What Are the Notes, Constraints, and Precautions for Server Migration?
This section outlines key considerations, limitations, and precautions for server migration. Understanding these factors helps you thoroughly prepare and ensure a seamless migration process.
Notes and Constraints for Using SMS
MgC server migration workflows use SMS to manage migration tasks. Therefore, all notes and constraints of SMS also apply to server migration using MgC.
|
Item |
Constraint |
|---|---|
|
Server specifications |
|
|
CPU and memory |
|
|
OSs |
|
|
Available disk space |
|
|
Disk quantity |
SMS imposes a disk limit on source servers due to ECS constraints. While an ECS supports up to 24 disks, SMS reserves one slot for a temporary disk during migration. This means that a source server can have a maximum of 23 disks. |
|
Disk size |
|
|
File systems |
|
|
Shared file systems |
Only files on local disks can be migrated. Shared file systems cannot be migrated. For example, files in Network File System (NFS), Common Internet File System (CIFS), and Network Attached Storage (NAS). |
|
Nested LVM systems |
Nested LVM systems cannot be migrated. |
|
Required components |
Source servers must contain the components required for migration.
|
|
Source character set encoding |
Windows: Code page 437 and code page 936 are supported. Linux: UTF-8 is supported. |
|
Linux source key exchange algorithm |
ssh-rsa is supported. |
|
Item |
Constraint |
|---|---|
|
Source server quantity |
A maximum of 1,000 source servers are allowed per account. Delete the records of migrated servers in a timely manner so that other servers can continue to be migrated. |
|
Number of concurrent migrations |
A maximum of 100 source servers can be migrated at the same time. |
|
External storage of servers |
SMS cannot migrate data from the external storage attached to a source server. |
|
Encrypted files |
SMS cannot migrate OSs that contain protected folders or encrypted volumes. |
|
Encrypted systems |
SMS cannot migrate OSs that are encrypted, such as Windows OSs protected with BitLocker. |
|
Servers that run multi-node databases and Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) |
SMS cannot migrate servers that host active directories or multi-node databases. |
|
Data of database applications and domain controller applications |
SMS cannot migrate data of database applications and domain controller applications. |
|
Applications bound to hardware |
SMS cannot migrate OSs that contain applications bound to hardware. |
|
Dynamic disks |
Dynamic disks in Windows systems are migrated as basic disks. After the migration is complete, the target server will not have dynamic disks. |
|
Unmounted or uninitialized disks (empty disks) |
SMS only migrates data on disks that are mounted and actively used on a source server. Data on unmounted or uninitialized disks will not be migrated. SMS requires that the source and target servers have the same number of disks, including any unmounted or uninitialized disks.
NOTE:
If you want to migrate data from an unmounted disk on the source server, mount the disk to the source server before the migration. |
|
Servers with system volumes located on disks other than the first disk |
SMS cannot migrate servers whose system volumes are not on the first disk. |
|
Thinly-provisioned logical volumes |
SMS cannot migrate thinly-provisioned volumes tagged with pool. |
|
Servers with RAID arrays |
SMS cannot migrate servers with RAID arrays. |
|
Big data clusters and container clusters |
SMS cannot migrate clusters including but not limited to container clusters and big data clusters. |
|
Compressed RAM-based block devices (ZRAM devices) |
SMS cannot migrate ZRAM devices. These devices are ignored during the collection phase, as they temporarily store compressed memory blocks. Manual configuration is required after the migration is complete. |
Precautions for Using SMS
MgC server migration workflows use SMS to manage migration tasks. Therefore, all precautions of SMS also apply to server migration using MgC.
- You need to check the OS version of the server you are migrating. If it is too early, for instance, Windows Server 2008, the kernel may be incompatible and services on the server may fail to start after the migration is complete. To avoid this issue, you need to evaluate whether a lift-and-shift migration is suitable for the server before the migration.
- You need to disable any software such as antivirus or security software that may prevent the SMS-Agent from starting on the source server. If you are not sure whether there is a software conflict with the SMS-Agent, back up your data before the migration.
- Linux block-level migration is in the open beta test (OBT) and is only recommended for testing scenarios.
- The VirtIO drivers must be installed in the source server OS, or the target server may fail to start after the migration is complete. If your source server runs on Huawei Cloud, you can install the drivers by referring to Installing VirtIO Drivers.
- There are differences between the source and target servers after the migration. For details, see What Are the Differences Between the Source and Target Servers After the Migration?
- Before using SMS, you need to set up a secure network. For details about the network requirements, see How Do I Set Up a Secure Migration Network for Using SMS?
- You need to correctly configure security group rules for the target server. For details, see How Do I Configure Security Group Rules for Target Servers?
- The migration occupies some source server resources, such as memory, CPU, disk I/O, and bandwidth. You can limit the resource allocation for the migration. If the source server runs Linux, Traffic Control (TC) must be installed and run properly on it. Otherwise, traffic limiting may not be applied.
- The migration speed is affected by factors, such as the network bandwidth, disk I/O, CPU and memory usage, as well as file size and quantity, so it is impossible to accurately estimate the migration duration. The remaining migration duration estimated by SMS for a migration task is for reference only. For more information, see Migration Duration.
- It is recommended that data migration and service cutover be completed within 30 days.
- The time required for an incremental synchronization is affected by many factors, such as the number of incremental files, the continuity of valid blocks, and the size of incremental data. It is impossible for SMS to estimate the required time.
- Before a migration is complete, do not perform operations on the OS or disks of the target server, including but not limited to changing or reinstalling the OS.
- Do not change the billing mode of the target server or its disks to Yearly/Monthly during a migration.
- Make sure you have backed up any data on the target server that you need to save and ensure that the disks can be formatted. Disks on the target server will be formatted and re-partitioned based on the source disk settings during the migration.
- During the migration of a Windows source server, do not restart the source server. The restart will disconnect the source server from the SMS console. To retry the migration, you need to delete the migration task and create a new one.
- Do not restart the SMS-Agent during a Windows migration or a Linux block-level migration.
- You are advised not to start the SMS-Agent during a Linux file-level migration unless necessary, even though resumable data transfer is supported.
- During the migration, a temporary pay-per-use disk is created and attached to the target server to ensure that the migration runs normally. Once the migration is complete, the disk is automatically detached and deleted. If you manually delete the migration task before it completes, you need to manually delete the temporary disk to avoid extra expenses.
- If an error occurs during the migration, you are advised to provide migration logs to technical support engineers so that the fault can be resolved quickly.
For details about how to get migration logs, see Where Can I Find the Agent Run Logs?
- SMS migrates OS and data. It ensures data consistency before and after the migration, but does not ensure that your applications will run properly on the target server after the migration is complete. You may need to adjust your applications by yourself.
- SMS gives you the capability to verify data consistency before and after the migration. You can enable verification when you configure the target server or initiate an incremental synchronization. Note that consistency verification cannot be performed for servers with Btrfs file systems.
Precautions for Using Key SMS Features
You need to note the following content before using the key features of SMS:
After the full migration of a Linux server, some parameter settings in the directories below on the target server are modified to make the target server compatible with Huawei Cloud and ensure that the target server can start properly. During incremental synchronization, data in these directories is not synchronized by default to prevent parameter settings in these directories on the target server from being overwritten or modified.
/proc/*, /sys/*, /lost+found/*, /tmp/_MEI*, /var/lib/ntp/proc/*, / /etc/fstab, /etc/X11/*, /root/initrd_bak/*, /lib/modules/*, /boot/grub2/x86_64-efi/*, /boot/grub2/i386-pc/*
To limit the migration speed for a Linux source server, the tc command and cbq or htb kernel module must be installed on the source server.
- To check whether the tc command is installed, run the following command on the Linux terminal. If the system returns the tc function list, the tc command has been installed.
# tc
- To check whether the cbq module is installed, run the following command on the Linux terminal. If the system returns the related information, the cbq module is loaded.
lsmod | grep sch_cbq
- If the cbq module does not exist, check the htb module. Run the following command on the Linux terminal. If the system returns the related information, the cbq module is loaded.
lsmod | grep sch_htb
- Resumable transfer is supported following network interruptions.
- Resumable transfer is supported following a Linux restart but is not available after a Windows restart.
Precautions for Using the MgC Agent
The MgC Agent is a tool you need to deploy at the edge of your cloud network. In server migration scenarios, it works with migration workflows to collect server details and migrate data.

Do not install the MgC Agent on a source server to be migrated.
- High resource consumption: The MgC Agent consumes CPU and memory resources during collection and migration. If a large number of migration tasks are performed by the MgC Agent, services on the source server may be affected.
- Port occupation: The MgC Agent occupies some ports on the server, which may affect services running on it.
- Allow access from the server where the MgC Agent is installed over port 5985 or 5986.
- Use PowerShell 3.0 or later.
- Have WinRM enabled and be able to access the server where the MgC Agent is installed. For more information, see How Do I Configure WinRM and Troubleshoot WinRM Connection Problems?
- Allow the execution of shell scripts. To review the current execution policy, you can open PowerShell on the source servers as an administrator and run the following command:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
If Restricted is returned, no scripts can be executed. Run the following command and enter Y to change the policy to RemoteSigned:Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
- Allow access from the server where the MgC Agent is installed over port 22.
- Allow direct root access. This means remote connections using root with SSH or other tools must be allowed on these Linux source servers.
- Have SFTP and SSH enabled.
- Support the following key exchange algorithms and MAC algorithms:
- Key exchange algorithms: ssh-ed25519, ecdsa-sha2-nistp256, ecdsa-sha2-nistp384, ecdsa-sha2-nistp521, rsa-sha2-512, and rsa-sha2-256
- MAC algorithms: hmac-sha2-256 and hmac-sha2-512
If a server does not support the preceding security algorithms, you are advised to upgrade OpenSSH to 8.0 or later. Otherwise, deep collection cannot be performed for that server.
- Have their iptables configured to allow all communications with the server where the MgC Agent is installed. To verify that, you can run the following command on the source servers. If the source field in the command output contains the IP address and port of the server where the MgC Agent is installed, the MgC Agent is not allowed to access these source servers. In this case, you need to allow access from the MgC Agent.
iptables -L INPUT -v -n
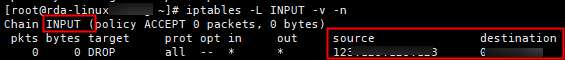 Run the following command to allow the access.
Run the following command to allow the access.iptables -D INPUT -s <IP-address-of-the-MgC-Agent-server-indicated-by-the-source-field>
OSs Supported by MgC
MgC allows collection and migrations of the following OSs:
Table 1 lists the Windows OSs that can be collected and migrated by MgC.
To check the Windows OS version and boot mode, perform the following steps:
- Press Win and R to open the Run window.
- Enter msinfo32 and click OK. The System Information window is displayed. Check the OS version.
- Check the value of BIOS Mode, which can be one of the following:
- UEFI
- Legacy (BIOS)
|
OS Version |
Bit |
UEFI Supported |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Windows Server 2008 |
64 |
NO |
Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 cannot boot in UEFI mode. |
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 |
64 |
NO |
|
|
Windows 7 |
64 |
NO |
|
|
Windows 8.1 |
64 |
NO |
|
|
Windows Server 2012 |
64 |
Yes |
- |
|
Windows Server 2012 R2 |
64 |
Yes |
|
|
Windows Server 2016 |
64 |
Yes |
|
|
Windows Server 2019 |
64 |
Yes |
|
|
Windows Server 2022 |
64 |
Yes |
|
|
Windows 10 |
64 |
Yes |
MgC supports collection and migration for Linux distributions and versions that use OpenSSH 7.0 or later. If a source server uses OpenSSH earlier than 7.0, perform the following operations:
- Upgrade OpenSSH to 7.0 or later.
- If the OpenSSH version cannot be upgraded, add an environment variable on the server where the MgC Agent is installed. For details, see How Do I Set Environment Variables to Collect and Migrate Linux Servers That Use OpenSSH Earlier Than 7.0?
Table 2 lists the Linux OSs that can be collected and migrated by MgC.
|
OS Distribution |
OS Version |
Default OpenSSH Version |
|---|---|---|
|
CentOS |
CentOS 6.5 or later |
OpenSSH 5.3 Upgrade OpenSSH to 7.0 or later, or configure environment variables. |
|
CentOS 7.x |
OpenSSH 7.4 |
|
|
CentOS 8.x |
OpenSSH 8.0 |
|
|
CentOS Stream 8, 9, and 10 |
OpenSSH 8.0 |
|
|
Ubuntu |
Ubuntu Server 16.04 |
OpenSSH 7.2 |
|
Ubuntu Server 18.04 |
OpenSSH 7.6 |
|
|
Ubuntu Server 20.04 |
OpenSSH 8.2 |
|
|
Ubuntu Server 22.04 |
OpenSSH 8.9 |
|
|
Ubuntu Server 24.04 |
OpenSSH 9.6p1 |
|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.x |
OpenSSH 7.4 |
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.x |
OpenSSH 8.0 |
|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.x |
OpenSSH 8.7 |
|
|
Oracle Linux |
Oracle Linux 7.x |
OpenSSH 7.4 |
|
Oracle Linux 8.x |
OpenSSH 8.0 |
|
|
Oracle Linux 9.x |
OpenSSH 9.0 |
|
|
Amazon Linux |
Amazon Linux 2 |
OpenSSH 7.4 |
|
Amazon Linux 2018.03 or later |
OpenSSH 7.4 |
|
|
Amazon Linux 2023 |
OpenSSH 8.9 |
|
|
Alibaba Cloud Linux |
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2.x |
OpenSSH 7.4 |
|
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.x |
OpenSSH 8.2 |
|
|
openSUSE |
openSUSE Leap 15.4 |
OpenSSH 8.1 |
|
openSUSE Tumbleweed |
OpenSSH 9.0 |
|
|
Kylin |
Kylin Operating System V10 |
OpenSSH 8.4 |
|
openEuler |
openEuler 22.03 LTS |
OpenSSH 8.8 |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





