Relational Database Datasets
Datasets created from relational databases such as Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, GaussDB, or PostgreSQL.
Prerequisites
The data source to be connected has been created. For details, see Relational Database Data Sources.
Constraints
When configuring data in SQL mode, if the SQL statement contains keywords that match database field names, format them according to these rules:
- MySQL: Use backquotes (`) around keywords.
Common keywords: value, data, desc, day, all, add. For more, see MySQL 5.7 Official Reserved Words and Keywords and MySQL 8.0 Official Reserved Words and Keywords.
- PostgreSQL/GaussDB: Use double quotation marks (") around keywords.
Common keywords: value, user, date, desc, day, and all. For more, see SQL Key Words.
- SQL Server: Enclose keywords in square brackets ([]).
Common keywords: value, user, date, desc, day, and all. For more, see Reserved Keywords (Transact-SQL).
- Oracle: Use double quotation marks (") around keywords.
Common keywords: value, user, date, desc, day, and all. For more, see Oracle SQL Reserved Words.
Creating a Dataset from Relational Database
- Log in to Huawei Cloud Astro Canvas by referring to Logging In to Huawei Cloud Astro Canvas.
- Choose Data Center from the main menu.
- Choose Datasets > All in the navigation pane.
- On the Dataset Management page, click Create.
- Set the dataset name, specify the data type, data source, and folder, and click Save.
Figure 1 Creating a dataset
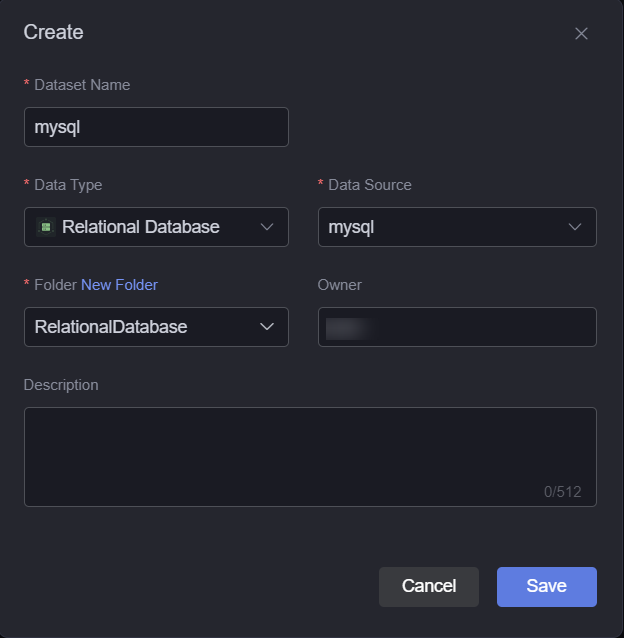
- Dataset Name: A dataset is identified by its name. The name contains 1 to 60 characters, including letters, digits, and underscores (_).
- Data Type: Select Relational Database.
- Data Source: Select the data source created in Relational Database Data Sources.
- Folder: Set the folder for storing the dataset. You can select the folder created in (Optional) Creating a Folder or click New Folder.
- Owner: Creator of the dataset.
- Description: Description of the new dataset, which is usually the function of the dataset.
- Set dataset parameters.
Figure 2 Setting dataset parameters for a relational database
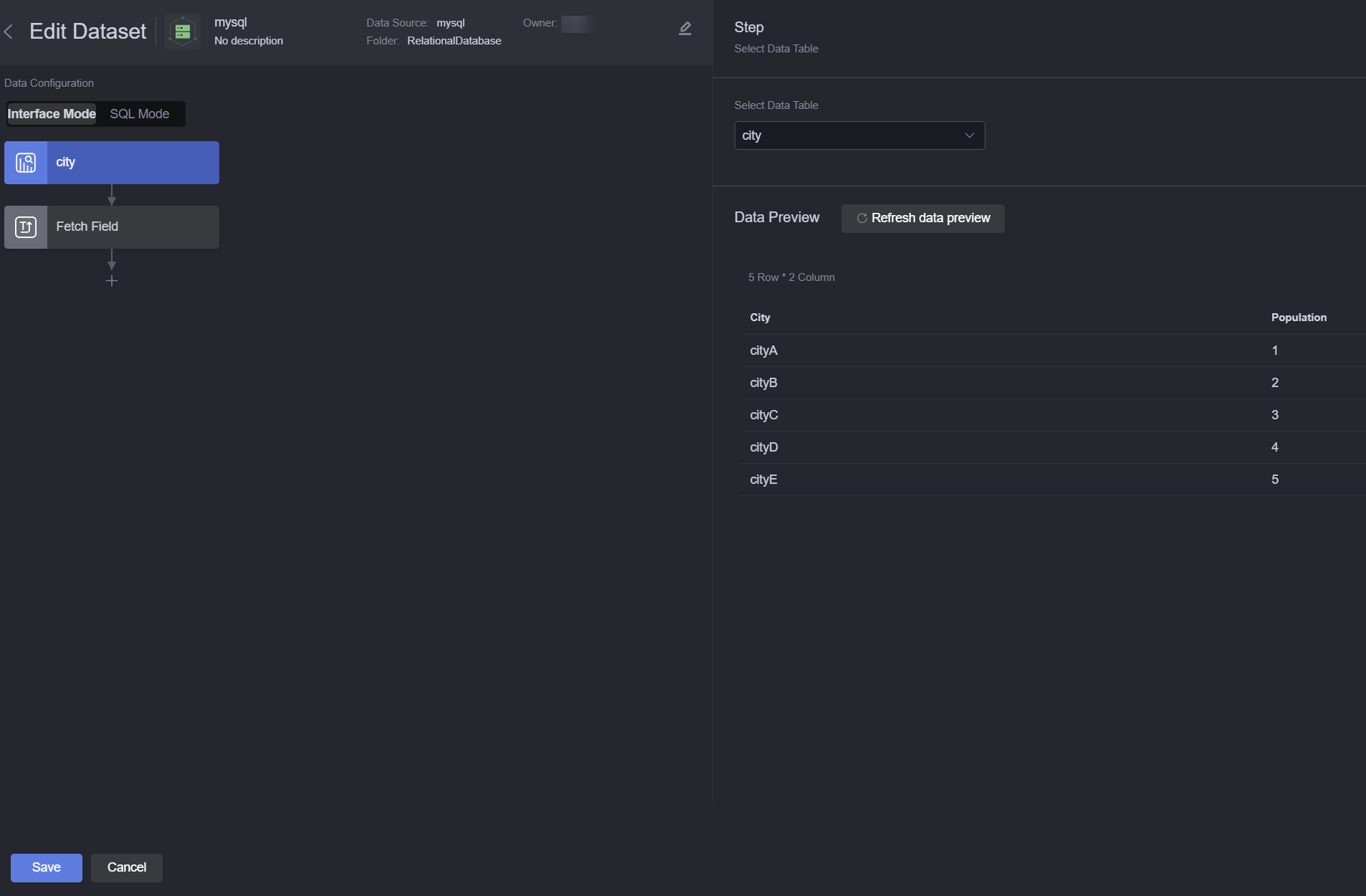
- Interface Mode
In this mode, you need to select a specific data table and fetch field. You can click + to add grouping fields, set filter criteria for displayed data, sort the displayed results in ascending or descending order based on a field, and limit the total number of returned records. For example, select the table city and set fetch fields as following:
- Fetch Field: Set fields to be returned and field alias.
Figure 3 Selecting fetch fields
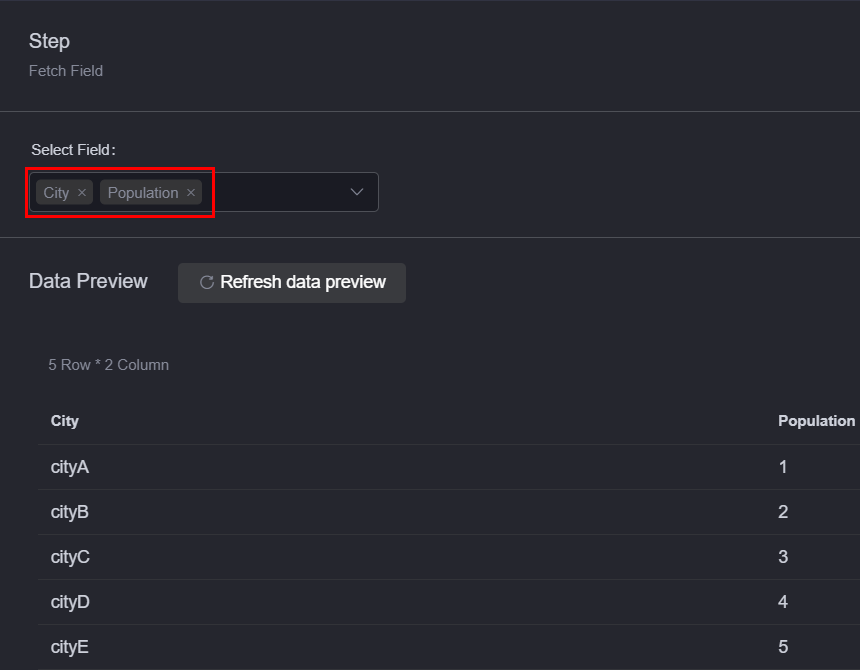
- Group Field: Group by fields. Click + to add this parameter.
- Filter: Set the filter criteria for displayed data. Click + to add this parameter.
- Sort: Sort the displayed results in ascending or descending order based on a field. Click + to add this parameter.
- Limit: Set the number of rows of returned data. Click + to add this parameter.
- Fetch Field: Set fields to be returned and field alias.
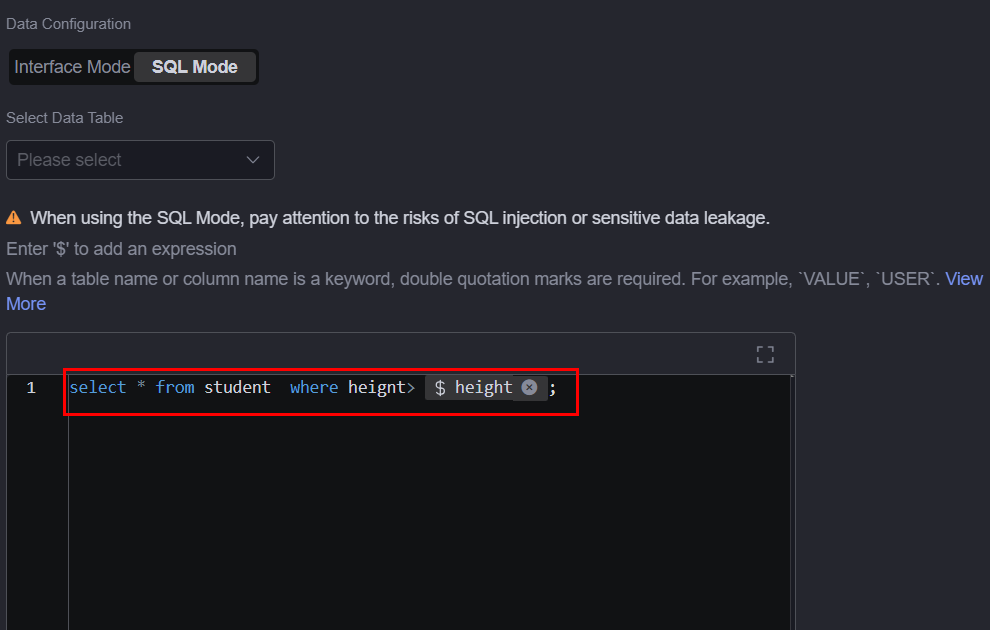
- SQL Mode
In this mode, you need to enter SQL statements. You can select data tables and set variables. The variable definition format is ${variable name}, for example, see Figure 4. You need to customize SQL statements (starting with select or with only). If the returned data field is a variable, an alias must be specified. In addition, the sample data must use an alias.
select * from student where height> ${height};When creating a data source from relational database, if you select GaussDB or PostgreSQL for Database Type, you can select data tables from the specified schema. If no schema is specified, data is obtained from public database tables by default. pg_catalog indicates the specified schema, and pg_index indicates the table in the database.select * from pg_catalog."pg_index"
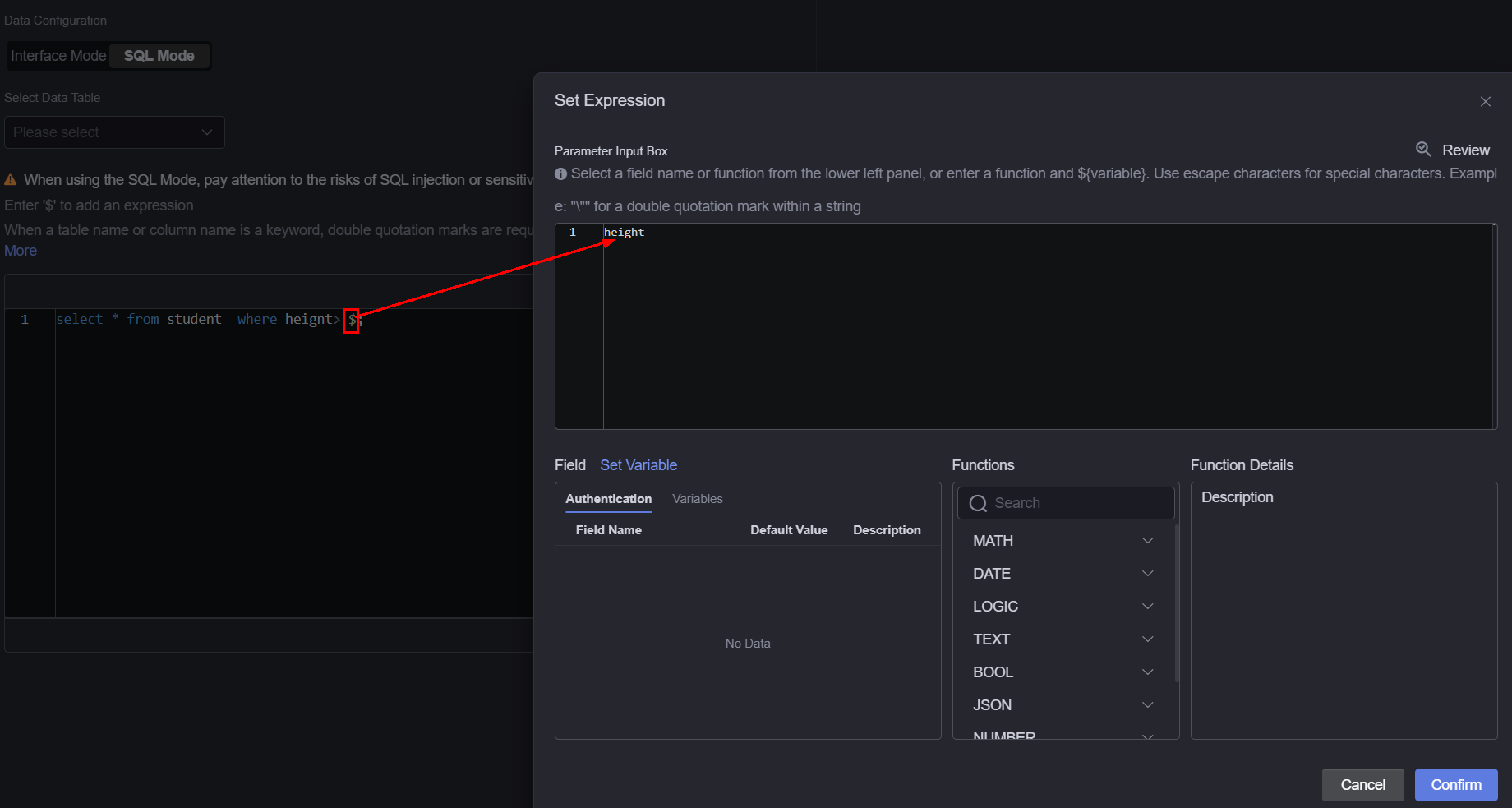
When customizing SQL statements, you can enter $ to access the expression setting page. On the displayed page, you can select a field or function from the left pane or enter a function, for example, see Figure 5.
- Interface Mode
- Click Save. The dataset is created.
Using the Dataset in Widgets
- Return to the Projects page.
- Go to the development page and drag required widgets (for example, basic bar chart) to the canvas.
Figure 6 Dragging a basic bar chart widget to the canvas
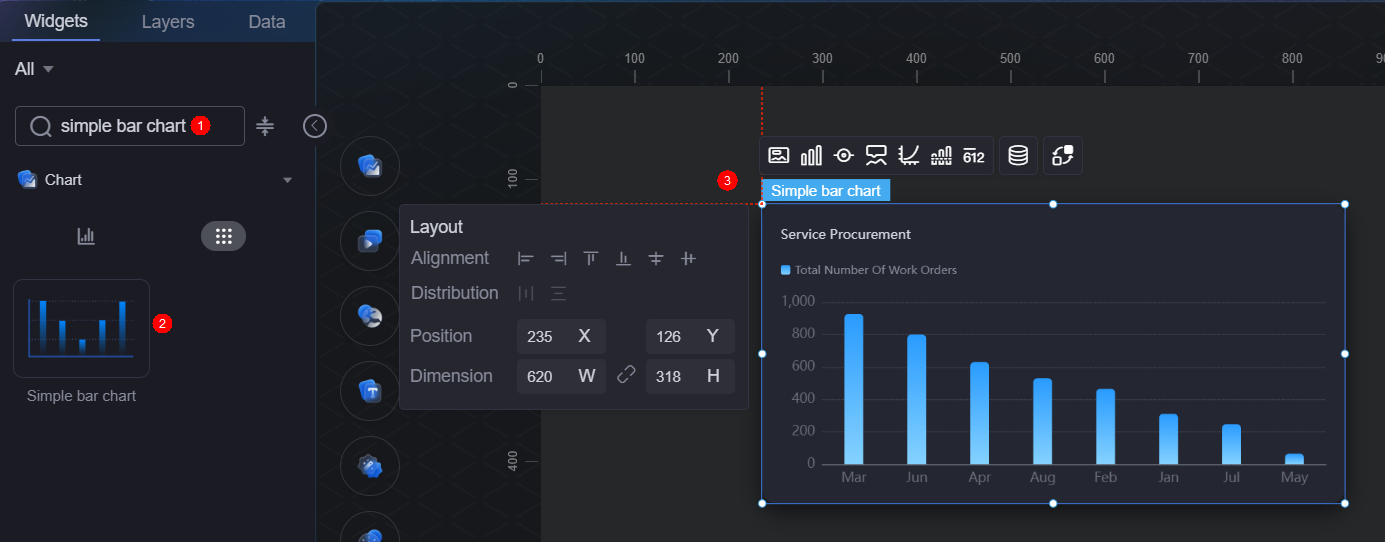
- Select the widget and click
 .
. - Select Dataset from the Data Type drop-down list and select the dataset created in Creating a Dataset from Relational Database.
- Set global variables.
Global variables can be regarded as parameter variables and used to control parameter transfer between widgets for interactions such as diagram and table association and field customization.
- In Widget Preview, select the form fields to be displayed by dragging them from the left column to the right column, and click Save.
Figure 7 Dragging a field to the corresponding axis
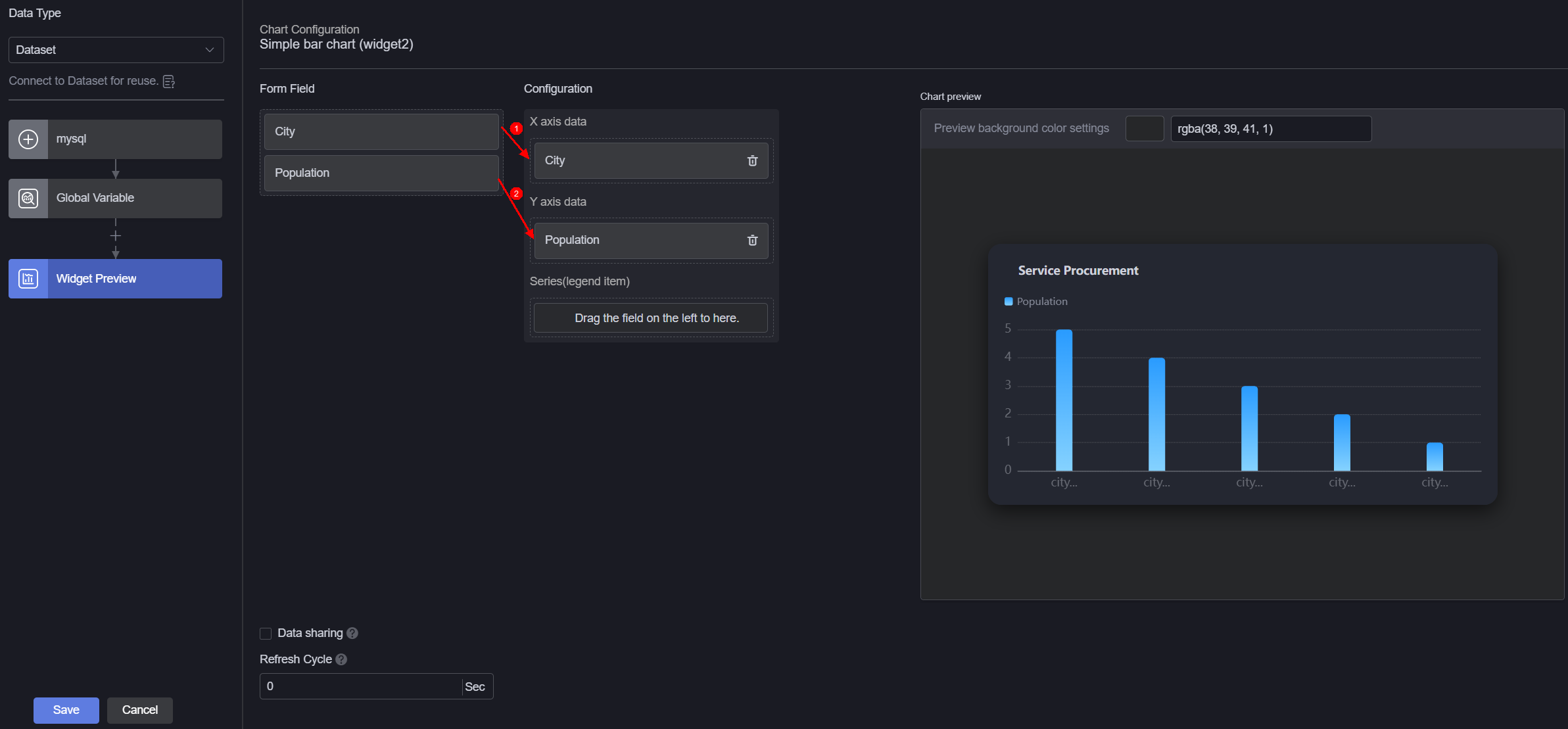
- Form field: Data from relational database recorded in section Creating a Dataset from Relational Database.
- Configuration: Drag the required fields from the form field area to the X-axis data, Y-axis data, or series.
- Refresh cycle: The interval for obtaining data from the relational database. Default is 0, meaning the data is obtained only once.
- Data sharing: When enabled, multiple widgets calling the same relational database request will share the result data.
- Select the bar chart widget, click
 , and set the title to "Population Of Cities In Province N (Ten Million)".
Figure 8 Setting the chart title
, and set the title to "Population Of Cities In Province N (Ten Million)".
Figure 8 Setting the chart title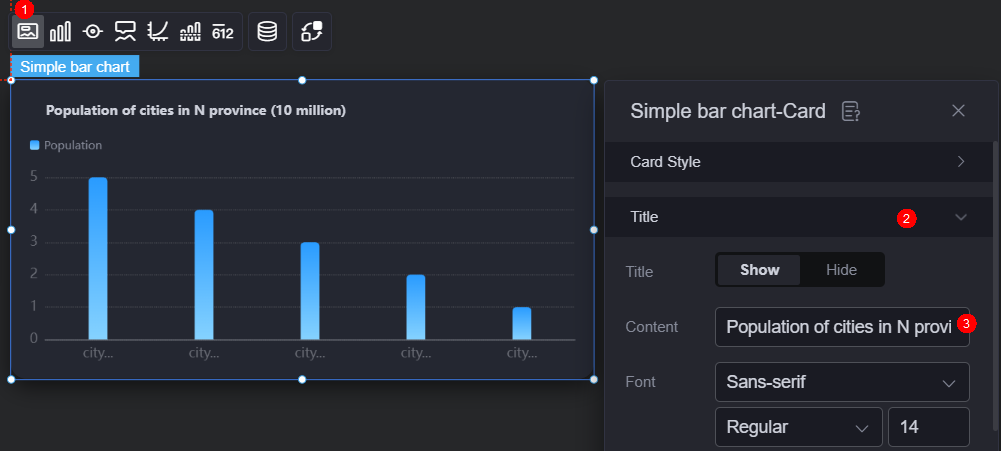
- Click
 in the upper part of the page to save the settings.
in the upper part of the page to save the settings. - Click
 to preview.
to preview.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot