Device Management
After a device is registered, you can manage the device, view device information, and freeze the device on the IoTDA console.
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose . By default, all devices in the current instance are displayed in the device list.
Figure 1 Device - Device list

Table 1 Device list functions Function
Description
Search for a device
Search for a specific device based on the status, device name, node ID, device ID, resource space, product, and node type.
View device information
View the device status, device name, and node ID in the device list. Click View in the row of a device to access the device details.
Delete a device
Click Delete in the row of a device to delete the device.
NOTE:When a device is deleted, its associated data is also deleted. Back up the data before the deletion.
To delete a large number of devices, you can call the API for creating a batch task or delete devices in batches on the IoTDA console. For details, see Device Batch Deletion.
Freeze a device
Click Freeze in the row of a device to freeze the device.
NOTE:A frozen device cannot go online. Only devices that are directly connected to the platform can be frozen.
To freeze a large number of devices, you can call the API for creating a batch task.
Unfreeze a device
Click Unfreeze in the row of a device to unfreeze the device.
To unfreeze a large number of devices, you can call the API for creating a batch task.
Debug a device
Click Debug in the row of a device to debug the device.
Device Status
You can view the device status (online, offline, inactive, abnormal, or frozen) on the IoTDA console. You can also learn the device status by means of subscription. The table below describes the device statuses.
|
Type |
Status |
Short-Connection Device (Such as NB-IoT Devices) |
Persistent Connection Device (MQTT Device) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Connection status |
Online |
If a device has reported data within 25 hours, the device status is Online. If no data has been reported within the past 25 hours, the device status is Abnormal. |
The device is connected to the platform. |
|
Offline |
If a device reports no data for 49 hours after connecting to the platform, the platform sets the device status to Offline. |
After the device is disconnected from the platform for 1 minute (the data is automatically updated every minute), the device status is set to Offline. If you manually refresh the status on the page, the device status is displayed as Offline. |
|
|
Abnormal |
If a device reports no data for 25 hours after connecting to the platform, the platform sets the device status to Abnormal. |
This status does not apply to persistent connection devices. |
|
|
Inactive |
The device is registered with but does not connect to the platform. To access the device, see Initializing a Device. |
The device is registered with but does not connect to the platform. To access the device, see Initializing a Device. |
|
|
Management status |
Frozen |
After a device is frozen, it cannot be connected to the IoT platform. Currently, only devices directly connected to the IoT platform can be frozen. |
|
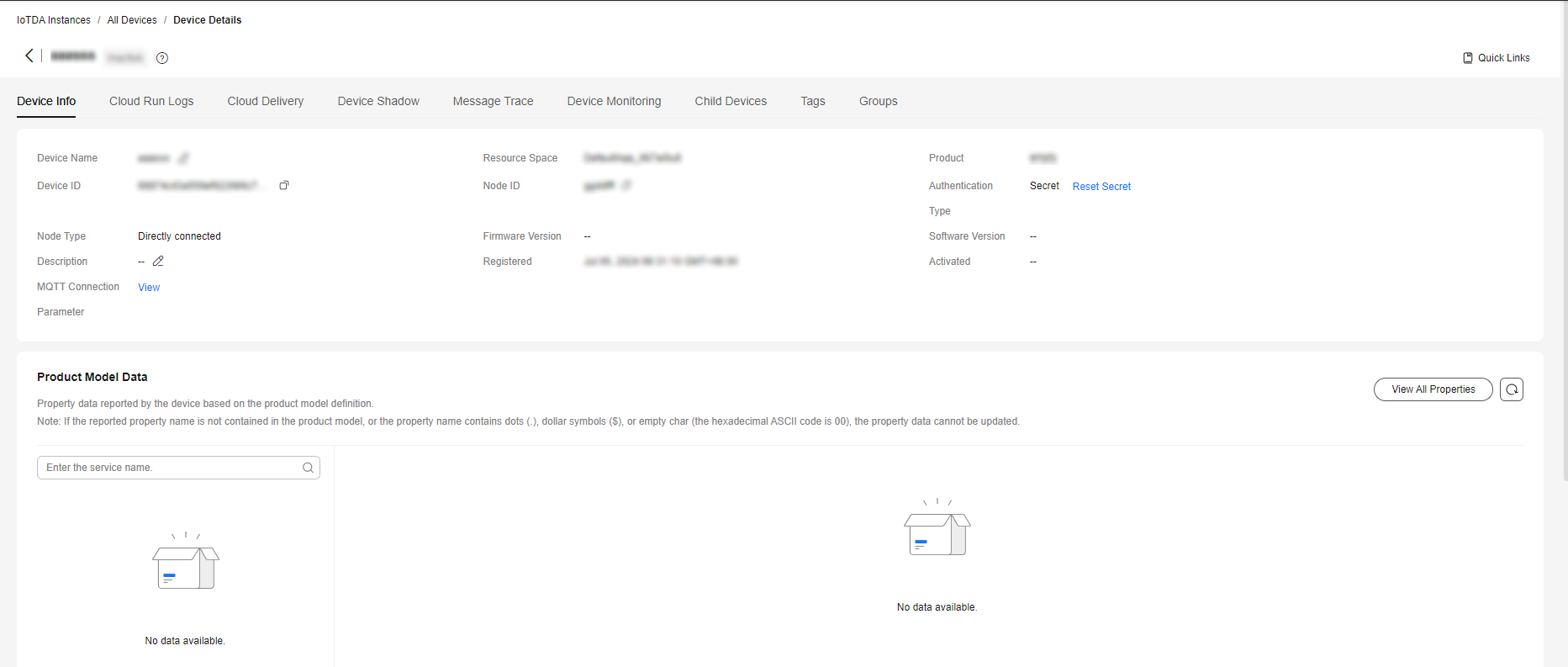
Device Details
In the device list, click View in the row of a device to access its details.
|
Tab |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Device Info |
|
|
Cloud Run Logs |
IoTDA records connections with devices and applications. You can view the information on the console. For details, see Run Logs (New Version). |
|
Cloud Delivery |
You can create a command or message (MQTT device only) delivery task for an individual device on the IoTDA console. For details, see Data Delivery. |
|
Device Shadow |
The platform provides the device shadow to cache the device status. When the device is online, delivered commands can be directly obtained. When the device is offline, it can proactively obtain the delivered commands after going online. For details, see Device Shadow. |
|
Message Trace |
The platform supports quick fault locating and cause analysis through message trace. For details, see Message Trace. |
|
Device Monitoring |
|
|
Child Devices |
Devices can be directly or indirectly connected to the IoT platform. Indirectly connected devices access the platform through gateways. For details, see Gateways and Child Devices. |
|
Tags |
You can define tags and bind tags to devices. For details, see Tag Introduction. |
|
Groups |
You can add devices to different groups for batch operations. For details, see Groups and Tags. |
Device Batch Deletion
To delete devices in batches on the IoTDA console, perform the following steps:
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices, click the Batch Deletion tab, and click Batch Deletion.
- In the displayed dialog box, download Batch Device Deletion Template, enter the IDs of the devices to be deleted in the template, specify Task Name, upload the file, and click OK. Alternatively, you can specify a product to delete devices in batches.
Figure 3 Device - Deleting devices in batches (by file)
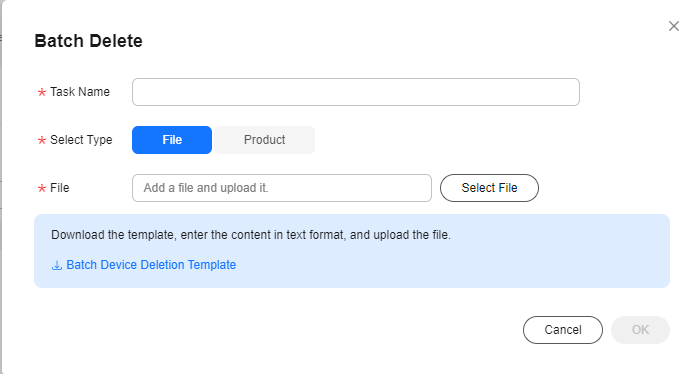 Figure 4 Device - Deleting devices in batches (by product)
Figure 4 Device - Deleting devices in batches (by product)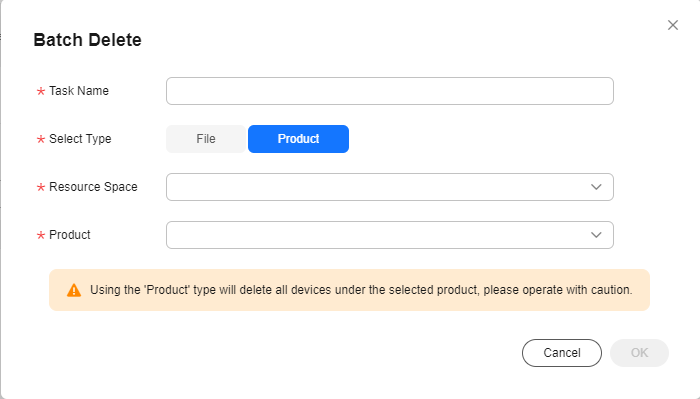
The task execution status and result are displayed. If the success rate is not 100%, click the task name to open the task details page and view the failure cause.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





