Changing the Storage Class of a Bucket or Object
Scenarios
This section describes how to change the storage classes of a bucket or object.
Constraints
- The storage class of a bucket can only be manually changed. The storage class of an object can be changed manually or automatically based on lifecycle rules.
- The data redundancy policy remains unchanged when the storage class is changed. If a bucket or object is configured with multi-AZ redundancy, it can only be moved to a storage class that supports multi-AZ redundancy, such as the Standard or Infrequent Access storage class. However, it cannot be moved to the Archive storage class, which does not support multi-AZ redundancy.
Manually Changing the Storage Class of a Bucket
OBS allows you to move a bucket to any storage class manually, but does not support using lifecycle rules to do that.

- Changing the storage class of a bucket does not change the storage classes of existing objects in the bucket. The storage class of an object uploaded later will inherit the new storage class of the bucket by default. You can configure lifecycle rules to change storage classes of objects in batches.
For example, suppose a bucket, bucket1, is in the Standard storage class and contains an object, object1, also in the Standard storage class. If bucket1's storage class is transitioned to Infrequent Access, then object1 will remain in the Standard storage class, but a new object, object2, uploaded after the change of the bucket storage class, will be in the Infrequent Access storage class.
- After a bucket is changed from Archive or Deep Archive to Standard or Infrequent Access, existing Archive or Deep Archive objects in the bucket will not be automatically restored.
You can use OBS Console, APIs, OBS SDKs, or obsutil to change the storage class of a bucket.
Manually Changing the Storage Class of an Object
OBS allows you to move an object to any storage class manually. For objects that are in the Archive or Deep Archive storage class, you must restore them first before changing their storage classes. OBS also supports automatic change of object storage classes. For details, see Transitioning Objects Between Storage Classes Using Lifecycle Rules.

- If the objects are in the Infrequent Access, Deep Archive, or Archive storage class, changing their storage class may incur costs for the minimum storage duration.
- Even though objects that are in the Infrequent Access storage class do not need to be restored manually, you still need to pay for restoration requests and traffic.
- When changing the storage class of objects that are in the Archive or Deep Archive storage, you are charged for restoration requests, traffic, and temporary copy storage.
You can use OBS Console, APIs, OBS SDKs, OBS Browser+, or obsutil to change the storage class of an object.
Transitioning Objects Between Storage Classes Using Lifecycle Rules
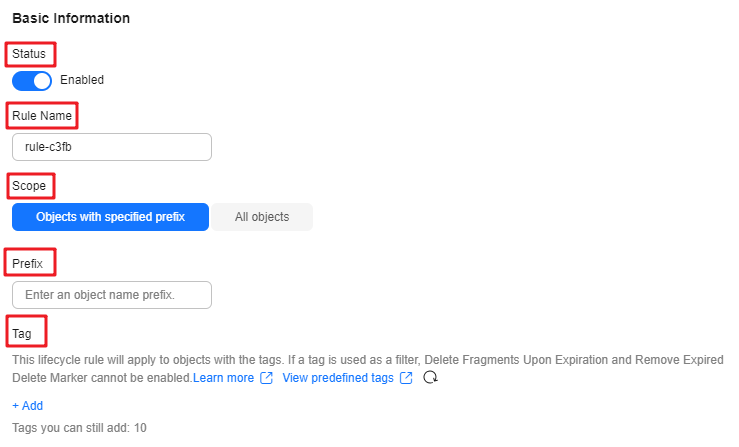
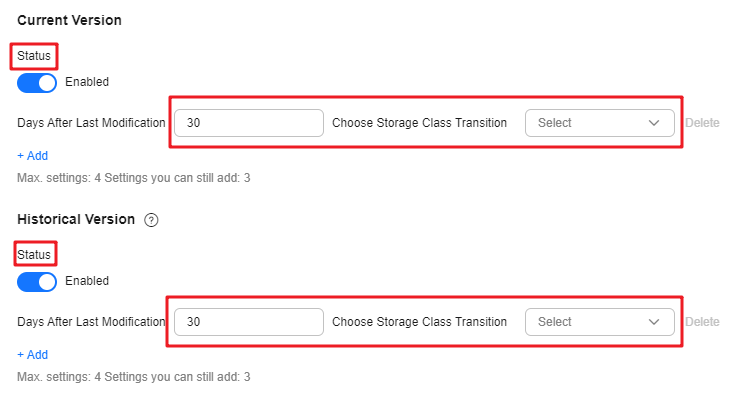
You can configure lifecycle rules to automatically transition objects between storage classes, which reduces storage costs. Because multi-AZ redundancy is not supported for Archive and Deep Archive, you cannot use lifecycle rules to transition the storage class of multi-AZ objects to Archive or Deep Archive. For more information, see Transitioning Object Storage Classes Through Lifecycle Rules.
If versioning is disabled, the lifecycle of an object starts when it is uploaded. If versioning is enabled, the lifecycle of current starts when it is uploaded. The lifecycle for historical versions of an object starts when they become historical.

As shown in the figure, you can configure OBS lifecycle rules to transition objects between storage classes:
- From Standard to Deep Archive, Archive, or Infrequent Access.
- From Infrequent Access to Archive or Deep Archive.
- From Archive to Deep Archive.

- If the objects are in the Infrequent Access, Deep Archive, or Archive storage class, transitioning them may incur costs for the minimum storage duration.
You can use OBS Console, APIs, SDKs, or OBS Browser+ to configure storage classes for buckets at bucket creation.
Precautions
- Minimum billable object size
Objects smaller than 64 KB are billed as 64 KB.
- Minimum storage duration
This means that objects will be billed for the minimum storage duration even if they are not stored for that long. For example, if an object is transitioned to Archive after being stored in Infrequent Access for 20 days, it will be billed for the storage of 30 days (the minimum storage duration for Infrequent Access).
Item
Standard
Infrequent Access
Archive
Deep Archive (Under Limited Beta Testing)
Minimum storage duration
N/A
30 days
90 days
180 days
- Object restoration duration
Object restoration is required for accessing Archive and Deep Archive objects. The restoration will take some time. If your services require real-time data access, these two storage classes are not recommended.
Table 4 Object restoration duration Restoration Speed
Duration of Restoration from Archive
Duration of Restoration from Deep Archive
Standard
3 to 5 hours
5 to 12 hours
Expedited
1 to 5 minutes
3 to 5 hours
- Data restoration billing
Table 5 Data restoration billing Operation
Billing Item
Description
Infrequent Access objects
Requests
You are billed for the number of successfully restored objects.
If N objects were successfully restored, you are billed for N requests.
Data transfer
You are billed for the bandwidth you consumed during data retrievals.
Archive or Deep Archive objects
Requests
You are billed for the number of successfully restored objects.
If N objects were successfully restored, you are billed for N requests.
Data transfer
You are billed for the bandwidth you consumed during data retrievals.
Temporary file storage
When an Archive or a Deep Archive object is restored, a copy in the Standard storage class will be generated for the object. That means the object and its Standard copy will co-exist in the bucket. During the validity period of a restoration, you will be billed for the space taken up by both the object and its copy. The copy will be automatically deleted once the validity period ends.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot