Using DWS
DWS is an online data processing database that uses the Huawei Cloud infrastructure to provide scalable, fully managed, and out-of-the-box analytic database service, freeing you from complex database management and monitoring. It is a native cloud service based on the Huawei converged data warehouse GaussDB, and is fully compatible with the standard ANSI SQL 99 and SQL 2003, as well as the PostgreSQL and Oracle ecosystems. DWS provides competitive solutions for PB-level big data analysis in various industries.
DWS provides an easy-to-use management console, allowing you to quickly create clusters and easily manage data warehouses.
Procedure Description
|
Process |
Task |
Description |
Operation Instruction |
|---|---|---|---|
|
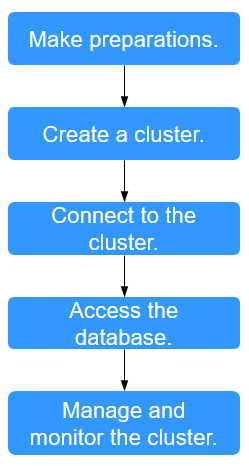
Make preparations. |
- |
Before using DWS, you need to apply for a Cloud account. |
|
|
Create a cluster. |
- |
Create a cluster before using DWS to execute data analysis tasks. A DWS cluster contains nodes in the same subnet. These nodes jointly provide services. During cluster creation, the system creates a default database. |
|
|
Connect to the cluster. |
- |
After the DWS cluster is created, use the SQL client tool or a third-party driver such as JDBC or ODBC to connect to the database in the cluster. You can download the SQL client tool and JDBC/ODBC driver on the Client Connections page of the DWS console. |
|
|
Access the database. |
- |
After connecting to the cluster, you can create and manage databases, manage users and permissions, import and export data, and query and analyze data. |
|
|
Manage and monitor the cluster. |
Cluster management |
View the cluster status, modify cluster configurations, add cluster tags, and scale out, restart, and delete the cluster. |
|
|
Snapshot management |
Create snapshots to back up and restore the cluster. |
||
|
O&M and monitoring |
View the running status and performance of the cluster through cluster monitoring, log auditing, event notification, and alarm management. |
||
|
Scaling and specification change |
|
||
|
Cluster upgrade |
Cluster 8.1.1 and later versions allow users to deliver cluster upgrade operations on the console. |
||
|
Resource load management |
DWS provides the resource management function. You can put resources (CPU, memory, I/O, and storage space) into different resource pools, which are isolated from each other. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





