Using gsql to Connect to an Instance
This section describes how to use the gsql client to connect to a GaussDB instance you have bought on the GaussDB management console.
- Step 1: Buy an ECS
- Step 2: Query the IP Address and Port Number of the Instance to Be Connected
- Step 3: Test the Connectivity
- Step 4: Obtain the Driver Package
- Step 5: Connect to the Database
Buying an ECS
If you want to connect to a database using the command-line interface (CLI), like gsql, you need to create an ECS and install gsql on it.
- Log in to the management console and check whether there is an available ECS.
Figure 1 ECS instances

- Buy an ECS that runs EulerOS.
For details about how to buy a Linux ECS, see Purchasing an ECS in Elastic Cloud Server Getting Started.
gsql supports the following OS versions:
- For x86 servers: EulerOS V2.0SP5 and Kylin V10 SP2
- For Kunpeng servers: EulerOS V2.0SP8 and Kylin V10 SP1
This section uses EulerOS as an example.
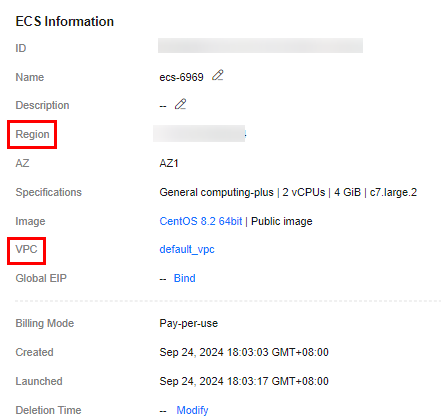
- On the ECS Information page of the target ECS, view the region and VPC of the ECS.
Figure 2 ECS basic information
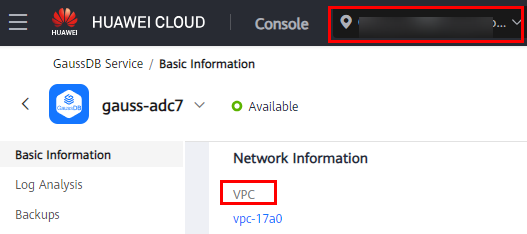
- On the Basic Information page of your GaussDB instance, view the region and VPC of the instance.
Figure 3 Basic information about a GaussDB instance
- Check whether the ECS and GaussDB instance are in the same region and VPC.
- If the ECS and GaussDB instance are in the same region and VPC, the DB instance can be connected through a private network. For details about how to obtain the private IP address, see Querying the IP Address of the Instance to Be Connected.
- If the ECS and DB instance are in different VPCs, the DB instance must be connected over a public network. For details about how to obtain the public IP address, see Querying the IP Address of the Instance to Be Connected. Ensure that both the ECS and GaussDB instance have EIPs.
- For details about how to bind an EIP to an ECS, see Binding an EIP.
- For details about how to bind an EIP to a GaussDB instance, see Binding an EIP.
Querying the IP Address and Port Number of the Instance to Be Connected
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose .
in the upper left corner of the page and choose . - On the Instances page, click the name of the target instance to go to the Basic Information page.
- In the Node List area, view the IP address. In the Network Information area, view the port number.
For a centralized instance, obtain the IP address of the primary DN. For a distributed instance, obtain the IP address of any CN.
- If the ECS and GaussDB instance are in the same VPC, obtain the private IP address.
- If the ECS and GaussDB instance are in different VPCs, obtain the EIP.
Testing Connectivity
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Logging In to a Linux ECS Using VNC in Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- On the ECS, check whether it can connect to the target GaussDB instance using the IP address and port number obtained in Querying the IP Address and Port Number of the Instance to Be Connected.
telnet IP address Port number
Example:
telnet 192.168.0.16 8000
If the message "command not found" is displayed, install a Telnet client that matches the OS of the ECS.
- If the ECS can connect to the DB instance, no further action is required.
- If the communication fails, check the security group rules.
- On the Outbound Rules page of the ECS, add the IP address and port of the GaussDB instance to the outbound rules.
- If the ECS and GaussDB instance are in the same VPC, add the private IP address and port of the GaussDB instance to the outbound rules.
- If the ECS and GaussDB instance are in different VPCs, add the EIP address and port of the GaussDB instance to the outbound rules.
Figure 4 ECS security group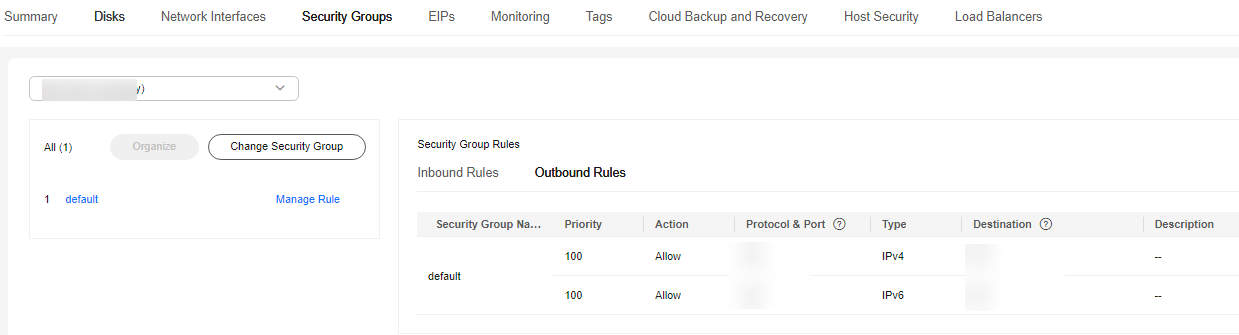
- On the Inbound Rules page of the GaussDB instance, add the IP address and port of the ECS to the inbound rules.
- If the ECS and GaussDB instance are in the same VPC, add the private IP address and port of the ECS to the inbound rules.
- If the ECS and GaussDB instance are in different VPCs, add the EIP address and port of the ECS to the inbound rules.
For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules.Figure 5 GaussDB security group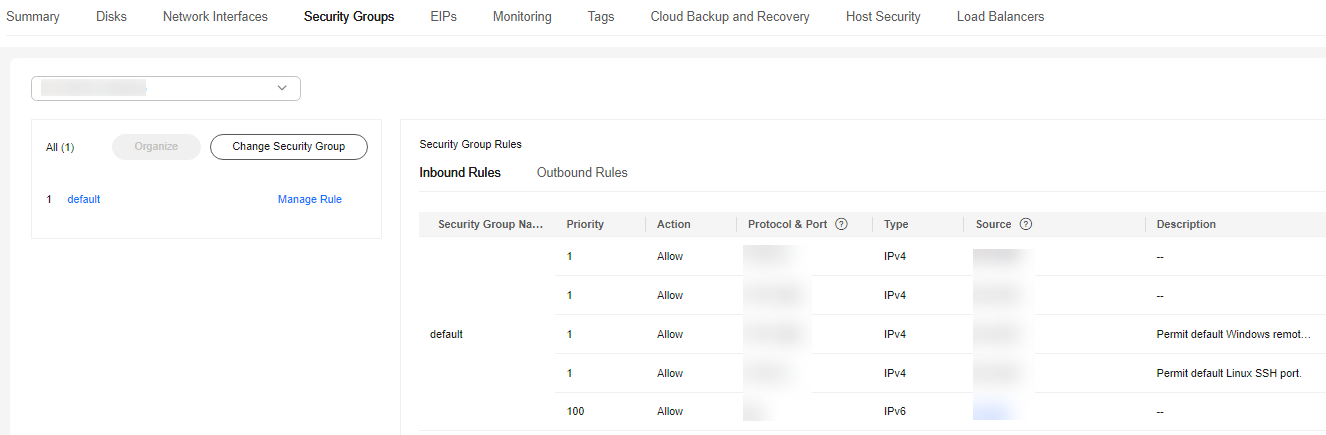
- On the Outbound Rules page of the ECS, add the IP address and port of the GaussDB instance to the outbound rules.
Obtaining the Driver Package
Download particular packages listed in Table 1 based on the version of your instance.
To prevent a software package from being tampered with during transmission or storage, download the corresponding verification package and perform the following steps to verify the software package:
- Upload the software package and verification package to the same directory on a Linux VM.
- Run the following command to verify the integrity of the software package:
cat GaussDB_driver.zip.sha256 | sha256sum --check
If OK is displayed in the command output, the verification is successful.
GaussDB_driver.zip: OK
- Log in as the root user to the ECS you have created.
- Upload the client tool package and configure gsql environment variables.
- Run the following command to create the /tmp/tools directory for storing the client tool package:
mkdir /tmp/tools
- Download the GaussDB_driver.zip driver package of the required version by referring to Obtaining the Driver Package, and upload it to the /tmp/tools directory of the created ECS.
- Run the following commands to decompress the GaussDB_driver.zip driver package:
cd /tmp/tools unzip GaussDB_driver.zip
- Run the following commands to copy the decompressed GaussDB-Kernel_***_EULER_64bit-Gsql.tar.gz client tool package to the /tmp/tools directory:
This section uses the gsql tool package suitable for the centralized instances running on Euler2.5_x86_64 as an example. The relative path of the tool package varies depending on where you decompressed it.
cd /tmp/tools/GaussDB_driver/Centralized/Euler2.5_X86_64/ cp GaussDB-Kernel_***_EULER_64bit-Gsql.tar.gz /tmp/tools
- Run the following commands to decompress the package:
cd /tmp/tools tar -zxvf GaussDB-Kernel_***_EULER_64bit-Gsql.tar.gz
- Configure environment variables.
Run the following command to open the ~/.bashrc file:
vim ~/.bashrc
Press G to move the cursor to the last line, press i to enter Insert mode, and type the following information. Then, press Esc to exit Insert mode, and run :wq to save the settings and exit.
export PATH=/tmp/tools/bin:$PATH export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/tmp/tools/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
Run the following command to make the environment variables take effect permanently:source ~/.bashrc
- Run the following command to create the /tmp/tools directory for storing the client tool package:
- Enter the password when prompted to connect to the database.
After an instance is created, a postgres database is generated by default. Database postgres is used as an example.
gsql -d postgres -h 10.0.0.0 -U root -p 8000 Password for user root:
postgres is the name of the database you want to connect to. 10.0.0.0 is the IP address of the instance obtained in Querying the IP Address of the Instance to Be Connected. root is the username for logging in to the database. 8000 is the database port obtained in Querying the Port Number of the Instance to Be Connected.
If the following information is displayed, the connection is successful:gaussdb=>
For more information about gsql commands, see Tool Reference.
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose .
in the upper left corner of the page and choose . - On the Instances page, click the name of the target instance. In the Configuration area on the Basic Information page, click
 next to the SSL field to download the root certificate or certificate bundle.
next to the SSL field to download the root certificate or certificate bundle. - Upload the root certificate to the ECS or save it to the device to be connected to the GaussDB instance.
Import the root certificate to the Linux ECS. For details, see How Can I Import the Root Certificate to a Windows or Linux OS?
- Connect to a GaussDB instance.
A Linux ECS is used in this example. Run the following command to set environment variables on the ECS:
export PGSSLMODE=<sslmode> export PGSSLROOTCERT=<ca-file-directory>
gsql -h <host> -p <port> -d <database> -U <user>
Example:
export PGSSLMODE="verify-ca" export PGSSLROOTCERT="/home/Ruby/ca.pem"
gsql -h 10.0.0.0 -p 8000 -d postgres -U root
Password for user root:
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Description
<host>
IP address of the DB instance. To obtain the IP address, click the instance name on the Instances page to go to the Basic Information page of the instance. The IP address can be found in the Private IP Address column of the Node List area.
<port>
Database port number. The default value is 8000. To obtain the database port, click the instance name on the Instances page to go to the Basic Information page of the instance. The database port can be found in the Database Port field of the Network Information area.
<database>
Name of the database to connect to. The default database is postgres.
<user>
Username of the GaussDB database account. The default administrator is root.
<ca-file-directory>
Directory of the CA certificate for SSL connection.
<sslmode>
SSL connection mode. Set it to verify-ca to verify that the server is trustworthy by checking the certificate chain.
For more information about gsql commands, see Tool Reference.
- Check the command output after you log in to the database. If information similar to the following is displayed, the SSL connection has been established.
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256)
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





