API Gateway (Dedicated) Trigger
This section describes how to create an APIG trigger on the FunctionGraph console to invoke a function using an API.
Event Description
Dedicated APIG triggers are used together with APIG to invoke functions over HTTPS or HTTP. You can map specific API operations (such as GET, POST, and PUT) to the corresponding functions using the custom REST APIs and endpoints of APIG. When you send an HTTPS request to an APIG endpoint, APIG automatically triggers the corresponding function.
Video Tutorial
This video shows how to configure a dedicated APIG trigger and verify the function execution.
As product functions evolve, the GUI may vary. This tutorial is for reference only.
Notes and Constraints
- The regions and runtimes supported for dedicated APIG triggers are subject to the console.
- Dedicated APIG triggers cannot be disabled and can only be deleted.
- The function response for APIG invocation is encapsulated and must contain body(String), statusCode(int), headers(Map), and isBase64Encoded(boolean).
{ "isBase64Encoded": true|false, "statusCode": httpStatusCode, "headers": {"headerName":"headerValue",...}, "body": "..." }isBase64Encoded is valued true by default, indicating that the request body transferred to FunctionGraph is encoded using Base64 and must be decoded for processing.
- The valid payload size of a request body is 4 MB when a dedicated APIG trigger is used.
Prerequisites
- You have created a dedicated APIG gateway. For details, see Creating a Gateway.
- To invoke a function over the public network, enable the public access and configure the required bandwidth when creating an APIG gateway.
- To configure a function to access resources in a VPC in the production environment, select the same VPC when creating an APIG gateway.
- You have created an API group, for example, APIGroup_test. For details, see Creating an API Group.
Creating an APIG (Dedicated) Trigger
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console. In the navigation pane, choose Functions > Function List.
- On the Function List page, click Create Function in the upper right corner.
- Select Create from scratch, configure the following function information, and retain the default values for other parameters.
- Function Name: Enter a function name, for example, apig_demo.
- Enterprise Project: Select default.
- Agency: Select Use no agency.
- Runtime: Select Python 3.12.
- Click Create Function. The function creation is complete, and the function details page is displayed.
- On the Code tab page, copy the following code to the code editing area and click Deploy.
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import json def handler (event, context): body = "<html><title>Functiongraph Demo</title><body><p>Hello, FunctionGraph!</p></body></html>" print(body) return { "statusCode":200, "body":body, "headers": { "Content-Type": "text/html", }, "isBase64Encoded": False } - Choose Configuration > Triggers and click Create Trigger as shown in Figure 1.
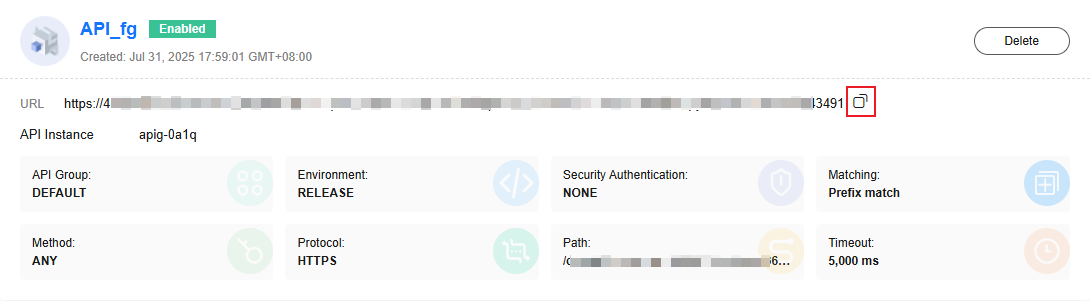
- Set trigger parameters by referring to Table 2.
Table 2 Parameters for creating a dedicated APIG trigger Parameter
Description
Example Value
Trigger Type
Select API Gateway (Dedicated).
API Gateway (Dedicated)
API Instance
APIG gateway. If no gateway is available, click Create API Instance.
apig-fg
API Name
Name of a dedicated APIG trigger.
The name can contain 3 to 64 characters and must start with a letter. Only letters, digits, and underscores (_) are allowed.
For details about API configuration, see Creating an API.
API_apig
API Group
Select an API group. An API group is a collection of APIs. You can manage APIs by API group.
If no group is available, click Create API Group.
APIGroup_test
Environment
The environment where the API is published. An API can be called in different environments, such as production, test, and development environments only when the parameter is set to RELEASE.
If no environment is available, click Create Environment.
RELEASE
Security Authentication
Security authentication mode used by the API.
Options:
- App: AppKey and AppSecret authentication. This mode is of high security and is recommended. For details, see App Authentication.
- IAM: IAM authentication. This mode grants access permissions to IAM users only and is of medium security. For details, see IAM Authentication
- None: No authentication. This mode grants access permissions to all users.
In this example, Security Authentication is set to None. You are advised to enable App or IAM authentication in the production environment.
None
Protocol
Request protocol of the API.
Supported request protocols:
- HTTP: Data is not encrypted during transmission.
- HTTPS: Data is encrypted during transmission. HTTPS is recommended for transmitting important or sensitive data.
- HTTP&HTTPS: Both HTTP and HTTPS protocols are supported.
HTTPS
Path
Enter the API request path.
It is a part of the API access address and is used to specify resource IDs or hierarchy.
The path is case-sensitive. It starts with a slash (/) and contains a maximum of 512 characters. Enclose parameters in braces. For example: /a/{b}. Or use a plus sign (+) to match parameters starting with specific characters. For example: /a/{b+}.
/ttest
Matching
Select a matching mode for the API.
Matching mode of the API. Options:
- Exact match: The request path must be the same as the defined path.
- Prefix match: The request path must start with the defined path.
Prefix match
Method
Request method of the API.
Options: GET, POST, DELETE, PUT, PATCH, HEAD, OPTIONS, and ANY.
ANY indicates that the API can be called using any request method.
ANY
Timeout (ms)
API backend timeout in milliseconds. Range: 1–60,000.
5000
- Click OK.
Invoking the Function
Viewing the Execution Result
- Return to the FunctionGraph console. In the navigation pane, choose Functions > Function List.
- Click a function to go to its details page.
- Choose Monitoring > Logs to query function running logs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot