Managing Indoor Air Conditioners Using Custom Topics
Scenarios
Custom topics apply to MQTT devices connected to IoTDA. Topics for message reporting and message delivery can be customized. Applications can implement different service logic processing based on topics. Custom topics can also be used in the scenario where a device cannot report properties or receive delivered commands defined in the product model.
In this example, an application receives data reported by a device and determines whether to turn on or off the indoor air conditioner.
Prerequisites
- You have registered a Huawei ID and enabled Huawei Cloud services.
- You have subscribed to IoTDA.
- You have created an MQTT product, developed a product model, and registered a device on the IoTDA console. For details, see Products, Developing a Product Model Online, Registering an Individual Device, or Registering a Batch of Devices.
- The connection between the device and platform has been established. For details, see Device Connection Authentication.
Customizing a Topic
For details, see Custom Topic Communications.
Reporting MQTT Messages
- Visit the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices, locate the target device, and click View to access its details page.
- Click the Message Trace tab, click Start Trace, and set the trace duration as required.
- Use the MQTT.fx simulator to simulate a device to report a custom topic message. For details, see Quick Device Access.
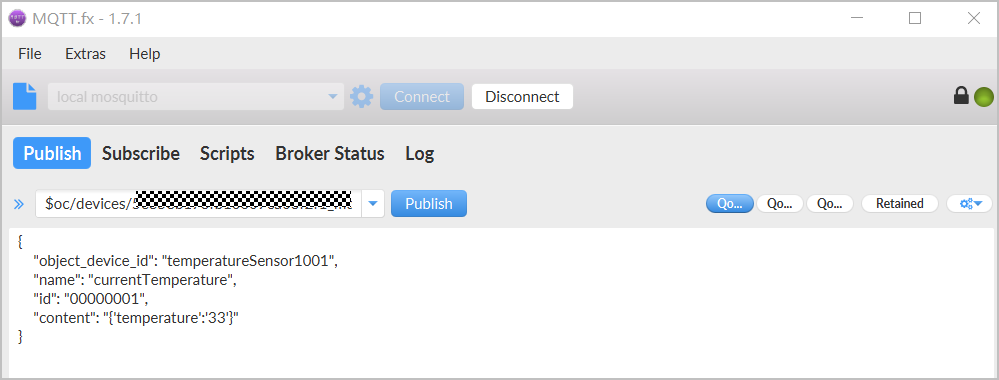
For devices connected using the IoT Device SDK or native MQTT protocol, you need to set the name of the custom topic reported by the device in the device program.
- On the Message Trace page, view the custom topic messages reported by the device.
Figure 1 Viewing message trace

- An application obtains the custom topic message reported by the device through data forwarding. For details, see Data Forwarding. You can also refer to Forwarding Device Data to OBS for Long-Term Storage.
Delivering MQTT Messages
In this example, the Postman is used to deliver an instruction for starting the indoor air conditioner.
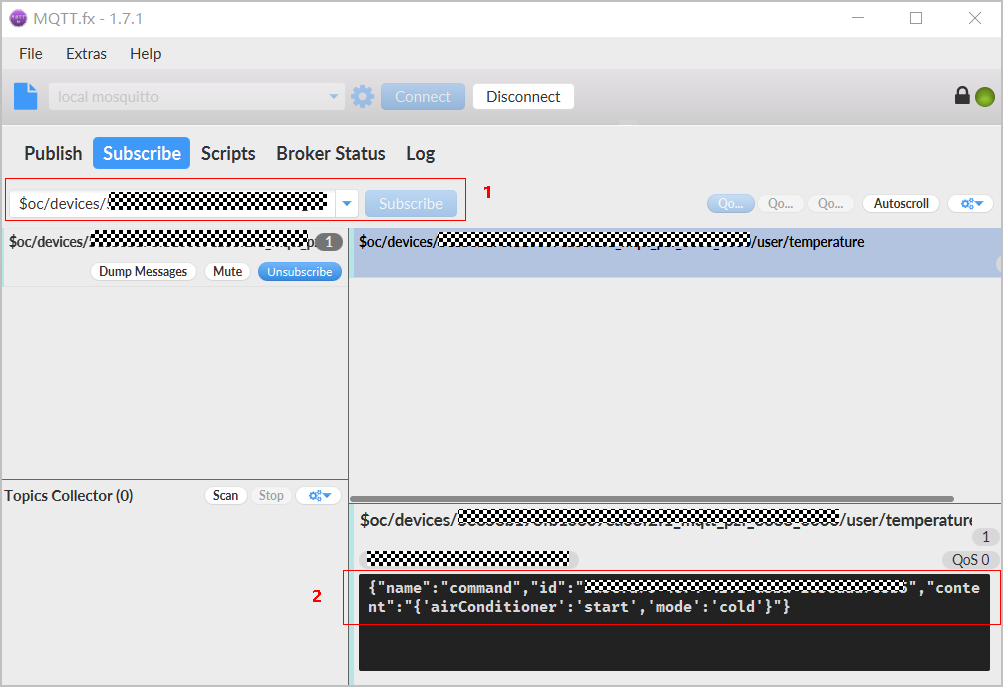
- Use the MQTT.fx simulator to subscribe to a custom topic.
- Ensure that the device operation permissions contain the subscription function when you create a custom topic. For details, see Custom Topic Communications.
- For devices connected using the IoT Device SDK or native MQTT protocol, you need to set the name of the custom topic to which the device subscribes in the device program.
- Use the Postman to simulate the application to call the API Delivering a Message to a Device to deliver a command for starting the indoor air conditioner.
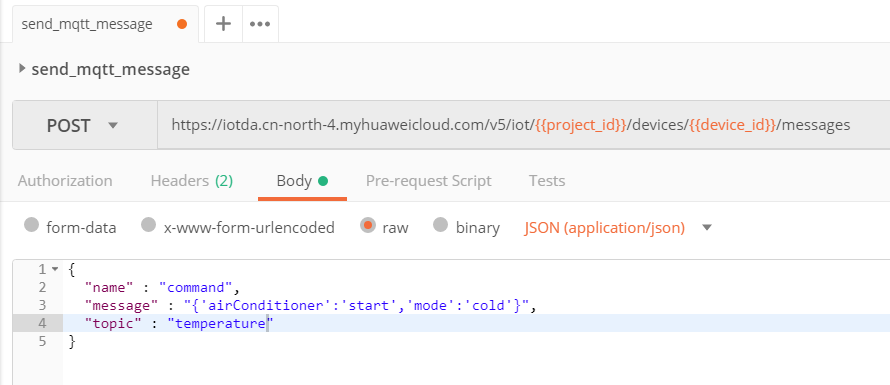
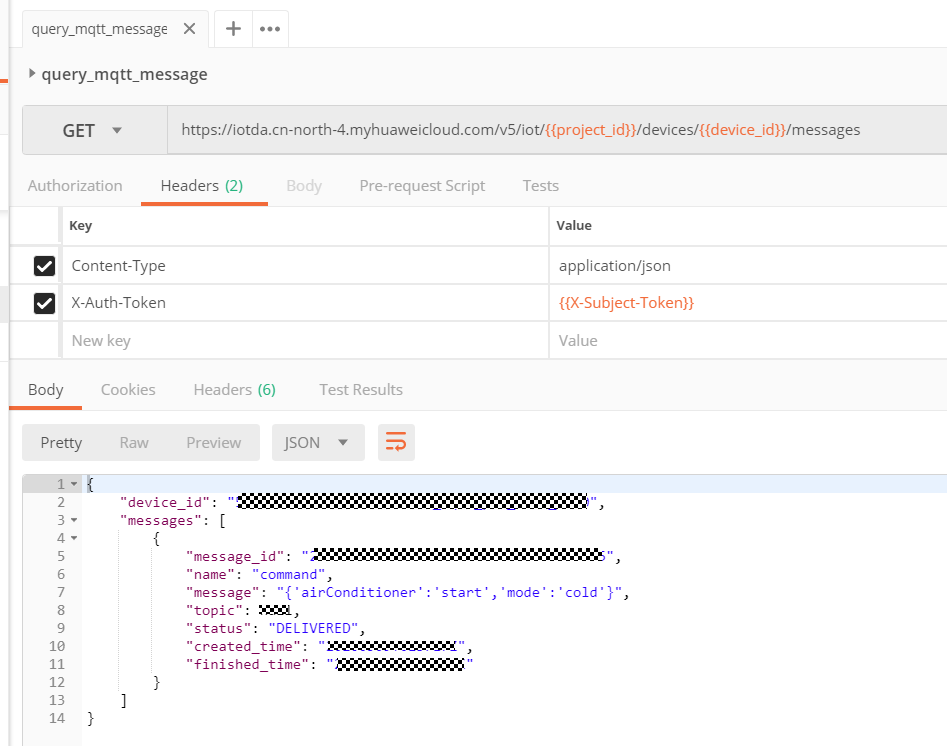
- Call the API Querying Device Messages to check whether the command is delivered. If the command is delivered, the indoor air conditioner will be started.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot