Java Demo Usage Guide
Overview
This topic uses Java as an example to describe how to connect a device to the platform over MQTTS or MQTT and how to use platform APIs to report properties and subscribe to a topic for receiving commands.
The code snippets in this document are only examples and are for trial use only. To put them into commercial use, obtain the IoT Device SDKs of the corresponding language for integration by referring to Obtaining Resources.
Prerequisites
- You have obtained the device access address from the IoTDA console. For details about how to obtain the address, see Platform Connection Information.
- You have created a product and a device on the IoTDA console. For details, see Creating a Product, Registering an Individual Device, and Registering a Batch of Devices.
Preparations
Installing IntelliJ IDEA
- Go to the IntelliJ IDEA website to download and install a desired version. The following uses Windows 64-bit IntelliJ IDEA 2019.2.3 Ultimate as an example.

- After the download is complete, run the installation file and install IntelliJ IDEA as prompted.
Importing Sample Code
- Download the Java demo.
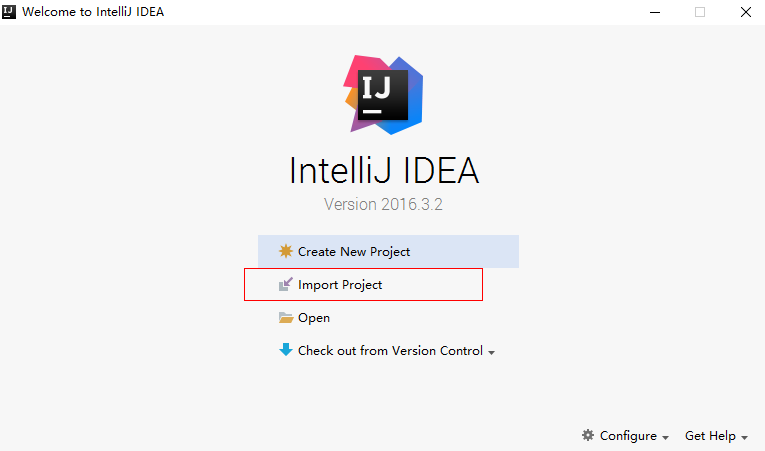
- Open the IDEA developer tool and click Import Project.
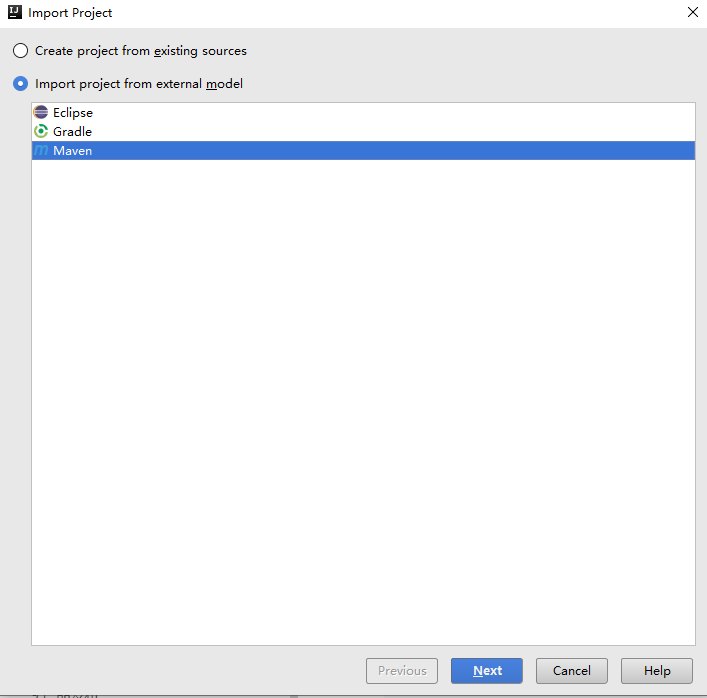
- Select the downloaded Java demo and click Next.
- Import the sample code.

Establishing a Connection
To connect a device or gateway to the platform, upload the device information to bind the device or gateway to the platform.
- Before establishing a connection, modify the following parameters:
1 2 3 4 5
// MQTT connection address of the platform (Replace it with the domain name of the IoT platform that the device is connected to.) static String serverIp = "xxx.myhuaweicloud.com"; // Device ID and secret obtained during device registration (Replace them with the actual values.) static String deviceId = "722cb****************"; static String secret = "******";
- serverIp indicates the device connection address of the platform. To obtain this address, see Platform Connection Information. (After obtaining the domain name, run the ping Domain name command in the CLI to obtain the corresponding IP address.)
- deviceId and secret indicate the device ID and secret, which can be obtained after the device is registered.
- Use MqttClient to set up a connection. The recommended heartbeat interval for MQTT connections is 120 seconds. For details, see Constraints.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
MqttConnectOptions options = new MqttConnectOptions(); options.setCleanSession(false); options.setKeepAliveInterval(120); // Set the heartbeat interval from 30 to 1200 seconds. options.setConnectionTimeout(5000); options.setAutomaticReconnect(true); options.setUserName(deviceId); options.setPassword(getPassword().toCharArray()); client = new MqttAsyncClient(url, getClientId(), new MemoryPersistence()); client.setCallback(callback);
Port 1883 is a non-encrypted MQTT access port, and port 8883 is an encrypted MQTTS access port (that uses SSL to load a certificate).
1 2 3 4 5
if (isSSL) { url = "ssl://" + serverIp + ":" + 8883; // MQTTS connection } else { url = "tcp://" + serverIp + ":" + 1883; // MQTT connection }
To establish an MQTTS connection, load the SSL certificate of the server and add the SocketFactory parameter. The DigiCertGlobalRootCA.jks file is stored in the resources directory of the demo. It is used by the device to verify the platform identity when the device connects to the platform. You can download the certificate file using the link provided in Certificates.1options.setSocketFactory(getOptionSocketFactory(MqttDemo.class.getClassLoader().getResource("DigiCertGlobalRootCA.jks").getPath()));
- Call client.connect(options, null, new IMqttActionListener()) to initiate a connection. The MqttConnectOptions parameter is passed.
1client.connect(options, null, new IMqttActionListener()
- The password passed by calling options.setPassword() is encrypted during creation of MqttConnectOptions. getPassword() is used to obtain the encrypted password.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
public static String getPassword() { return sha256_mac(secret, getTimeStamp()); } /* Call the SHA-256 algorithm for hash calculation. */ public static String sha256_mac(String message, String tStamp) { String passWord = null; try { Mac sha256_HMAC = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256"); SecretKeySpec secret_key = new SecretKeySpec(tStamp.getBytes(), "HmacSHA256"); sha256_HMAC.init(secret_key);byte[] bytes = sha256_HMAC.doFinal(message.getBytes()); passWord = byteArrayToHexString(bytes); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return passWord;
- After the connection is established, the device becomes online.
Figure 1 Device list - Device online status

If the connection fails, the onFailure function executes backoff reconnection. The example code is as follows:
@Override public void onFailure(IMqttToken iMqttToken, Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("Mqtt connect fail."); // Backoff reconnection int lowBound = (int) (defaultBackoff * 0.8); int highBound = (int) (defaultBackoff * 1.2); long randomBackOff = random.nextInt(highBound - lowBound); long backOffWithJitter = (int) (Math.pow(2.0, (double) retryTimes)) * (randomBackOff + lowBound); long waitTImeUntilNextRetry = (int) (minBackoff + backOffWithJitter) > maxBackoff ? maxBackoff : (minBackoff + backOffWithJitter); System.out.println("---- " + waitTImeUntilNextRetry); try { Thread.sleep(waitTImeUntilNextRetry); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("sleep failed, the reason is" + e.getMessage().toString()); } retryTimes++; MqttDemo.this.connect(true); }
Subscribing to a Topic for Receiving Commands
Only devices that subscribe to a specific topic can receive messages about the topic published by the broker. For details on the preset topics, see Topics. For details about the API, see Platform Delivering a Command.
1 2 |
// Subscribe to a topic for receiving commands. client.subscribe(getCmdRequestTopic(), qosLevel, null, new IMqttActionListener(); |
1 2 3 |
public static String getCmdRequestTopic() { return "$oc/devices/" + deviceId + "/sys/commands/#"; } |
Reporting Properties
Devices can report their properties to the platform. For details, see Reporting Device Properties.
1 2 3 4 |
// Report JSON data. service_id must be the same as that defined in the product model. String jsonMsg = "{\"services\": [{\"service_id\": \"Temperature\",\"properties\": {\"value\": 57}},{\"service_id\": \"Battery\",\"properties\": {\"level\": 80}}]}"; MqttMessage message = new MqttMessage(jsonMsg.getBytes()); client.publish(getRreportTopic(), message, qosLevel, new IMqttActionListener(); |
The message body jsonMsg is assembled in JSON format, and service_id must be the same as that defined in the product model. properties indicates a device property, and 57 indicates the property value. event_time indicates the UTC time when the device reports data. If this parameter is not specified, the system time is used by default.
After a device or gateway is connected to the platform, you can call MqttClient.publish(String topic,MqttMessage message) to report device properties to the platform.
1 2 3 |
public static String getRreportTopic() { return "$oc/devices/" + deviceId + "/sys/properties/report"; } |
Viewing Reported Data
After the main method is called, you can view the reported device property data on the device details page. For details about the API, see Device Reporting Properties.
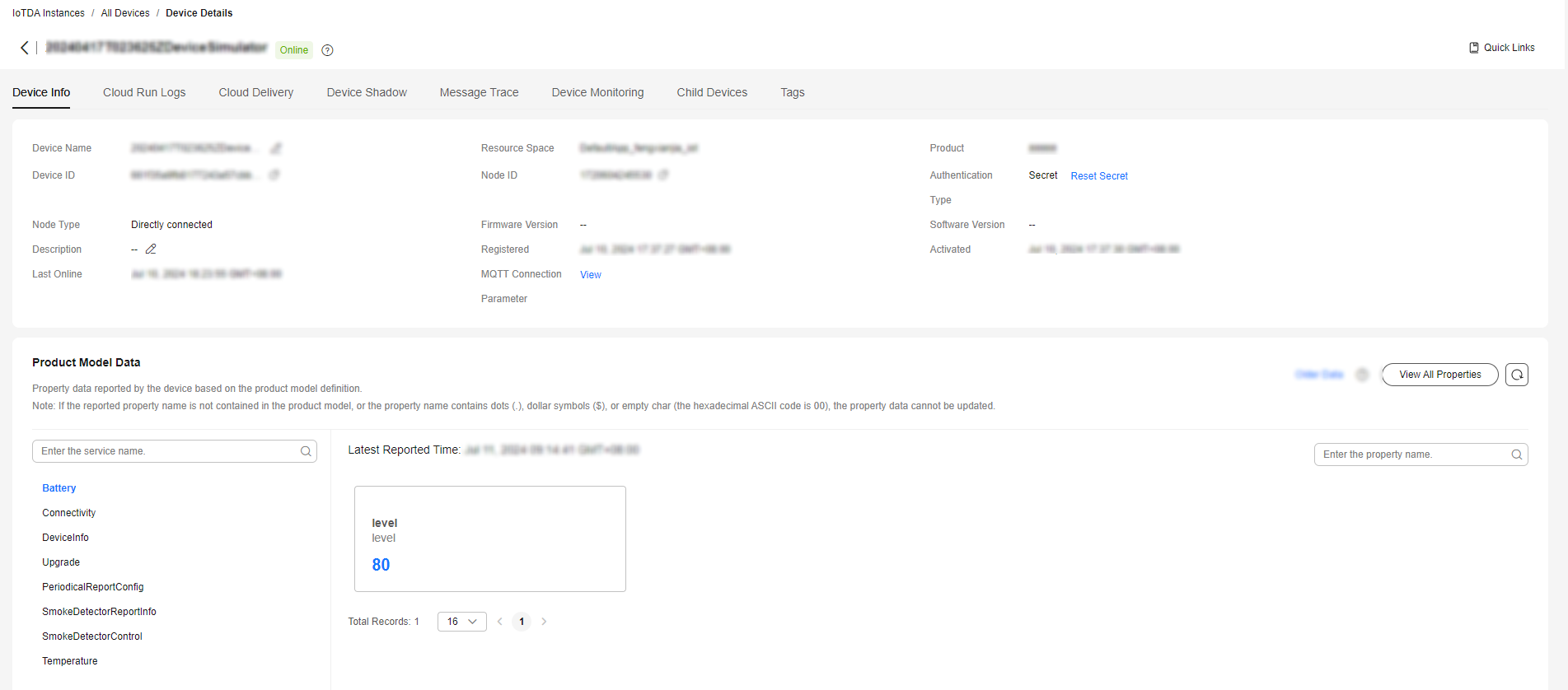
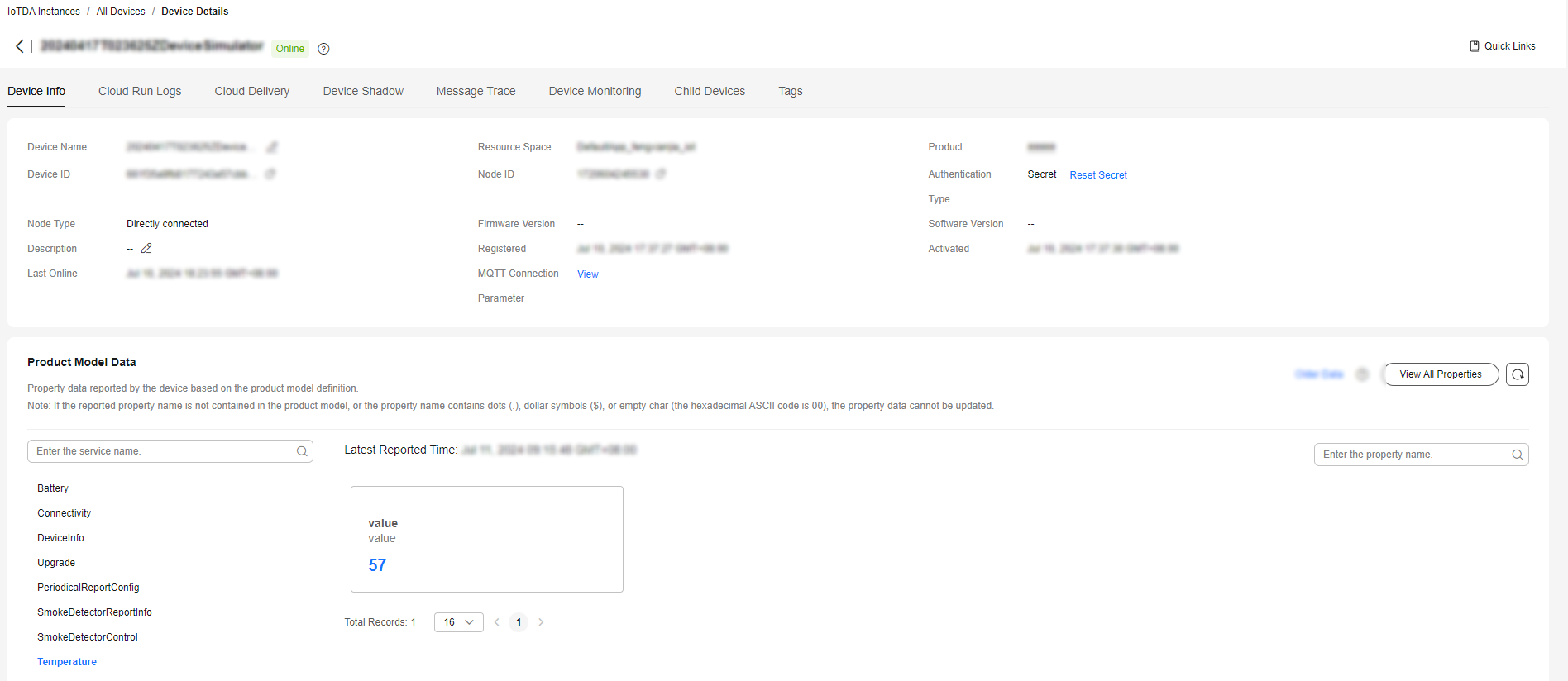
If the latest data is not displayed on the device details page, check whether the services and properties reported by the device are the same as those in the product model.
Related Resources
You can refer to the MQTT or MQTTS API Reference on the Device Side to connect MQTT devices to the platform. You can also develop an MQTT-based smart street light online to quickly verify whether they can interact with the IoT platform to publish or subscribe to messages.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





