Creating a VPC Peering Connection to Connect Two VPCs in the Same Account
Scenarios
VPCs are isolated from each other. You can create a VPC peering connection to connect two VPCs in the same region. You can refer to the following to create a VPC peering connection to connect two VPCs in the same account.
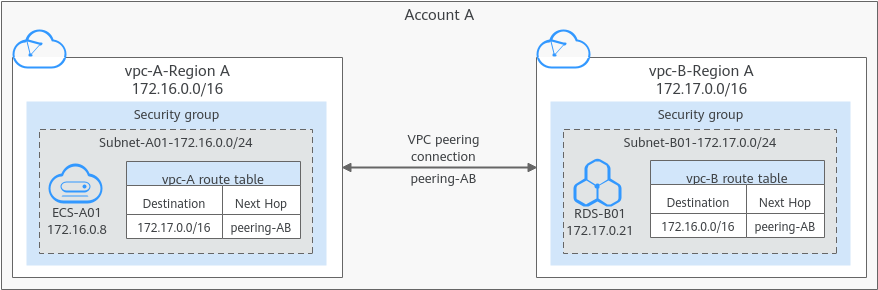
The following describes how to create a VPC peering connection to connect two VPCs (vpc-A and vpc-B in this example) in the same account. In this way, instances (the service server ECS-A01 and database server RDS-B01 in this example) in the two VPCs can communicate with each other.
The procedure is as follows:
Step 1: Create a VPC Peering Connection
Step 2: Add Routes for the VPC Peering Connection
Step 3: Configure Security Group Rules for Instances in Local and Peer VPCs
Step 4: Verify Network Connectivity
Currently, VPC peering connections are free.
Constraints
- If the local and peer VPCs have overlapping CIDR blocks, the VPC peering connection may not take effect. For example, if the CIDR block of a VPC is 192.168.0.0/16 and that of another VPC is 192.168.0.0/16 or 192.168.0.0/18, the CIDR blocks overlap.
In this case, you can configure the network by referring to VPC Peering Connection Usage Examples.
If there are CCE clusters, you need to avoid CIDR block overlapping between the subnets and container subnets in addition to the VPC CIDR blocks at both ends. Otherwise, communications will fail. For details, see Cross-VPC Cluster Interconnection.
- Only one VPC peering connection can be created between two VPCs at the same time.
- A VPC peering connection can only connect VPCs in the same region.
- A VPC peering connection can enable a VPC created on the Huawei Cloud Chinese Mainland website to connect to one created on the Huawei Cloud International website, but the VPCs must be in the same region. For example, if the VPC created on the Chinese Mainland website is in the CN-Hong Kong region, then the VPC created on the International website must also be in the CN-Hong Kong region.
- If you want to connect VPCs in different regions, you can use Cloud Connect.
- If you only need a few ECSs in different regions to communicate with each other, you can assign and bind EIPs to the ECSs.
Prerequisites
You have two VPCs from the same account in the same region. If you want to create one, see Creating a VPC with a Subnet.
Step 1: Create a VPC Peering Connection
- Go to the VPC peering connection list page.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Create VPC Peering Connection.
The Create VPC Peering Connection page is displayed.
- Configure the parameters as prompted.
For details, see Table 1.
Figure 2 Creating a VPC peering connection
Table 1 Parameters for creating a VPC peering connection Parameter
Description
Example Value
Region
Mandatory
The region where the VPC peering connection is created. Select the region nearest to you to ensure the lowest latency possible.
CN-Hong Kong
VPC Peering Connection Name
Mandatory
Enter a name for the VPC peering connection.
The name can contain a maximum of 64 characters, including letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
peering-AB
Description
Optional
Enter a description of the VPC peering connection in the text box as required.
peering-AB connects vpc-A and vpc-B.
Local VPC
Mandatory
VPC at one end of the VPC peering connection. You can select one from the drop-down list.
vpc-A
Local VPC CIDR Block
CIDR block of the selected local VPC
172.16.0.0/16
Account
Mandatory
- My account: The local and peer VPCs are from the same account.
- Another account: The local and peer VPCs are from different accounts.
My account
Peer Project
The project is selected in by default if Account is set to My account.
In this example, vpc-A and vpc-B are created in region A, and the corresponding project of the account in region A is selected by default.
ab-cdef-1
Peer VPC
This parameter is mandatory if Account is set to My account.
VPC at the other end of the VPC peering connection. You can select one from the drop-down list.
vpc-B
Peer VPC CIDR Block
CIDR block of the selected peer VPC.
If the local and peer VPCs have overlapping CIDR blocks, the VPC peering connection may not be usable. For details, see VPC Peering Connection Configuration Suggestions.
172.17.0.0/16
- Click Create Now.
A dialog box for adding routes is displayed.
- In the displayed dialog box, click Add Now. On the displayed page about the VPC peering connection details, go to Step 2: Add Routes for the VPC Peering Connection to add a route.
Step 2: Add Routes for the VPC Peering Connection
- In the lower part of the VPC peering connection details page, click Add Route.
The Add Route dialog box is displayed.
Figure 3 Adding a route
- Add routes to the route tables as prompted.
Table 2 describes the parameters.
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Example Value
VPC
Select a VPC that is connected by the VPC peering connection.
vpc-A
Route Table
Select the route table of the VPC that the route will be added to.
Each VPC comes with a default route table to control the outbound traffic from the subnets in the VPC. In addition to the default route table, you can also create a custom route table and associate it with the subnets in the VPC. Then, the custom route table controls outbound traffic of the subnets.- If there is only the default route table in the drop-down list, select the default route table.
- If there are both default and custom route tables in drop-down list, select the route table associated with the subnet connected by the VPC peering connection.
rtb-vpc-A (Default)
Destination
An IP address or address range in the VPC being connected by the VPC peering connection. The value can be a VPC CIDR block, subnet CIDR block, or ECS IP address. For details about the route configuration example, see VPC Peering Connection Configuration Suggestions.
vpc-B CIDR block: 172.17.0.0/16
Next Hop
The default value is the current VPC peering connection. You do not need to specify this parameter.
peering-AB
Description
Supplementary information about the route. This parameter is optional.
The description can contain a maximum of 255 characters and cannot contain angle brackets (< or >).
Route from vpc-A to vpc-B
Add a route for the other VPC
If you select this option, you can also add a route for the other VPC connected by the VPC peering connection.
To enable communications between VPCs connected by a VPC peering connection, you need to add both forward and return routes to the route tables of the VPCs. For details, see VPC Peering Connection Configuration Suggestions.
Selected
VPC
By default, the system selects the VPC connected by the VPC peering connection. You do not need to specify this parameter.
vpc-B
Route Table
Select the route table of the VPC that the route will be added to.
Each VPC comes with a default route table to control the outbound traffic from the subnets in the VPC. In addition to the default route table, you can also create a custom route table and associate it with the subnets in the VPC. Then, the custom route table controls outbound traffic of the subnets.- If there is only the default route table in the drop-down list, select the default route table.
- If there are both default and custom route tables in drop-down list, select the route table associated with the subnet connected by the VPC peering connection.
rtb-vpc-B (Default)
Destination
An IP address or address range in the other VPC connected by the VPC peering connection. The value can be a VPC CIDR block, subnet CIDR block, or ECS IP address. For details about the route configuration example, see VPC Peering Connection Configuration Suggestions.
vpc-A CIDR block: 172.16.0.0/16
Next Hop
The default value is the current VPC peering connection. You do not need to specify this parameter.
peering-AB
Description
Supplementary information about the route. This parameter is optional.
The description can contain a maximum of 255 characters and cannot contain angle brackets (< or >).
Route from vpc-B to vpc-A
- Click OK.
You can view the routes in the route list.
Step 3: Configure Security Group Rules for Instances in Local and Peer VPCs
|
Direction |
Action |
Type |
Protocol & Port |
Source/Destination |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Inbound |
Allow |
IPv4 |
All |
Source: current security group |
Allows the instances in the security group to communicate with each other over any IPv4 protocol and port. |
|
Inbound |
Allow |
IPv6 |
All |
Source: current security group |
Allows the instances in the security group to communicate with each other over any IPv6 protocol and port. |
|
Outbound |
Allow |
IPv4 |
All |
Destination: 0.0.0.0/0 |
Allows all IPv4 traffic from the instances in the security group to external resources over any protocol and port. |
|
Outbound |
Allow |
IPv6 |
All |
Destination: ::/0 |
Allows all IPv6 traffic from the instances in the security group to external resources over any protocol and port. |
- If the local and peer VPCs connected by a VPC peering connection are associated with the same security group, instances in the VPCs can communicate with each other.
For example, if ECS-A01 and RDS-B01 are associated with security group Sg-AB, you only need to perform the operations in 1.
- If the local and peer VPCs are associated with different security groups, instances in the VPCs cannot communicate with each other unless you add rules to allow them to.
For example, if ECS-A01 is associated with security group Sg-A, and RDS-B01 is associated with security group Sg-B, you need to perform the operations in 1 and 2.
- Add security group rules in Table 4 to allow remote logins.
Table 4 Security group rules for remote logins Direction
Action
Type
Protocol & Port
Source
Description
Inbound
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 22
IP address: 0.0.0.0/0
Allows any IPv4 address to remotely log in to the Linux instances in Sg-AB over SSH port 22.
Inbound
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 3389
IP address: 0.0.0.0/0
Allows any IPv4 address to remotely log in to the Windows instances in Sg-AB over RDP port 3389.

Setting 0.0.0.0/0 as the source in an inbound rule allows all external IP addresses to remotely log in to your cloud server. If port 22 or 3389 is exposed to the public network, your cloud server is vulnerable to network risks. To address this issue, set the source to a trusted IP address, for example, the EIP of a cloud server.
- (Optional) Add security rules to allow the instances in Sg-A and Sg-B to communicate with each other.
Select either of the following solution based on your service requirements.
- Solution 1 in Table 5: Set Source to the CIDR block of peer VPC or subnet.
Table 5 Security group rules (CIDR block as the source) Security Group
Direction
Action
Type
Protocol & Port
Source
Description
Sg-A
Inbound
Allow
IPv4
All
IP address: 172.17.0.0/16 (vpc-B CIDR block)
Allows traffic from 172.17.0.0/16 to access instances in Sg-A over any IPv4 protocol and port.
Sg-B
Inbound
Allow
IPv4
All
IP address: 172.16.0.0/16 (vpc-A CIDR block)
Allows traffic from 172.16.0.0/16 to access instances in Sg-B over any IPv4 protocol and port.
- Solution 2 in Table 6: Set Source to Sg-A and Sg-B.
Table 6 Security group rules (security group as the source) Security Group
Direction
Action
Type
Protocol & Port
Source
Description
Sg-A
Inbound
Allow
IPv4
All
Sg-B
Allows instances in Sg-B to access those in Sg-A over any IPv4 protocol and port.
Sg-B
Inbound
Allow
IPv4
All
Sg-A
Allows instances in Sg-A to access those in Sg-B over any IPv4 protocol and port.
- Solution 1 in Table 5: Set Source to the CIDR block of peer VPC or subnet.
Step 4: Verify Network Connectivity
- Log in to ECS-A01 in the local VPC.
Multiple methods are available for logging in to an ECS. For details, see Logging In to an ECS.
- Check whether ECS-A01 can communicate with RDS-B01.
ping <peer-server-IP-address>
Example command:
ping 172.17.0.21
The IP address shown in the command is just an example. Replace it with the IP address of the instance, which can be obtained from the instance console.
If information similar to the following is displayed, ECS-A01 and RDS-B01 can communicate with each other, and the VPC peering connection between VPC-A and VPC-B is successfully created.
[root@ecs-A01 ~]# ping 172.17.0.21 PING 172.17.0.21 (172.17.0.21) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 172.17.0.21: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.849 ms 64 bytes from 172.17.0.21: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.455 ms 64 bytes from 172.17.0.21: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.385 ms 64 bytes from 172.17.0.21: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.372 ms ... --- 172.17.0.21 ping statistics ---
In this example, ECS-A01 and RDS-B01 are associated with the same security group, so they can communicate with each other once a VPC peering connection is created between VPC-A and VPC-B. If the instances are associated with different security groups, you need to add inbound rules to allow access from instances of the peer security group. For details, see Enabling Communications Between Instances in Different Security Groups.
If VPCs connected by a VPC peering connection cannot communicate with each other, refer to Why Did Communication Fail Between VPCs That Were Connected by a VPC Peering Connection?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





