Creating a DWS Storage-Compute Coupled Cluster
To use Huawei Cloud DWS, create a data warehouse cluster first. When you create a data warehouse cluster, the yearly/monthly billing mode is used by default, which is more favorable than the pay-per-use billing mode. You can customize the computing resources and storage space of the cluster. If you select the pay-per-use mode, nodes will be billed by actual duration of use, with a billing cycle of one hour. This mode is flexible. You can enable or disable the service whenever you like.
This section describes how to create a data warehouse cluster on the DWS console.
Constraints and Limitations
- You are advised not to use clusters with low specifications, such as clusters with 16 GB memory and 4-core vCPUs, in the production environment. Otherwise, resource overload may occur.
- To ensure load balancing and high availability for the cluster and prevent service interruptions, you are not advised to connect services directly to a single CN. Instead, configure load balancing to balance the connection to each CN.
- The DWS clusters under the same account are physically isolated and cannot share data.
- To ensure stable service running, read Before You Start: Performance Management Requirements and Before You Start: High Availability and Reliability Requirements after creating a cluster.
Prerequisites
- Evaluate the flavor of cluster nodes.
You can select the number of nodes by data volume, service load, and performance. More nodes bring you stronger storage and compute capabilities.
When first using DWS, you can create a cluster with a smaller flavor. Then, you can adjust the cluster scale and node flavor based on the data volume and service load changes without interrupting services. For details, see Scaling Out a Cluster.
- Determine the number of available nodes.
The number of available nodes is determined by the product type you select, and there must be at least three available nodes. Otherwise, the system displays a message indicating that the cluster cannot be created.
If you have yearly/monthly nodes that meet service requirements, you are advised to use these nodes first to save costs. You can select Yearly/Monthly for Billing Mode.
If the number of requested nodes, vCPU (cores), or memory (GB) exceed the user's remaining quota, a warning dialog box is displayed, indicating that the quota is insufficient and displaying the detailed remaining quota and the current quota application. You can click Increase quota in the warning dialog box to submit a service ticket and apply for higher node quota. Once approved, we will update your resource quota accordingly and send you a notification. For details about quota operations, see Quotas.
Procedure
- Go to the page for creating a DWS cluster. Configure the DWS cluster information as prompted.
- Configure the parameters in the Basic Configuration and Data Warehouse Configuration areas for the cluster.
- Click Next: Configure Network and configure the parameters in the Network and Others areas.
- Click Next: Configure Advanced Settings and configure the parameters in the Management and Advanced Settings areas.
- Click Next: Confirm.
- Select a billing mode. If you select the yearly/monthly mode, you also need to configure the service duration. For details, see Yearly/Monthly Subscription.
- Click Buy Now. If the billing mode is yearly/monthly billing, click Buy Now. The payment page is displayed.
- After the submission is successful, the creation starts. Click Back to Cluster List. The cluster management page is displayed. The initial status of the cluster is Creating. Cluster creation takes some time. Wait for a while. Clusters in the Available state are ready for use.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Precaution |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Region |
Select the AZ for the cluster nodes to run. |
For more information about regions, visit Regions and Endpoints. |
- |
|
Billing Mode |
Select a billing mode as required. For details, see Billing Description.
|
- |
Yearly/Monthly |
|
AZ |
You can select to create a single-AZ or multi-AZ cluster. For more information, see Regions and AZs. |
|
Single-AZ, AZ 1 |
|
Parameter |
Description |
Precaution |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Version |
Product type. It can be:
|
- |
Coupled storage and compute |
|
Storage Type |
It can be:
|
Local SSD disks do not support disk scale-out. For more information, see Disk Types and Performance. |
- |
|
CPU Architecture |
The CPU architecture includes:
|
- |
- |
|
Node Flavor |
Select the desired node flavor based on service requirements. Each node flavor shows the vCPU, memory, and recommended application scenario. |
|
dws.dc.4xlarge |
|
Hot Storage |
Available storage capacity of each node. |
|
- |
|
Nodes |
Number of nodes in the cluster. The number of nodes ranges from 3 to 256. |
The number of nodes in a new cluster cannot exceed the quota that can be used by a user or 256. Click Increase quota to submit a service ticket and apply for higher node quota if the node quota is insufficient. |
3 |
|
Total |
Total capacity of a cluster. |
The storage capacity of each flavor is the actual database space used for storing data. The displayed storage capacity has deducted the disk space consumed by backups and RAIDs. |
- |
|
Parameter |
Description |
Precaution |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VPC |
Specify a VPC to isolate the cluster's network.
|
|
vpc-dws |
|
Subnet |
VPC subnet. A subnet provides dedicated network resources that are isolated from other networks, improving network security. |
Once a cluster is created, its subnet cannot be changed. To update the subnet, restore the cluster's snapshot into a new cluster. The new cluster will have identical data, and you can adjust the subnet during its creation. |
subnet-dws |
|
Security Group |
VPC security group. A security group restricts access rules to enhance security when DWS and other services access each other.
|
|
Automatic creation |
For how to set the parameters in this area, see Table 4.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Precaution |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
EIP |
Whether users can use a client to connect to a cluster's database over the Internet. The following methods are supported:
|
|
Buy Now |
|
Bandwidth |
When EIP is set to Buy now, you need to specify the bandwidth of the EIP. The value ranges from 1 Mbit/s to 100 Mbit/s. |
- |
50 Mbit/s |
|
ELB |
Whether ELB is bound. With ELB health checks, CN requests of a cluster can be quickly forwarded to normal CNs. If a CN is faulty, the workload can be immediately shifted to a healthy node, minimizing cluster access faults. Currently, ELBs can be bound in the same VPC or across VPCs.
|
Configure load balancing to ensure load balancing and high availability of the cluster and prevent service interruptions. You are not advised to directly connect services to a single CN. |
Specify |
For how to set the parameters in this area, see Table 5.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Precaution |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cluster Name |
Name of the data warehouse cluster. |
Enter 4 to 64 characters. Only letters (case-insensitive), digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed. The name must start with a letter. |
dws-demo |
|
Cluster Version |
Version of the database instance installed in the cluster. The example version number is for reference only. |
- |
- |
|
Default Database |
The default database name of the cluster is gaussdb. |
This name cannot be changed. |
gaussdb |
|
Administrator Account |
Database administrator name. |
The administrator username must:
|
dbadmin |
|
Administrator Password |
Password of the database administrator account. Change the password regularly and keep it secure. |
The password must:
|
- |
|
Confirm Password |
Enter the database administrator password again. |
- |
- |
|
Database Port |
Port used when the client or application connects to the database in the cluster. The port number ranges from 8000 to 30000. |
The database port of a created cluster cannot be changed. You can specify the database port only when creating a cluster. |
8000 |
|
Time Zone |
You can set the time zone for the tenant cluster, including the system OS time zone and cluster data warehouse time zone. |
- |
- |
- Select the enterprise project of the cluster. You can configure this parameter only when the Enterprise Project Management service is enabled. The default value is default.
An enterprise project facilitates project-level management and grouping of cloud resources and users.
You can select the default enterprise project default or other existing enterprise projects. To create an enterprise project, log in to the Enterprise Management console. For details, see the Enterprise Management User Guide.
- Configure advanced parameters. Select Default to keep the default values of the advanced parameters. You can also select Custom to modify the values.
- Backup Device
Set the backup device used by the current cluster. For details about the parameter configuration principles, see Table 6.
Table 6 Automated snapshot parameters Parameter
Description
Backup Device
Select OBS or NFS from the drop-down list.
NFS backup file system address (NFS parameter)
NFS shared IP address. To mount the SFS shared path, enter its IP address. If successful, a mount directory will be created in the /var/chroot/nfsbackup directory of the cluster instance.
- CNs
CNs, or Coordinators, receive access requests from the clients and return the execution results. They also split and distribute tasks to the data nodes (DNs) for parallel execution.
The value ranges from 3 to the number of cluster nodes. The maximum value is 20 and the default value is 3. In a large-scale cluster, you are advised to deploy multiple CNs.
- Tag
A tag is a key-value pair used to identify a cluster. For details about the keys and values, see Table 7. By default, no tag is added to the cluster.
If your organization has configured DWS tag policies, you need to add tags to clusters based on the tag policies. If a tag does not comply with the tag policies, cluster creation may fail. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
For details about tags, see Overview.
Table 7 Tag parameters Parameter
Description
Key
A key must be unique in a given cluster. You can:
- Select a predefined tag key or an existing resource tag key from the drop-down list of the text box. To add a predefined tag, create a predefined tag on TMS and select it from the Key drop-down list. You can click View predefined tags to enter the Predefined Tag page of TMS. Then, click Create Tag to create a predefined tag. For more information, see Creating Predefined Tags in the Tag Management Service User Guide.
- Enter a tag key in the text box. A tag key can contain a maximum of 128 characters. It cannot be an empty string, start with _sys, or start or end with a space.
The value can contain only letters, numbers, spaces, and the following characters: _ . : = + - @
Value
You can:
- Select a predefined tag value or resource tag value from the drop-down list of the text box.
- Enter a tag value in the text box. A tag value can contain a maximum of 255 characters, which can be an empty string. It cannot start or end with a space.
The value can contain only letters, numbers, spaces, and the following characters: _ . : = + - @
- Encrypt DataStore
If this function is enabled, Key Management Service (KMS) encrypts the cluster and the cluster's snapshot data.
If you have not created an agency with the KMS Administrator permissions, the Create Delegation dialog box is displayed when you enable database encryption for the first time. Click OK to grant DWS the permissions to access KMS. Select the created KMS key from the KMS Key Name drop-down list. If no KMS key is available, log in to KMS and create one. For details, see Data Encryption Workshop User Guide.

- Only users with the Tenant Admin permission can view and toggle the Encrypt DataStore switch.
- By default, only Huawei Cloud accounts or users with Security Administrator permissions can query and create agencies. IAM users under an account do not have the permission to query or create agencies by default. Contact a user with that permission and complete the authorization on the current page. For details, see Allowing DWS to Manage Resources.
- The database encryption function cannot be disabled once it is enabled.
- After Encrypt DataStore is enabled, the key cannot be disabled, deleted, or frozen when being used. Otherwise, the cluster becomes abnormal and the database becomes unavailable.
- After database encryption is enabled, you cannot use open APIs to restore created snapshots.
- Method 1: Select a key name. You can create a resource share to share KMS resources with other members. After accepting the sharing invitation, members can select the shared KMS resource from the key source.
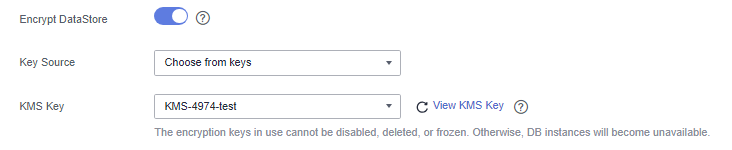
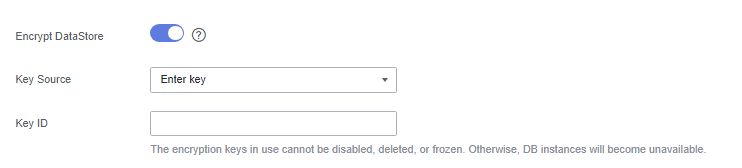
- Method 2: Enter the key ID. Enter the key ID used for authorizing the current tenant. For details, see Viewing a CMK.
When you grant permissions on the Creating a Grant page, the authorized object must be an account instead of a user. The authorized operations must at least contain Querying key details, Encrypting data, and Decrypting data.
- Backup Device
- Specify whether to enable the IPv6 dual stack for the cluster. If this function is enabled, a client or application can connect to the database using an IPv6 address.
To enable IPv6, the following conditions must be met:
- The subnet configured in Table 3 is an IPv6 dual-stack subnet.
- The cluster supports IPv6 addresses and should have at least three NICs.
- The cluster version must be 8.2.1.210 or later.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Required Duration (Yearly/Monthly) |
Configure the required duration. You get a greater discount if you purchase a longer period. Price is displayed at the bottom of the page for your reference. You can click Pricing details to view the detailed price. |
|
Auto-renewal (Yearly/Monthly) |
|
Handling the Cluster Creation Failure
If a cluster fails to be created, go to the DWS console and choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters to view the cluster status and the cause of failure.
Viewing the cause of creation failure
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters.
- In the cluster list, locate the cluster whose Cluster Status is Creation failed.
- Click View Details in the Cluster Status column to view the cause of the cluster creation failure.
If the fault persists, contact technical support.
Deleting a cluster that fails to be created
You can delete a cluster that fails to be created if you do not need it. Before deletion, check the cause of creation failure.
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters.
- In the cluster list, locate the row containing the failed cluster to be deleted, and choose .
- In the displayed dialog box, confirm the deletion.
- After confirming that the information is correct, enter DELETE or click Auto Enter and click OK to delete the cluster. The cluster status in the cluster list will change to Deleting and the cluster deletion progress will be displayed.
If the cluster to be deleted uses an automatically created security group that is not used by other clusters, the security group is automatically deleted when the cluster is deleted.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot







