Creating a Batch Server Migration Workflow
This section describes how to create a batch server migration workflow using a template.
Constraints
- A workflow can contain a maximum of 100 servers.
- Source servers in workflows created by the same user must have unique MAC addresses. Duplicate MAC addresses may cause network conflicts or task execution errors.
- You can migrate up to 150 servers at the same time. Any additional servers beyond this limit will have their workflows paused at the initial step and stay in a pending state. Once other migrations complete, these workflows will automatically resume in the order they were created.
- If this is your first time to create a server migration workflow, you need to assign MgC the required permissions. For more information about the required permissions, see Agency Permissions.
Precautions
Before creating a server migration workflow, read and understand the items below.
|
Item |
Precaution |
|---|---|
|
Source download bandwidth |
Used to download the SMS-Agent to source servers.
|
|
Migration bandwidth |
|
|
Available CPUs and memory |
|
|
OS compatibility |
For details, see Supported OSs. |
|
Server migration statements |
For details about the important statements you need to understand before the migration, see What Are the Important Statements of SMS? |
|
Constraints |
For details about the notes and constraints for server migration, see Notes and Constraints. |
|
Billing |
For details about the costs that may be incurred during the migration, see Billing. |
|
Permissions configuration |
IAM is used for fine-grained permissions management. For details, see Permissions Management. |
|
Migration network and ports |
For details about the requirements for the migration network and ports, see How Do I Set Up a Secure Migration Network for Using SMS? |
|
Changes in server configurations before and after migration |
For details about the configurations that may change after the migration, see What Are the Differences Between the Source and Target Servers After the Migration? |
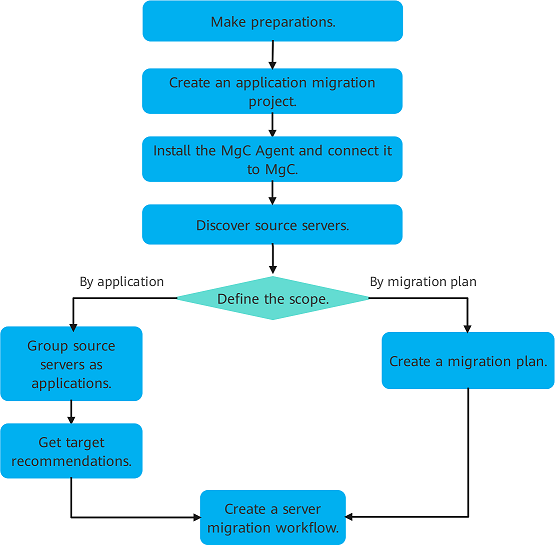
Operation Process
|
Step |
Operation |
|---|---|
|
Preparations |
For details, see Preparations. |
|
Create an application migration project. |
Create a project to segregate and manage your migration resources. For details, see Creating an Application Migration Project. |
|
Install the MgC Agent and connect it to MgC. |
The MgC Agent is a tool used to discover resources and collect their details. It is also used for executing migration workflow tasks. For more details, see: |
|
Discover source servers. |
Discover source servers and collect their details. MgC provides the following methods for you to do this work. |
|
Select source resources. |
You can specify the migration scope by application or migration plan when creating a server migration workflow.
|
|
Create a server migration workflow. |
After the preceding steps are complete, create a server migration workflow. |
Procedure
- Sign in to the MgC console. In the navigation pane, under Project, select your application migration project from the drop-down list.
- In the navigation pane, choose Workflows.
- Click Create Workflow in the upper right corner of the page.
- In the Batch Server Migration card, click Preview Steps to view the steps predefined in the template and the detailed description of each step. MgC handles Automated steps, while Manual steps require your action. Click Configure Workflow in the lower right corner.
- Configure the workflow parameters based on Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters for configuring a server migration workflow Area
Parameter
Description
Workflow Details
Name
User-defined
Description
Select Source Resources
- By application: Servers in the selected application will be migrated together.
- By migration plan: Servers in the selected migration plan will be migrated together.
Application
Application
If Select Source Resources is set to By application, select the application that contains the servers to be migrated.
Migration Plan
Migration Plan Name
If Select Source Resources is set to By migration plan, select the plan that contains the servers to be migrated. For details about how to create a migration plan, see Creating a Server Migration Plan.
Migration Network
Network Type
If you select Public, ensure that all target servers have EIPs bound. These EIPs will be used for the migration.
If you select Private, configure Direct Connect connections, VPN connections, VPC peering connections, or subnets in the target VPC in advance to connect the source environment to the target environment.
- If the source environment cannot access the Internet, enter the private IP address of the source proxy server and the port used by the proxy software.
- If the source proxy server cannot access the Internet, put the SMS-Agent installation package at a location where the source servers can access directly or over a proxy. You can download the SMS-Agent installation package from the SMS console.
Target Environment
Region
The target region. It defaults to the one you selected when you assessed the application.
Project
A project in the target region.
VPC
- If the source IP address is 192.168.X.X, you are advised to create a VPC and a subnet that both belong to network range 192.168.0.0/16.
- If the source IP address is 172.16.X.X, you are advised to create a VPC and a subnet that both belong to network range 172.16.0.0/12.
- If the source IP address is 10.X.X.X, you are advised to create a VPC and a subnet that both belong to network range 10.0.0.0/8.
Subnet
The subnet has to be in the same network segment as the VPC.
Security Group
- Inbound ports 8899, 8900, and 22 must be allowed for Windows migrations.
- Inbound port 22 must be allowed for Linux file-level migrations.
CAUTION:
- For security purposes, you are advised to only allow traffic from the source servers on these ports.
- These ports must also be opened on the firewalls of target servers.
Migration Port
It defaults to 22. If port 22 is occupied, you can use one from 10000 to 65535.
CAUTION:The following ports are blacklisted as the migration port:
135, 139, 445, 5357, 5985, 5986, 8899, 8900, 47001, 49664, 49665, 49666, 49668, 49669, 49671, 49674, 49677, 49679, 49680, 49681, 49682, 49683, 49685, 49690, 49691, 49693, 49694, 49695, 49698, 49699, 49700, 49702, 49703, 49704, 49705, 49706, 49707, 49708, 49709, 49710, 49711, 49712, and 49713
Ensure the specified port is not in the blacklist above or occupied by another service on source servers, and verify that network settings permit traffic over this port.
The functions of the port are as follows:
- For Linux servers, this port is used to establish transmission channels and transmit data.
- For Windows servers, this port is used to establish transmission channels.
Control Port
This port is used to transmit task control signals for Windows servers. It defaults to 8899 and cannot be changed.
Transmission Port
This port is used to transmit data for Windows servers. It defaults to 8900 and cannot be changed.
Encryption
If you select No, the system and data disks will not be encrypted for target servers newly created in the workflow.
If you select Yes, the system and data disks will be encrypted for target servers newly created in the workflow.
NOTICE:- This setting does not apply to the existing target servers associated with the source servers.
- This setting applies to all target servers newly created in the workflow. Their disks will be encrypted using the same key.
- Once a disk is created, the encryption attribute of the disk cannot be modified.
- Keys can be shared with accounts, not IAM users.
To enable disk encryption, you need to create an agency to authorize EVS to access KMS. If you have the right to grant the permissions, grant the KMS access permissions to EVS directly. Once the authorization succeeds, you no longer need to perform the authorization again. If you do not have the right to grant the permissions, contact a user with the Security Administrator permissions to grant you the right and then repeat the preceding operations. After the authorization is successful, configure the following parameters:
- Select an existing key
NOTICE:
Only enabled keys generated using the AES_256 encryption algorithm are supported.
Select one of the following keys from the drop-down list:
Default keys: After the KMS access permissions have been granted to EVS, the system automatically creates a default key and names it evs/default.
Custom keys: You can choose an existing key or create a new one. For details about how to create a key, see Creating a Key.
- Enter a key ID
Enter the ID of a key shared from another user. Ensure that the key is in the target region. For details, see Creating a Grant.
Advanced Settings
Verify Data Consistency
- If you select Yes, the system will automatically verify data consistency after the full replication is complete. This is a quick verification, and only the file size and last modification time will be verified. You can modify the verification policy after the incremental synchronization is complete.
- If you select No, data consistency will not be verified after the full replication is complete. You can modify the verification policy after the incremental synchronization is complete.
Start Target After Migration
- If you select No, the target servers will be stopped after the migration is complete.
- If you select Yes, the target servers will be started after the migration is complete.
Set Bandwidth Limit
- If you select No, the migration traffic is not limited.
- If you select Yes, you can limit the bandwidth that can be used for migration based on the source bandwidth and service requirements.
CAUTION:Consider the migration scale to set an appropriate bandwidth limit. If too small a bandwidth is allocated to a workflow that includes 10 servers, migration tasks in the workflow may preempt the limited bandwidth resource, and some servers may fail to be migrated.
Install rsync on Source
Linux migrations depend on rsync. If rsync is not installed on a source server, the server will fail to be migrated.
- If this option is not selected, rsync will not be installed on the source servers.
- If this option is selected, rsync will be automatically installed on the source servers. The installation can succeed only if the source servers:
- Have the Internet access. If a proxy server is required, ensure that the proxy settings are correctly set in /etc/yum.conf (for CentOS and Red Hat) or /etc/apt/apt.conf (for Ubuntu).
- Have outbound ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) enabled by the firewalls and security groups.
- Have accessible software sources. You are advised to configure a source based on your location. Cross-country access to the official source may experience high latency and packet loss, which may result in download failures.
- Have sufficient CPU, memory, and I/O resources to prevent latencies or interruptions during installation.
NOTE:If the automatic installation fails, manual installation is required. For details, see rsync Not Installed on the Source Server.
Retain IP Address
Enable this option to retain the private IP addresses of the source servers on the target servers. Enabling it may cause risks. You need to evaluate and take responsibility for any potential risks. For details, see How Do I Keep the Private IP Address of a Server Unchanged After the Migration?
Enable Quick Mode
Enable this option if incremental synchronization is not required. This option is disabled by default. If it is enabled, incremental synchronization is skipped and then subsequent steps are performed after full replication is complete in the workflow. Set this option based on your requirements.
Enterprise Project
Select the enterprise project you want to migrate to. The enterprise project default is selected by default.
Send SMN Notifications
Determine whether to get SMN notifications about the migration. You can configure Topic, Language, and Trigger Condition.
Before enabling this function, create an SMN topic and subscribe to it. For details, see Publishing a Template Message.
NOTE:You can only choose an SMN topic in the default IAM project of the region where you currently use MgC.
To enable this function, you need to authorize MgC when the system prompts you.
Select one or more trigger conditions.
- Migration succeeded: A notification will be sent if all resources in the migration workflow are migrated.
- Migration failed: A notification will be sent if any resource in the migration workflow fails to be migrated.
- Manual checkpoint: A notification will be sent if all resources in the migration workflow are waiting for manual confirmation.
Tags
You can add tags to the target servers automatically created by the workflow to facilitate resource management.
Click Add Tag and enter a tag key and tag value. For details about tags and tag naming rules, see Tag Overview.
To add the same tag to multiple servers or other types of resources, you can create a predefined tag on the TMS console and then select it for the servers or resources. This frees you from repeatedly entering tag keys and values. For details, see Creating Predefined Tags.
- Click Next: Confirm.
- Confirm the workflow settings and click Confirm. The Run Workflow dialog box is displayed, which indicates that the workflow has been created.
- If you want to start the migration immediately, click Confirm to run the workflow.
- If you want to add a stage or step to the workflow, click Cancel. The workflow enters a Waiting state, and the migration has not started yet. To start the migration, click Run in the Operation column.
- On the migration workflow details page, view the workflow settings and the migration progress. After the step for starting the migration Agent is completed, a migration task is automatically created on the SMS console. For details about the server information mapping between MgC and SMS, see What Are the Information Mappings Between MgC and SMS?
- Move the cursor to the migration progress bar. In the box that is displayed, view more migration details.
- When the migration progress bar reaches a step that requires manual confirmation, move the cursor to the progress bar and click Confirm next to the step status in the displayed window, so that the subsequent migration steps can be executed.
- When the workflow reaches the ResizeDiskPartition step, the system identifies whether disk capacity reduction has been performed on the target server.
- If yes, go to the SMS console and resize disks and partitions for the target server. For details, see the Resize Disks and Partitions parameter in Configuring a Target Server. After the adjustment is complete, go back to the MgC console and click Confirm next to the step status so that the workflow can continue.
- If no, skip this step.
- When the workflow on a resource reaches the StartMigration or StartSynchronization step, you can click Pause to pause the migration of the resource. To resume the migration, click Run.

- The StartSynchronization step in the Migrate stage can be repeated. When the migration workflow reaches the BusinessValidation step that needs confirmation, you can click Run Previous Step to launch an incremental synchronization again.
- When the progress bar reaches Cutover, the migration is complete. You need to check whether your service systems can run properly on the target server. If they can, manually switch service traffic to the target server. After the switchover is complete, click Confirm in the workflow. The system automatically performs the following steps: SourceClear and MigrationTaskClear.
Deletes Resources

- You cannot delete all resources from a workflow. Retain at least one resource.
- Only resources in the Failed, Paused, or Completed state can be deleted.
- Click the workflow name to view its details.
- In the resource list, select the resources to be deleted and click Delete above the list.
- Confirm the selected resources, enter DELETE, and click Confirm.

This operation only deletes the resource data from MgC. It may not delete the related tasks and resources in other clouds services like SMS, OMS, and OBS. After the deletion, you need to manually delete the related tasks and resources in the related cloud services.
When to Use the Retry and Full Retry Buttons
During the running of the server migration workflow, the MgC Agent (formerly Edge) launches an SMS-Agent migration process on each source server. After the process is started, it communicates with the SMS console and receives commands to perform migration. During the StartMigration and StartSynchronization steps in the workflow, if the SMS-Agent process on a source server disconnects from the SMS console, the MgC console will detect the disconnection, causing the migration workflow to fail on that source server. On the migration workflow details page, you will see options Retry and Full Retry. The appropriate choice depends on the cause of the disconnection. The possible causes for the disconnection include:
- Possible cause 1: There is a network exception.
In this case, the SMS-Agent process still opens on the source server. You only need to restore the network, wait until the connection to the SMS console is restored, and click Retry to resume the migration.Figure 2 Retry

Command for checking the SMS-Agent process on Linux:
# ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep linuxmain
PowerShell command for checking the SMS-Agent process on Windows:
# Get-Process -Name SMSAgentDeploy -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
- Possible cause 2: The source server was restarted.
In this case, the SMS-Agent process is stopped, and the migration cannot be resumed. You need to create an SMS migration task again by clicking the Full Retry button. Then the workflow will directly go to the MigrationTaskClear step. After the migration task is cleared, the workflow will start from the StartUpAgent step to restart the SMS-Agent process on the source server and create an SMS migration task again.Figure 3 Full Retry


Clicking the Full Retry button will delete the original migration task and create a new one. The migrated data will be overwritten.
Enabling or Modifying the Data Consistency Verification Policy After Incremental Synchronization Is Complete
After incremental synchronization is complete, you can enable or modify the consistency verification policy.
- Move the cursor to the progress bar. In the displayed dialog box, click Modify next to Consistency Verification Policy.
Figure 4 Modifying the consistency verification policy

- Select Verify Data Consistency and configure the verification policy based on Table 2.
Figure 5 Configuring the consistency verification policy

Table 2 Parameters for configuring the consistency verification policy Parameter
Description
Enable Hash Verification
If this option is enabled, the system will generate and compare hash values for each file to be verified. Hash verification is recommended when individual files are large and important. Enabling this option will increase CPU and disk I/O overheads for the source server and extend the verification time.
CAUTION:- Hash values cannot be calculated for files in use, so these files will be skipped during the verification.
- Enabling this option requires you to specify the verification scope, and only files in the specified scope will be verified.
Verification Scope
- Under Exclude paths, enter the paths you want to exclude from the verification. A maximum of 30 paths can be entered. Use commas (,) to separate the paths. For example, /root/data,/var. Leaving it empty will initiate a full verification.
- Under Include paths, enter the paths you want to verify.
NOTICE:- If the entered paths are incorrect or empty, 0 will be displayed for them in the verification results.
- The more data you need to verify, the longer the verification will take. It is wise to narrow the verification scope to only key paths.
- The following paths will be excluded from consistency verification by default:
- Linux: /bin, /boot, /dev, /home, /etc, /lib, /media, /proc, /sbin, /selinux, /sys, /usr, /var, /run, and /tmp
- Windows: top-level directories of partitions, for example, C:\ and O:\.
Verify Inconsistencies
This option can only be enabled after at least one consistency verification is complete. If this option is enabled, the system verifies only the files were found to be inconsistent during the last verification.
- Click Save. After the incremental synchronization is complete, the system will automatically verify data consistency.
- After the synchronization and verification are complete, go to the SMS console and view the verification results.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot