Managing Functions Using KooCLI
FunctionGraph provides the command line interface (CLI) for you to manage functions, triggers, and aliases, and invoke functions.
Notes and Constraints
- When you access Huawei Cloud through an API, you must undergo access key–based identity authentication with the access request encrypted, and ensure that the access request is secret, complete, and correct. Properly keep the config.yaml file to prevent unauthorized use of your access key. Use temporary access keys (Access Key ID, Secret Access Key, and Token) to enhance security. For details about the temporary access keys, see Temporary Access Key (for Federated Users).
- If your access key is used by an unauthorized person (due to a loss or leakage), you can delete the access key or notify the administrator of resetting it and configure it again.
- Deleted access keys cannot be recovered.
KooCLI Download Links
KooCLI can run on a 64-bit Linux x86 operating system (OS), 64-bit Windows OS, or macOS. Table 1 provides the download links of KooCLI.
Installing KooCLI
- Install KooCLI. For details, see Installing KooCLI in Linux.
- Obtain an access key (access key ID and secret access key, also called "AK/SK").
- If you have access to the console, log in to it, and create an access key on the My Credentials page. For details, see Creating an Access Key. An AK/SK file is downloaded. Generally, it is named credentials.csv. As shown in the following figure, the file contains a username, AK, and SK.
Figure 1 Content of the credentials.csv file

- If you do not have access to the console, request the administrator to create an access key for you on the IAM console in case your access key is lost or needs to be reset. For details, see Managing Access Keys for an IAM User.
- If you have access to the console, log in to it, and create an access key on the My Credentials page. For details, see Creating an Access Key. An AK/SK file is downloaded. Generally, it is named credentials.csv. As shown in the following figure, the file contains a username, AK, and SK.
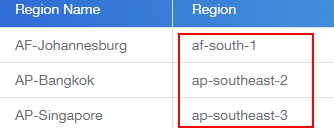
- Obtain a region name. For details, see Regions and Endpoints.
Figure 2 Obtaining region information
- Initialize KooCLI.
Run the following command to initialize KooCLI:
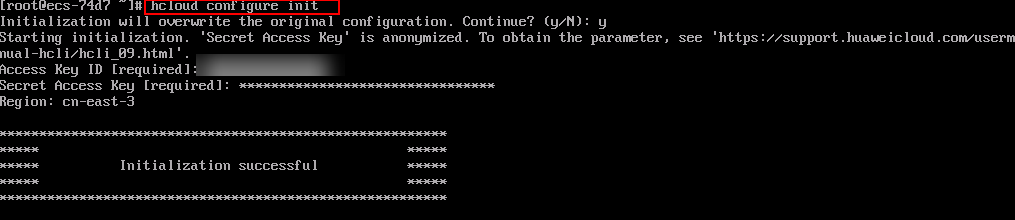
hcloud configure init
Enter an access key ID, secret access key, and region name. If the information shown in Figure 3 is displayed, the initialization is successful.
You can also configure authentication information using the temporary AK, SK, and token.
hcloud configure set --cli-profile=default --cli-access-key=your-ak --cli-secret-key=your-sk --cli-security-token=your-token
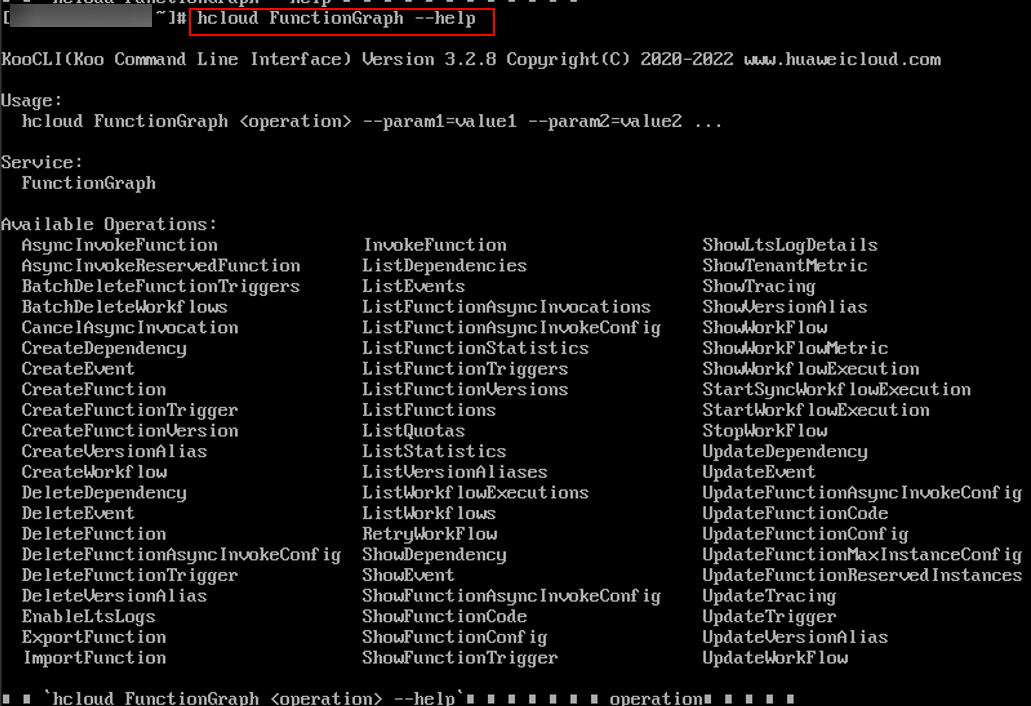
- Run the following command to view the commands supported by FunctionGraph. As shown in Figure 4, Available Operations lists the operations supported by FunctionGraph.
hcloud FunctionGraph --help
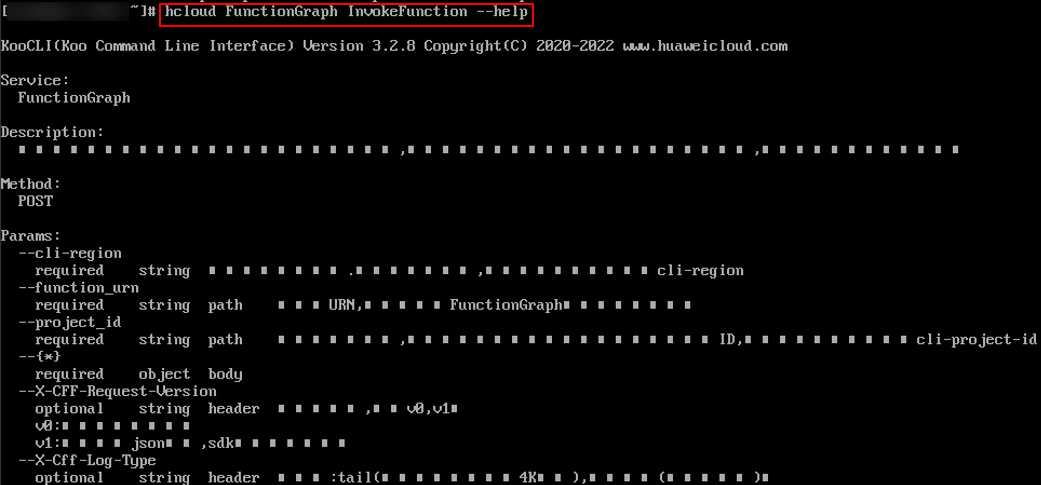
Run the following command to obtain help information about operation InvokeFunction. If the command is successfully executed, the information shown in Figure 5 is displayed.
hcloud FunctionGraph InvokeFunction --help
Invoking a Function
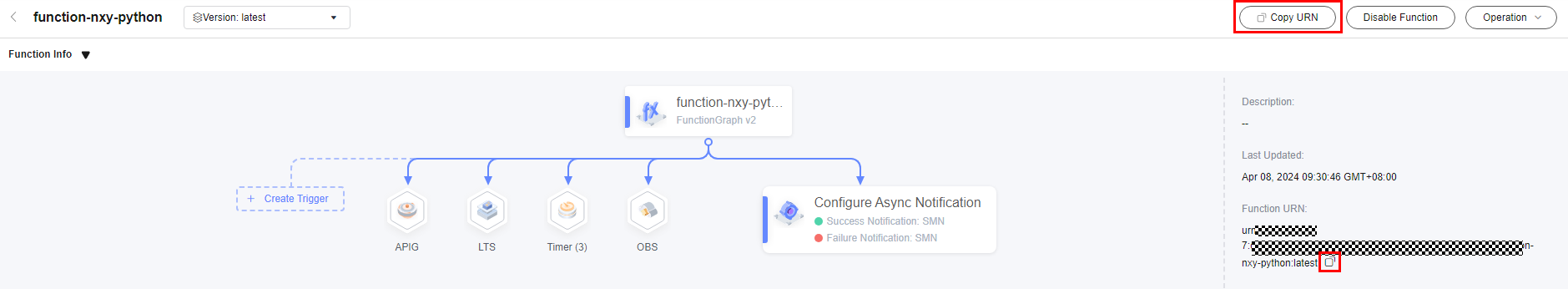
Before invoking a function, obtain the URN, as shown in Figure 6.
- Synchronous invocation
The following is an example command for synchronous invocation. For details about the parameters, see Table 2.
hcloud FunctionGraph InvokeFunction --cli-region="ap-southeast-1" --X-Cff-Log-Type="tail" --X-CFF-Request-Version="v1" --function_urn="urn:fss:cn-east-3:******:function:default:hcloud-invoke:latest" --project_id="******" --key="value"
Table 2 Parameters Parameter
Mandatory
Description
--cli-region
Yes
Region where the target function is located.
--function_urn
Yes
Function URN.
--project_id
Yes
Project ID.
--X-Cff-Log-Type
No
Options: tail (4 KB logs will be returned in the header) and null (no logs will be returned).
X-CFF-Request-Version
No
Response body format. Options:
- v0: text format.
- v1: JSON format. Use this format when using an SDK.
Body
Yes
Request body in --key="value" format. The JSON structure is {"key":"value"}.
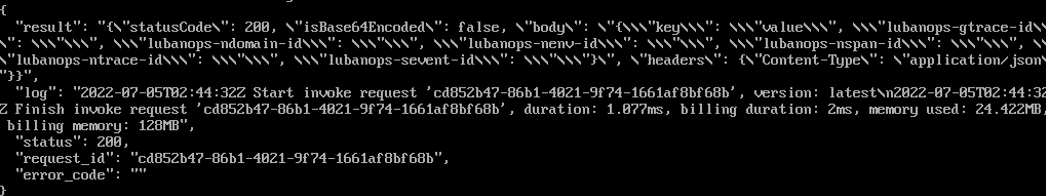
Figure 7 shows the output result. For details about the response parameters, see Table 3.
- Asynchronous invocation
The following is an example command for asynchronous invocation. For details about the parameters, see Table 4.
hcloud FunctionGraph AsyncInvokeFunction --cli-region="cn-east-3" --function_urn="urn:fss:cn-east-3:******:function:default:hcloud-invoke:latest" --project_id="******" --key="value"
Table 4 Parameters Parameter
Mandatory
Description
--cli-region
Yes
Region where the target function is located.
--function_urn
Yes
Function URN.
--project_id
Yes
Project ID.
Body
Yes
Request body in --key="value" format. The JSON structure is {"key":"value"}.
Figure 8 shows the output result. For details about the response parameters, see Table 3.
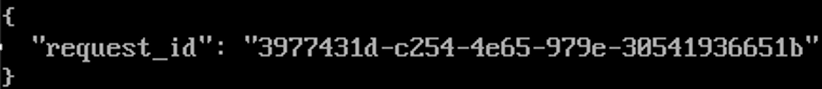
Table 5 Parameters in the response body Parameter
Type
Description
request_id
String
Request ID.
Configuring a Network Proxy Using KooCLI
Run the following command to set a proxy:
export HTTP_PROXY="http://user:password@proxyIp:proxyPort"
For details, see Set/Export http_proxy With Special Characters In Password Under Unix / Linux.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot