Viewing Real-Time SQL Records of DWS
You can check the real-time information about all queries and sessions running in the cluster.

- Real-time query is supported only in clusters of version 8.1.2 and later.
- To enable real-time query monitoring, choose Monitoring Settings. On the Monitoring Collection page, enable Real-Time Query Monitoring. For details, see Monitoring Collection. Exercise caution when enabling this as it may generate a large amount of data.
Going to the Real-time Query Page
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters and locate the cluster to be monitored.
- In the Operation column of the target cluster, click Monitoring Panel.
- In the navigation pane, choose Monitoring > Queries.
Prerequisites
You need to set GUC parameters before viewing data on the monitoring page. If GUC parameters are not set, real-time or historical query may be unavailable. However, if this parameter is set, the cluster performance may deteriorate. Therefore, you need to balance the settings of related parameters. The following table lists the recommended GUC parameter settings. For how to modify parameters, see Modifying GUC Parameters of the DWS Cluster. For details about the parameters, see Setting GUC Parameters.
|
GUC Parameter |
CN Configuration |
DN Configuration |
|---|---|---|
|
max_active_statements |
10 |
10 |
|
enable_resource_track |
on |
on |
|
resource_track_level |
query |
query |
|
resource_track_cost |
0 |
0 |
|
resource_track_duration |
60 |
60 |
|
enable_resource_record |
on |
on |
|
session_statistics_memory |
1,000 MB |
1,000 MB |
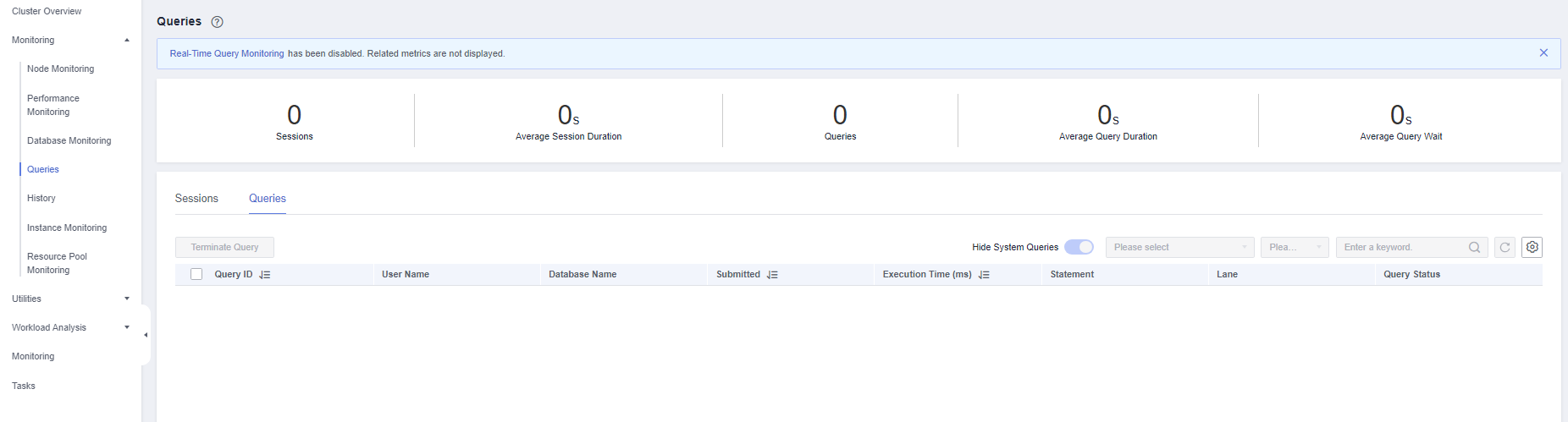
Querying Information
You can view the queries statistics, the number of sessions, average session duration (time of all session connections divided by the number of sessions), number of queries, average query duration, and average query waiting time.
Checking Live Sessions
On the Sessions page, you can browse the real-time information about all running queries. You can click the setting button in the upper right corner of the list to select the metrics to be displayed in the list. For details about the metrics, see Table 2.
- You can click a session ID to view the queries in the current session. For details, see Viewing Real-time Query Monitoring Details.
- To terminate a session, select the session, click Terminate a Session, and confirm your operation.
- If you want to terminate all idle sessions, click Clear Idle Sessions.
- The fine-grained permission control function is added. Only users with the operate permission are able to terminate sessions. For users with the read-only permission, the Terminate a Session button is grayed out.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Monitoring Interval (Raw Data) |
|---|---|---|
|
Session ID |
ID of a session |
180s |
|
Username |
Database username |
180s |
|
Session Duration (s) |
Session duration |
180s |
|
Application Name |
User application name |
180s |
|
QueryBand |
Job type, which can be set through GUC parameter query_band and is null string by default. |
180s |
|
Client IP Address |
IP address of the client connected to the backend. A null value suggests a Unix socket connection or an internal server process, such as autovacuum. |
180s |
|
Connected CN |
CN to which a session is connected |
180s |
|
Session Status |
Session status. The options are as follows:
|
180s |
|
Start Time |
Start time of a session |
180s |
|
Lock Mode |
Lock mode |
180s |
|
Lock Holding Status |
Whether to hold a lock when there are lock waits. Value true means to hold a lock. |
180s |
|
Locked Object |
Object that a lock waits for |
180s |
|
Query SQL |
SQL query statement |
180s |
|
Lock Wait |
Whether the backend is currently waiting on a lock. If yes, the value is true. |
180s |
|
Current Query Duration |
Actual execution duration of the statements by now |
180s |
|
Current Query Start Time |
Time when the statement starts to be executed |
180s |
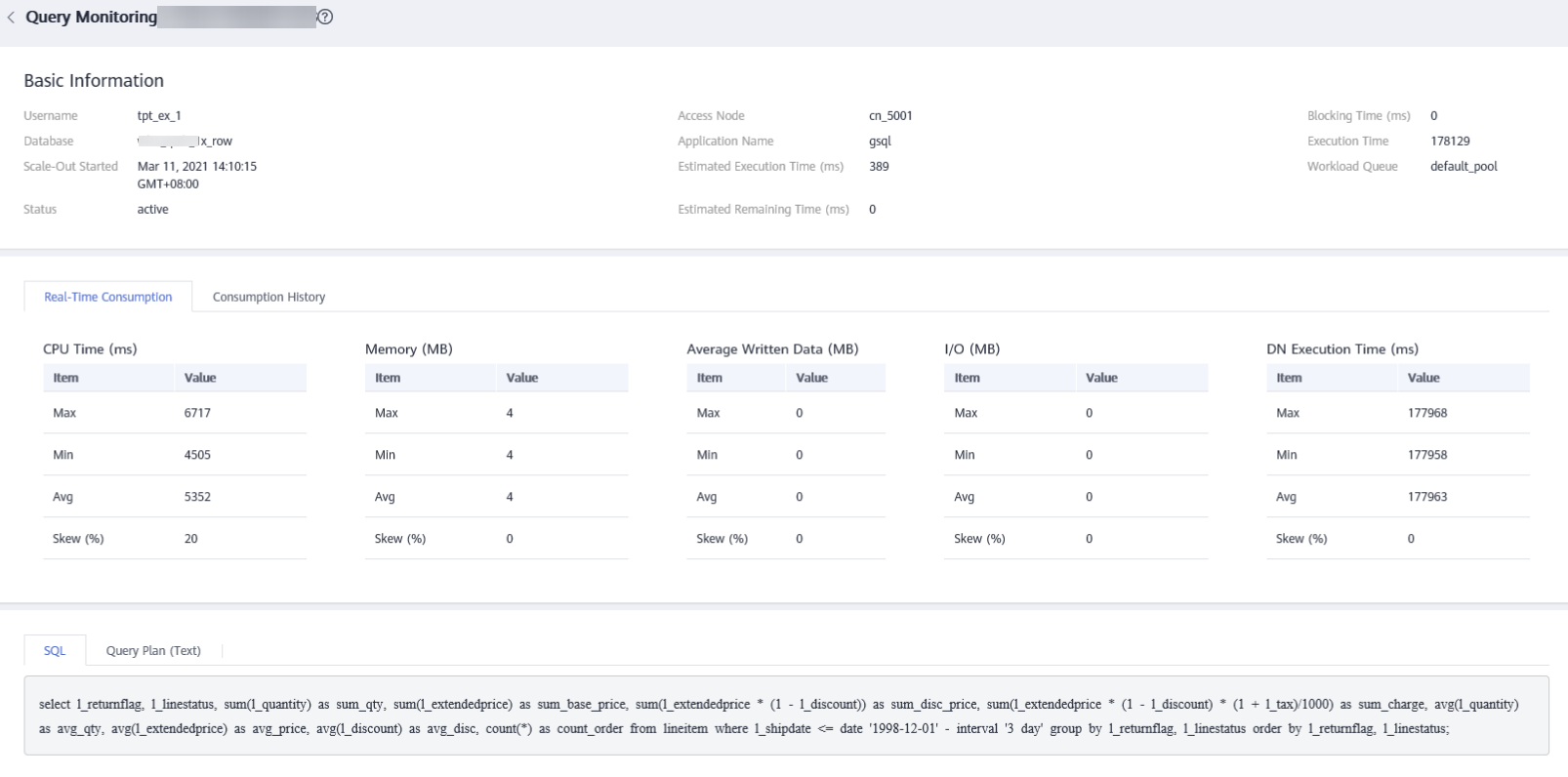
Checking Real-time Queries
In the real-time query area, you can view details on all queries that are currently active in the cluster during a specific time period. To customize the metrics displayed in the list, click the settings button in the top right corner. For details about the metrics, see Table 3.
- You can click a query ID to view the monitoring details. However, details cannot be displayed for queries whose ID is 0. Query 0 indicates that an exception occurs during the query.
- To terminate a query, select the query, click Terminate Query, and confirm your operation.
- The fine-grained permission control function is added. Only users with the operate permission are able to terminate queries. For users with the read-only permission, the Terminate Query button is grayed out.
- The fast and slow lanes are selected based on the cost in the execution plan. If the optimizer estimates that the memory usage of a statement is greater than 32 MB, the statement enters the slow lane. Otherwise, the statement enters the fast lane.
|
Metric Name |
Description |
Monitoring Interval (Raw Data) |
|---|---|---|
|
Query ID |
Internal query_ID used for statement execution |
60s |
|
Username |
Username used for connecting to the backend |
60s |
|
Application Name |
Name of the application that is connected to the backend |
60s |
|
Database Name |
Name of the database |
60s |
|
Resource Pool |
Resource pool used by the user |
60s |
|
Submission Time |
Time when a query statement is submitted |
60s |
|
Blocking Time (ms) |
Time when a query statement is blocked |
60s |
|
Execution Time (ms) |
Time when a query statement is executed |
60s |
|
Min. CPU Time (ms) |
Minimum CPU time of a statement across all DNs |
60s |
|
Max. CPU Time (ms) |
Minimum CPU time of a statement across all DNs |
60s |
|
CPU Time (ms) |
Total CPU time of a statement across all DNs. |
60s |
|
CPU Time Skew (%) |
CPU time skew of a statement among DNs. |
60s |
|
DN Spill Info |
Statement spill information on all DNs |
60s |
|
Min. DN Data Spill (MB) |
Minimum spilled data among all DNs when a spill occurs. The default value is 0. |
60s |
|
Max. DN Data Spill (MB) |
Maximum spilled data among all DNs when a spill occurs. The default value is 0. |
60s |
|
Average Spill to Disk (MB) |
Average spilled data among all DNs when a spill occurs. The default value is 0. |
60s |
|
DN Spill Skew |
DN spill skew when a spill occurs |
60s |
|
Statement |
Statement executed |
60s |
|
Connected CN |
CN that is connected |
60s |
|
Client IP Address |
IP address of the client connected to the backend. A null value suggests a Unix socket connection or an internal server process, such as autovacuum. |
60s |
|
Lane |
Fast or slow lane |
60s |
|
Query Status |
Here are the different query statuses:
|
60s |
|
Session ID |
ID of a session |
60s |
|
Queuing Status |
Queuing status |
60s |
|
Task Type |
Job type, which can be set using the guc parameter query_band. The default value is a null string. |
60s |
|
Task Name |
Job name |
60s |
|
Instance |
Task instance |
60s |
|
Host Name |
Host name of the connected client, as reported by a reverse DNS lookup of client_addr. This column will only be non-null for IP connections, and only when log_hostname is enabled. |
60s |
|
TCP Port |
TCP port number used by the client to communicate with the backend. If the Unix socket is used, the value is -1. |
60s |
|
Waiting |
Whether the query waits |
60s |
|
Estimated Execution Time (ms) |
Estimated execution time of the statement. |
60s |
|
Estimated Time Remaining (ms) |
Estimated remaining execution time of the statement |
60s |
|
cgroup |
Cgroup used by the statement |
60s |
|
Min. Peak DN Memory (MB) |
Minimum memory peak of a statement across all DNs. |
60s |
|
Max. Peak DN Memory (MB) |
Maximum memory peak of a statement across all DNs. |
60s |
|
Average Memory Usage (MB) |
Average memory usage during statement execution. |
60s |
|
DN Memory Usage Skew |
Memory usage skew of a statement among DNs. |
60s |
|
Estimated Memory Usage (MB) |
Estimated memory used by the statement. |
60s |
|
Min. DN Execution Time (ms) |
Minimum execution time of a statement across all DNs. |
60s |
|
Max. DN Execution Time (ms) |
Maximum execution time of a statement across all DNs. |
60s |
|
Average DN Execution Time (ms) |
Average execution time of a statement across all DNs. |
60s |
|
DN Execution Time Skew |
Execution time skew of a statement among DNs. |
60s |
|
Alarms |
Alarms related to SQL self-diagnosis tuning |
60s |
|
Average Peak IOPS on DN (unit: IOPS for column storage; 10,000 IOPS for row storage) |
Average peak IOPS of the statement across all DNs |
60s |
|
DN I/O Skew |
I/O skew of a statement among DNs. |
60s |
|
Statement Status |
Real-time running status of the current query statement. The value can be active, idle, idleintransaction, idleintransaction (aborted), fastpathfunctioncall, or disabled. |
60s |
|
Statement Attribute |
Statement attribute (ordinary, simple, complicated, or internal). |
60s |
|
Logical Cluster |
Logical cluster of the user running the statement |
60s |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot