SSE-KMS
SSE-KMS combines KMS and OBS to improve security and meet compliance requirements. KMS provides keys, and OBS uses the keys to encrypt data uploaded to it. These keys are generated by third-party validated Hardware Secure Modules (HSMs). Access to the keys is controlled, and all key-related operations are logged for auditing. You can also use KMS to manage keys, such as creating custom keys, as well as editing, querying, and deleting keys.
Context
Before using SSE-KMS, you may want to know:
- Key Management Service (KMS): It is a secure, reliable, and easy-to-use key hosting service provided by Huawei Cloud. You can use KMS to create and manage keys. The created keys can be used for server-side encryption. For more information, see KMS Overview.
- Customer Master Key (CMK): CMKs are top-level keys in KMS. They are used to create and manage other keys (including session keys and data encryption keys). CMKs fall into custom keys and default keys. You can use either of them for SSE-KMS. If you do not specify a key, OBS creates a default key for your account the first time you use SSE-KMS. For more information, see KMS Basic Concepts, How Are Default Keys Generated? What Are the Differences Between a Custom Key and a Default Key? and Creating a Custom Key.
- Data Encryption Key (DEK): DEKs are used to encrypt data. For more information, see How Do I Use a DEK?
- Envelope encryption: Instead of encrypting and decrypting data directly with a CMK, envelope encryption uses the CMK to generate a DEK to encrypt and decrypt data, and uses the CMK to encrypt and decrypt the DEK. For more information, see What Are the Benefits of Envelope Encryption?
Billing
You will be billed for using KMS keys. For details, see KMS Billing Items.
Important Notes
- Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) APIs have traffic control limits (see DEW API Overview). After SSE-KMS is enabled, your service access may be affected by traffic control.
- The ETag value of an encrypted object is the MD5 value of the ciphertext, rather than that of the plaintext.
Constraints
- SSE-KMS supports the AES-256 and SM4 algorithms.
- HTTPS is required for requests that configure SSE-KMS for buckets, as well as for all GET and PUT requests that use SSE-KMS.
- To access objects encrypted using SSE-KMS, anonymous users must use valid credentials (permanent or temporary access keys) to sign requests. For details, see OBS Signatures.
- To use a custom customer master key (CMK), the bucket with SSE-KMS enabled must be in the same region as the CMK. The default key is not region-specific or IAM user-specific. All IAM users under a HUAWEI ID share the same default key in all regions.
- Custom CMKs only support the AES-256 and SM4 algorithms.
- For cross-account access, use custom keys for SSE-KMS.
How SSE-KMS Works
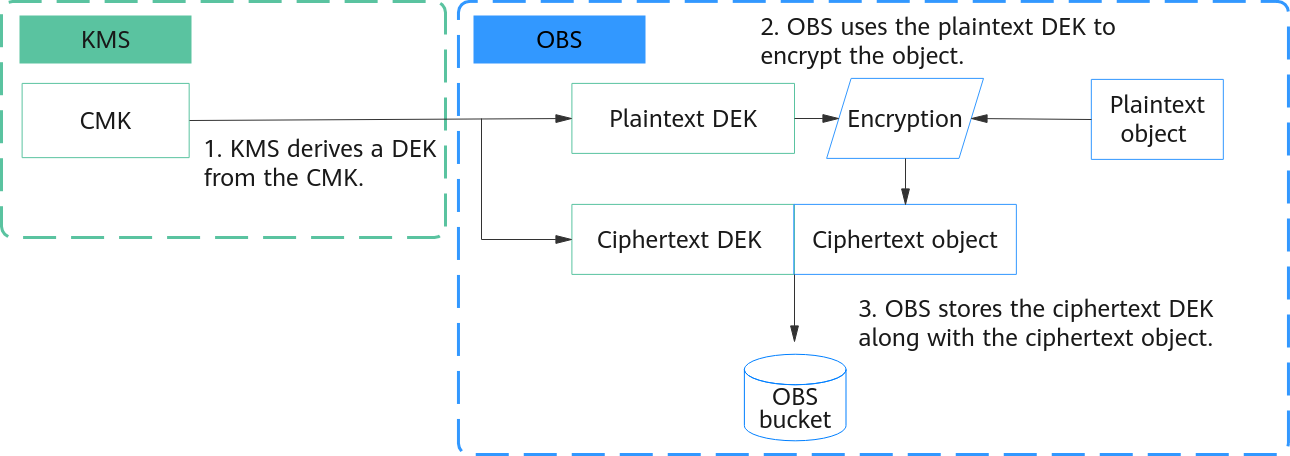
Figure 1 shows how SSE-KMS encryption works with envelope encryption:
- KMS derives a DEK from a CMK, uses the CMK to encrypt the DEK, and sends both the plaintext and ciphertext of the DEK to OBS.
- OBS uses the plaintext DEK to encrypt data and then promptly deletes the plaintext DEK from memory.
- OBS stores the ciphertext DEK as metadata along with the ciphertext object.
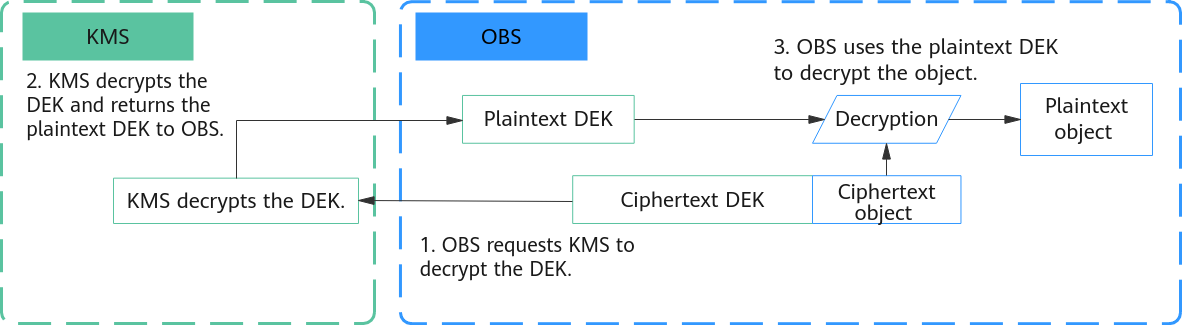
Figure 2 shows how SSE-KMS decryption works:
- OBS requests KMS to decrypt the ciphertext DEK.
- KMS uses the CMK used during encryption to decrypt the DEK and returns the DEK plaintext to OBS.
- OBS uses the plaintext DEK to decrypt the ciphertext object, obtains the plaintext object, and then promptly deletes the plaintext DEK from memory.
Permissions Configuration
- To set a bucket's encryption method to SSE-KMS, you must be the bucket owner or have the required permissions (obs:bucket:PutEncryptionConfiguration and obs:bucket:GetEncryptionConfiguration in IAM or PutEncryptionConfiguration and GetEncryptionConfiguration in a bucket policy). For details, see OBS Permissions Control Overview, IAM Custom Policies, and Creating a Custom Bucket Policy.
- To use SSE-KMS to encrypt the object you are uploading, you must have the upload permission and the kms:cmk:get, kms:cmk:list, kms:cmk:create, and kms:dek:create permissions granted using IAM.
- To download objects encrypted using SSE-KMS, you must have the download permission and the kms:cmk:get, kms:cmk:list, kms:cmk:create, kms:dek:create, and kms:dek:crypto permissions granted using IAM.
Enforce a specific server-side encryption method for objects uploaded to a bucket:
- You can configure a bucket policy to enforce a specific server-side encryption method for objects uploaded to that bucket. For example, to ensure that objects uploaded to bucket ExampleBucket via PUT are encrypted using SSE-KMS, you can configure a bucket policy that denies any upload requests lacking the x-obs-server-side-encryption:"kms" header:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
{ "Statement": [ { "Sid": "DenyUnEncryptedObjectUploads", "Effect": "Deny", "Principal": "*", "Action": "PutObject", "Resource": "ExampleBucket/*", "Condition": { "StringNotEquals": { "x-obs-server-side-encryption": "kms" } } } ] } - Authorize an account to access objects encrypted using server-side encryption in another account:
Assume that HUAWEI ID A uses its own key k to encrypt object a in bucket A. To access object a, HUAWEI ID B needs to be granted the permissions for the bucket, object, as well as the key:
- Bucket and object authorization: ID A authorizes ID B to access the bucket. For details, see Granting Permissions to Other Accounts.
- Key authorization: ID A authorizes ID B to access key k. For details, see Creating a Grant for a Custom Key.
For cross-account access, use custom keys for SSE-KMS.
Impacts of Server-Side Encryption on Other Operations
Object uploads and downloads
As long as your permissions are properly configured, there is no difference in how you access encrypted and unencrypted objects. For example, if you use a pre-signed URL to share your object, anyone with the shared URL can access your object, regardless of whether it is encrypted. This means that the encryption status does not affect how the URL works. In addition, when you list objects in a bucket, the API returns all objects, regardless of whether they are encrypted.
Object replication (within a region and across regions)
- If the destination bucket has server-side encryption enabled but the source bucket does not, the destination bucket's encryption method applies to the object copies. In this case, a source object and its copy have different ETags. If your application relies on ETags, make sure it accounts for this difference.
- If both the source and destination buckets have server-side encryption enabled but use different encryption methods, the destination bucket's encryption method applies to the object copies. In this case, a source object and its copy have different ETags. Make sure your application accounts for this difference.
- If the source bucket has server-side encryption enabled but the destination bucket does not, the source bucket's encryption method applies to the object copies.
Prerequisites
If you plan to use a custom CMK, create one before configuring SSE-KMS. For details, see Creating a Custom Key.
Configuring SSE-KMS for a Bucket
You can use OBS Console, APIs, or SDKs to configure SSE-KMS for a bucket.
Configuring SSE-KMS for an Object
You can use OBS Console, APIs, or SDKs to configure SSE-KMS for an object.
Changing the Encryption Status of an Existing Object
By copying an existing object to itself, you can apply encryption or change its encryption method.
You can use APIs and SDKs to change an object's encryption settings.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot