MQTT(S) Access
Overview
An MQTT message consists of fixed header, variable header, and payload.
Common MQTT message types include CONNECT, SUBSCRIBE, and PUBLISH.
- CONNECT: A client requests a connection to a server. For details about main parameters in the payload of a CONNECT message, see Device Connection Authentication.
- SUBSCRIBE: A client subscribes to a topic. The main parameter Topic name in the payload of a SUBSCRIBE message indicates the topic whose subscriber is a device. For details, see Topics.
- PUBLISH: The platform publishes a message.
- The main parameter Topic name in the variable header of a PUBLISH message indicates the topic whose publisher is a device. For details, see Topics.
- The payload contains the data reported or commands delivered. It is a JSON object.
Topics
If you connect devices to the platform using MQTT, you can use topics to send and receive messages.
- Topics starting with $oc are preset system topics in IoTDA. You can subscribe to and publish messages through these topics. For details about the topic list and functions, see Topics.
- You can create topics that do not start with $oc to send and receive custom messages.
Constraints
|
Description |
Constraint |
|---|---|
|
Number of concurrent connections to a directly connected MQTT device |
1 |
|
Connection setup requests of an account per second on the device side |
|
|
Number of upstream requests for an instance per second on the device side (when average message payload is 512 bytes) |
|
|
Number of upstream messages for an MQTT connection |
50 per second |
|
Bandwidth of an MQTT connection (upstream messages) |
1 MB (default) |
|
Length of a publish message sent over an MQTT connection (Oversized messages will be rejected.) |
1 MB |
|
Standard MQTT protocol |
MQTT v5.0, MQTT v3.1.1, and MQTT v3.1 |
|
Differences from the standard MQTT protocol |
|
|
Security levels supported by MQTT |
TCP channel and TLS protocols (TLS v1, TLS v1.1, TLS v1.2, and TLS v1.3) |
|
Recommended heartbeat interval for MQTT connections |
Range: 30s to 1200s; recommended: 120s |
|
MQTT message publish and subscription |
A device can only publish and subscribe to messages of its own topics. |
|
Number of subscriptions for an MQTT connection |
100 |
|
Length of a custom MQTT topic |
128 bytes |
|
Number of custom MQTT topics added to a product |
10 |
|
Number of CA certificates uploaded for an account on the device side |
100 |
Compatibility
IoTDA supports device access using MQTT 5.0, MQTT 3.1.1, and MQTT 3.1. However, IoTDA is not a simple MQTT broker. It also integrates capabilities such as message communications, device management, rule engine, and data forwarding. The differences between the MQTT function provided by IoTDA and standard MQTT specifications are as follows:
- Devices can communicate with IoTDA using CONNECT, CONNACK, PUBLISH, PUBACK, SUBSCRIBE, SUBACK, UNSUBSCRIBE, UNSUBACK, PINGREQ, PINGRESP, and DISCONNECT packets in MQTT specifications.
- IoTDA supports MQTT QoS 0 and QoS 1, but does not support QoS 2.
- IoTDA supports clean sessions.
- IoTDA does not support the will feature. IoTDA can push device statuses. After a device goes offline, IoTDA pushes its status to your application or other cloud services based on a forwarding rule.
- IoTDA does not support retained messages. IoTDA can cache messages during message reporting and delivery.
Supported MQTT 5.0 Features
Only enterprise edition instances support MQTT 5.0-related features.
IoTDA supports the following new MQTT 5.0 features:
- Topic aliases. Message communication topics are reduced to an integer to reduce MQTT packets and save network bandwidth resources.
- Response topics and correlation data. The two parameters can be carried during message reporting and delivery to implement cloud HTTP-like requests and responses.
- User property list. Each property consists of a key and a value and is used to transmit property data in the non-payload area.
- Content-Type. Message reporting packets can carry Content-Type to identify the packet type.
- Return codes can be carried in CONNACK and PUBACK packets, helping devices quickly locate request statuses and issues.
TLS Support for MQTT
TLS is recommended for secure transmission between devices and the platform. Currently, TLS v1.1, v1.2, v1.3, and GMTLS are supported. TLS v1.3 is recommended. TLS v1.1 will not be supported in the future. GMTLS is supported only by the enterprise edition using Chinese cryptographic algorithms.
When TLS connections are used for the basic edition, standard edition, and enterprise edition that support general cryptographic algorithms, the IoT platform supports the following cipher suites:
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
When the enterprise edition that supports Chinese cryptographic algorithms uses TLS connections, the IoT platform supports the following cipher suites:
- ECC_SM4_GCM_SM3
- ECC_SM4_CBC_SM3
- ECDHE_SM4_GCM_SM3
- ECDHE_SM4_CBC_SM3
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
CBC cipher suites may pose security risks.
Service Flow
MQTT devices communicate with the platform without data encryption. For security purposes, MQTTS access is recommended.
You are advised to use the IoT Device SDK to connect devices to the platform over MQTTS.
- Create a product on the IoTDA console or by calling the API Creating a Product.
- Register a device on the IoTDA console or calling the API Creating a Device.
- The registered device can report messages and properties, receive commands, properties, and messages, perform OTA upgrades, and report data using custom topics. For details about preset topics of the platform, see Topic Definition.
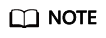
You can use MQTT.fx to debug access using the native MQTT protocol. For details, see Developing an MQTT-based Smart Street Light Online.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





