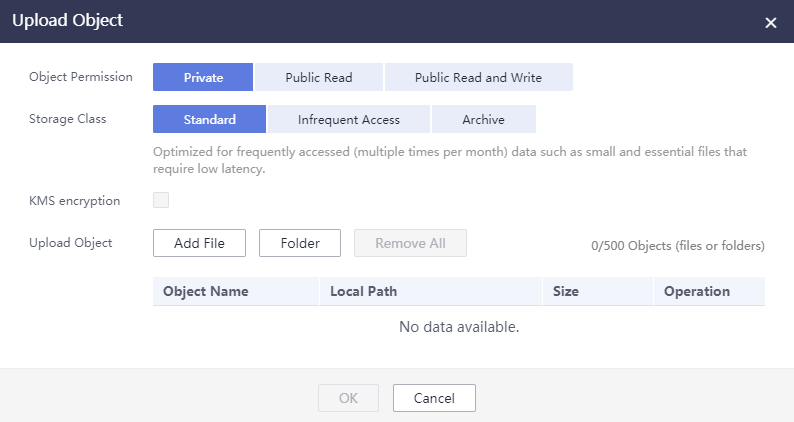
Table 7 Object parameters Parameter
Description
Object Permission
Controls read and write permissions for the object.
- Private: Only users granted permissions by the object ACL can access the object.
- Public Read: Anyone can read the current object.
- Public Read and Write: Anyone can read, write, or delete the current object.
Storage Class
The storage class of the object
You can choose a storage class that meets your needs for storage performance and costs.
- The Standard storage class is for storing a large number of hot files or small files that are frequently accessed (multiple times per month on average) and require fast access.
- The Infrequent Access storage class is for storing data that is less frequently accessed (less than 12 times per year on average), but when needed, the access has to be fast.
- The Archive storage class is for archiving data that is rarely accessed (once a year on average) and does not require fast access.
For more information, see Storage Class.
KMS encryption
Optional
After KMS encryption is enabled, the default key in the current region is used to encrypt the object you uploaded to the current bucket.
- Click Add File or Folder. In the dialog box displayed, select the file or folder to be uploaded and click Open.
- You must have access to the file you want to upload, or the upload will fail.
- The file or folder name cannot exceed 1,023 bytes. If there are upper-level directories, the length of the file name plus the length of all upper-level directory names (including the automatically added slash (/)) cannot exceed 1,023 bytes. For example, if the upper-level directory of file file01 is folder01, the file name length refers to the length of folder01/file01.
- A single file to be uploaded can be up to 48.8 TB.
- A maximum of 500 files can be uploaded at a time. If there are over 500 files to be uploaded, you are advised to put them into a folder and then upload the folder. You can upload one folder or multiple files at a time. To upload multiple files, hold down Ctrl or Shift to select the required files or press Ctrl+A to select all files and then upload them in a batch.

- If message "Service Unavailable" is displayed when files are being uploaded, try again later.
- If an access deny message is displayed when you are uploading a file or folder, possible causes are as follows:
- Access to the bucket is restricted by an ACL. For example, you do not have the write permission for the bucket.
- Access to the bucket is restricted by a bucket policy. For example, you do not have the write permission for the bucket, or write operations cannot be performed on the bucket during the current period.
If such message is displayed, check the ACL and policy settings of the bucket and resolve the problem accordingly.
- Click OK.
Using the CLI Tool - obsutil
Command Line Structure
- Windows:
- Uploading a file
obsutil cp file_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-p=1] [-threshold=5248800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
- Uploading a folder
obsutil cp folder_url obs://bucket[/key] -r [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-flat] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
- Uploading multiple files/folders
obsutil cp file1_url,folder1_url|filelist_url obs://bucket[/prefix] -msm=1 [-r] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-flat] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx][-timeRange=time1-time2] [-at] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]

In this command, /prefix is the name prefix for uploading folders.
- Uploading a file
- Linux or macOS:
- Uploading a file
./obsutil cp file_url obs://bucket[/key] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-p=1] [-threshold=5248800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-fr] [-o=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
- Uploading a folder
./obsutil cp folder_url obs://bucket[/key] -r [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-flat] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx] [-timeRange=time1-time2] [-at] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]
- Uploading multiple files/folders
./obsutil cp file1_url,folder1_url|filelist_url obs://bucket[/prefix] -msm=1 [-r] [-arcDir=xxx] [-dryRun] [-link] [-f] [-u] [-vlength] [-vmd5] [-flat] [-j=1] [-p=1] [-threshold=52428800] [-acl=xxx] [-sc=xxx] [-meta=aaa:bbb#ccc:ddd] [-ps=auto] [-include=*.xxx] [-exclude=*.xxx][-timeRange=time1-time2] [-mf] [-o=xxx] [-cpd=xxx] [-config=xxx] [-e=xxx] [-i=xxx] [-k=xxx] [-t=xxx]

In this command, /prefix is the name prefix for uploading folders.
- Uploading a file
Examples
- Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp d:\temp\test.txt obs://bucket-test/key command to upload the test.txt file in the temp directory in the D: drive to bucket bucket-test and rename the file as key.
obsutil cp d:\temp\test.txt obs://bucket-test/key Start at 2024-09-30 08:11:41.6724827 +0000 UTC Parallel: 5 Jobs: 5 Threshold: 50.00MB PartSize: auto VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false CheckpointDir: C:\Users\Administrator\.obsutil_checkpoint [====================================================] 100.00% 1.68 MB/s 8.46MB/8.46MB 5s Upload successfully, 8.46MB, n/a, d:\temp\test.txt --> obs://bucket-test/key, cost [5], status [200], request id [0000016979E1D2B2860BB5181229C72C]
- Take the Windows OS as an example. Run the obsutil cp d:\temp obs://bucket-test -f -r command to recursively upload all files and subfolders in the temp directory in the D: drive to the temp folder in bucket bucket-test.
obsutil cp d:\temp obs://bucket-test -f -r Start at 2024-09-30 08:14:12.1406275 +0000 UTC Parallel: 5 Jobs: 5 Threshold: 50.00MB PartSize: auto VerifyLength: false VerifyMd5: false CheckpointDir: C:\Users\Administrator\.obsutil_checkpoint Task id: 104786c8-27c2-48fc-bc6a-5886596fb0ed OutputDir: C:\Users\Administrator\.obsutil_output [========================================================] 100.00% tps:35.71 2.02 KB/s 7.20MB/7.20MB 0s Succeed count: 5 Failed count: 0 Succeed bytes: xxx Metrics [max cost:90 ms, min cost:45 ms, average cost:63.80 ms, average tps:35.71, transferred size: 7.20MB] Task id: 104786c8-27c2-48fc-bc6a-5886596fb0ed
Parameter Description
|
Parameter |
Optional or Mandatory |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
file_url |
Optional for uploading multiple files/folders Mandatory for uploading a file |
The local file path
|
|
folder_url |
Optional for uploading multiple files/folders Mandatory for uploading a folder |
The local folder path
|
|
filelist_url |
Optional for uploading multiple files/folders |
The path of the file that contains the list of files/folders to be uploaded. If this parameter is configured, msm must be set to 2. |
|
bucket |
Mandatory |
The name of the bucket where you will upload the file or folder |
|
key |
Optional |
The object name or object name prefix specified when uploading a file, or the object name prefix specified when uploading a folder When uploading a file or folder, the upload path and name change depending on the value of this parameter. The specific rules are as follows:
NOTE:
For details about how to use this parameter, see Upload. |
|
fr |
Optional for uploading a file (additional parameter) |
Generates an operation result file when uploading a file. |
|
flat |
Optional for uploading a folder or multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
Uploads all files in a folder but not the folder itself. |
|
arcDir |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The path to which the uploaded files are archived |
|
dryRun |
Optional (additional parameter) |
Conducts a dry run. |
|
link |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The actual path of a symbolic link for a file or folder
|
|
u |
Optional (additional parameter) |
Indicates incremental upload. If this parameter is set, each file can be uploaded only when it does not exist in the bucket, its size is different from the namesake one in the bucket, or it has the latest modification time. When you compare each local file with data in the bucket, a billable HEAD request is generated. For details, see Requests. |
|
vlength |
Optional (additional parameter) |
After the upload completes, checks whether the sizes of the objects in the bucket are the same as those of the local files. |
|
vmd5 |
Optional (additional parameter) |
After the upload completes, checks whether the MD5 values of the objects in the bucket are the same as those of the local files.
|
|
p |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The maximum number of concurrent uploads for a multipart upload The default value is the value of defaultParallels in the configuration file. |
|
threshold |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The threshold for enabling multipart upload. If the size of the file or folder to be uploaded is smaller than the threshold, upload it directly. Otherwise, a multipart upload is required. The default value is the value of defaultBigfileThreshold in the configuration file. Unit: byte This parameter value can contain a unit, for example, 1MB (indicating 1,048,576 bytes).
NOTE:
If you upload a file or folder directly, no part record is generated, and resumable transmission is not supported. |
|
acl |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The access control policies that can be specified for objects when uploading files. Possible values are:
|
|
sc |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The storage classes of objects that can be specified when uploading files Possible values are:
|
|
meta |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The standard or user-defined metadata that can be specified during file upload
|
|
ps |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The size of each part in a multipart upload task
|
|
cpd |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The folder where the part records reside. The default value is .obsutil_checkpoint, the subfolder in the home directory of the user who executes obsutil commands. A part record is generated during a multipart upload and saved to the upload subfolder. After the upload succeeds, its part record is deleted automatically. If the upload fails or is suspended, the system attempts to resume the task according to its part record when you perform the upload the next time. |
|
r |
Mandatory for uploading a folder (additional parameter) Optional for uploading multiple files/folders |
Recursively uploads all files and subfolders within a folder. |
|
f |
Optional for uploading a folder or multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
Runs in force mode. |
|
j |
Optional for uploading a folder or multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
The maximum number of concurrent tasks for uploading a folder. The default value is the value of defaultJobs in the configuration file.
NOTE:
The value is ensured to be greater than or equal to 1. |
|
msm |
Mandatory for uploading multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
Enables the mode for uploading multiple files/folders. Possible values are 1 and 2.
|
|
exclude |
Optional for uploading a folder or multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
The file matching patterns that are excluded. After this parameter is specified, if the name of the file to be uploaded matches the value of this parameter, the file is skipped. For example, if this parameter is set to *.txt, all files whose names end with .txt are skipped and not uploaded.
Restrictions: The matching pattern takes effect only for files in the folder.
NOTE:
|
|
include |
Optional for uploading a folder or multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
The file matching patterns that are included. After this parameter is specified, if the name of the file to be uploaded matches the value of this parameter, the file is uploaded. For example, if this parameter is set to *.txt, all files whose names end with .txt are uploaded.
Restrictions:
Example: ./obsutil cp /localpath/ obs://test/ -include=/localpath/2022-12-09/* -f -r This command uploads files that are under localpath and start with /localpath/2022-12-09/ to bucket test.
NOTE:
|
|
at |
Optional for uploading a folder or multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
Indicates that only the files whose latest access time is within the value of timeRange are uploaded. This parameter must be used together with timeRange. |
|
disableDirObject |
Optional for uploading multiple folders (additional parameter) |
Indicates the folders themselves are not uploaded as an object. Configuring this parameter can avoid uploading empty folders to a bucket. If a folder contains files, the files will be uploaded and the original path format is retained. |
|
timeRange |
Optional for uploading a folder or multiple files/folders (additional parameter) |
The time range matching pattern when uploading files. Only files whose latest modification time is within the configured time range are uploaded. This pattern has a lower priority than the file matching patterns (exclude/include). That is, the time range matching pattern is executed after the configured file matching patterns.
|
|
mf |
Optional (additional parameter) |
Indicates that the name matching pattern (include or exclude) and the time matching pattern (timeRange) also take effect on folders. |
|
o |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The folder that stores the result files. After the command is executed, result files (possibly success, failure, and warning files) will be created in the specified folder. The default value is .obsutil_output, a subfolder in the user's home directory where obsutil commands are executed.
|
|
config |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user-defined configuration file for executing the current command. For details about parameters that can be configured, see Configuration Parameters. |
|
e |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The endpoint |
|
i |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user's AK |
|
k |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user's SK |
|
t |
Optional (additional parameter) |
The user's security token |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






