Security Operations
After data integration is configured, you can perform operations such as asset management, threat detection, and alert investigation based on the integrated data.
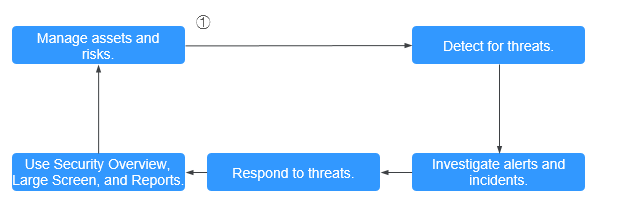
Step 1: Manage Assets and Risks
The essence of security operations is security risk management. According to the definition of ISO, there are three elements, assets, vulnerabilities, and threats involved in security operations. Sorting the assets you want to protect is the starting point of the security operations service flow.
- Resource Manager
SecMaster helps you:
- Aggregate cloud assets from different accounts and regions into one place.
- Import off-cloud assets to SecMaster and mark the environment assets belong to.
- SecMaster marks asset security status to show whether there are unsafe settings, OS or application vulnerabilities, suspicious intrusions, or unprotected cloud services. For example, all ECSs must be protected with HSS, and all domain names must be protected with WAF.
For details, see Managing Assets.
- Checking and clearing unsafe settings
During security operations, the most common "vulnerability" is unsafe settings. Based on security compliance experience, SecMaster forms a baseline for automatic checks and provides baseline check packages based on common specifications and standards in the industry.
- SecMaster can automatically check cloud service settings. For example, SecMaster can check whether permissions are assigned by roles in IAM, whether security groups allow all inbound access in VPC, and whether WAF protection policies are enabled. You can harden the configuration based on the recommended methods.
For details, see Baseline Inspection.
- Discovering and fixing vulnerabilities
SecMaster can also help you detect and fix security vulnerabilities. SecMaster allows you to manage Linux, Windows, Web-CMS, and application vulnerabilities. It also gives you an overview of vulnerabilities in real time, including vulnerability scan details, vulnerability statistics, vulnerability types and distribution, top 5 vulnerabilities, and the top 5 risky servers.
For details, see Vulnerability Management.
Step 2: Detect for Threats
After data sources are connected to SecMaster, we have counted the assets we need to protect and fixed unsafe settings and vulnerabilities. The next move is to identify suspicious activities and threats.
SecMaster provides multiple built-in templates designed by security experts and analysis teams based on known threats, common attack media, and suspicious activity reporting chains. With these templates, you will receive notifications of such threats when performing certain operations. These templates automatically search for suspicious activities throughout the environment. In addition, you can customize templates based on your needs to search for or find out activities.
SecMaster also supports cloud service security log data retrieval and analysis. In doing this, it provides professional security analysis and protects cloud workloads, applications, and data.
For details, see Viewing Existing Model Templates and Security Analysis Overview.
Step 3: Investigate Alerts and Incidents
- Investigating alerts
Threat detection models analyze a large number of security cloud service logs to find suspected intrusion behaviors and generate alerts. An alert in SecMaster contains the following fields: name, severity, asset/threat that initiates suspicious behavior, and compromised assets. On-duty security personnel need to determine how bad an alert is within a very short period of time. If the risk is low, they will disable the alert (such as repeated alerts and O&M operations). If the risk is high, they will convert the alert to an incident.
For more details, see Viewing Alerts and Converting an Alert to an Incident.
- Investigating incidents
After an alert is converted to an incident, you can view the incident on the incident management page and investigate and analyze it. You can associate an incident with entities related to suspicious behavior, such as assets (such as VMs), indicators (such as attack source IP addresses), accounts (such as leaked accounts), and processes (such as Trojans). You can also associate an incident with similar historical alerts or incidents.
For details, see Viewing an Incident and Editing an Incident.
Step 4: Respond to Threats
With real-time automation, SecMaster can automatically respond to duplicate alerts to reduce your analysis workloads. SecMaster also provides automatic playbooks so that some threats can be handled automatically.
For details, see Security Orchestration.
Step 5: Use Security Overview, Large Screen, and Reports
- Security Overview
This page displays the overall security assessment status of resources in the current workspace in real time so that you can learn cloud security posture and manage risks in a centralized manner.
- Large Screen
- Overall Situation: This screen gives an overview of attack status and predicts attack trends. You can view historical attacks and global metrics of security operations.
- Monitoring Statistics: You can view unhandled security risks, such as alerts, incidents, vulnerabilities, and unsafe baseline settings.
- Asset Security: On this screen, you can view risks by assets. You can learn how many assets you have, how many of them have been attacked, and how many of them are unprotected.
- Threat Situation: On this screen, you can view identified attacks, including the number of DDoS attacks, number of network attacks, number of blocked application attacks, and number of host attacks.
- Vulnerability screen: You can view the trend and distribution of vulnerable configurations or assets, such as vulnerable assets, vulnerabilities, baselines, and unprotected assets.
- Security Report
A security report includes details such as security scores, baseline check results, security vulnerabilities, and what policies are enabled. You can create security reports to learn about asset security status in a timely manner.
For more details, see Situation Overview, Large Screen, and Reports.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






