Using a Virtual Smart Street Light to Communicate with the Platform (C SDK)
Overview
This section describes how to connect a device to Huawei Cloud IoTDA through MQTTS/MQTT using C code, implement southbound data reporting and command delivery using platform APIs, and receive messages subscribed by the northbound server using the application-side sample code. Taking a smart street light as an example, the device reports information such as luminance to IoTDA, and an application receives device data pushed by IoTDA.
Prerequisites
You have installed Linux and GCC (4.8 or later).
Uploading a Product Model
A product model is a JSON file that describes device capabilities. It defines basic device properties and message formats for data reporting and command delivery. Defining a product model is to construct an abstract model of a device in the platform to enable the platform to understand the device function.
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
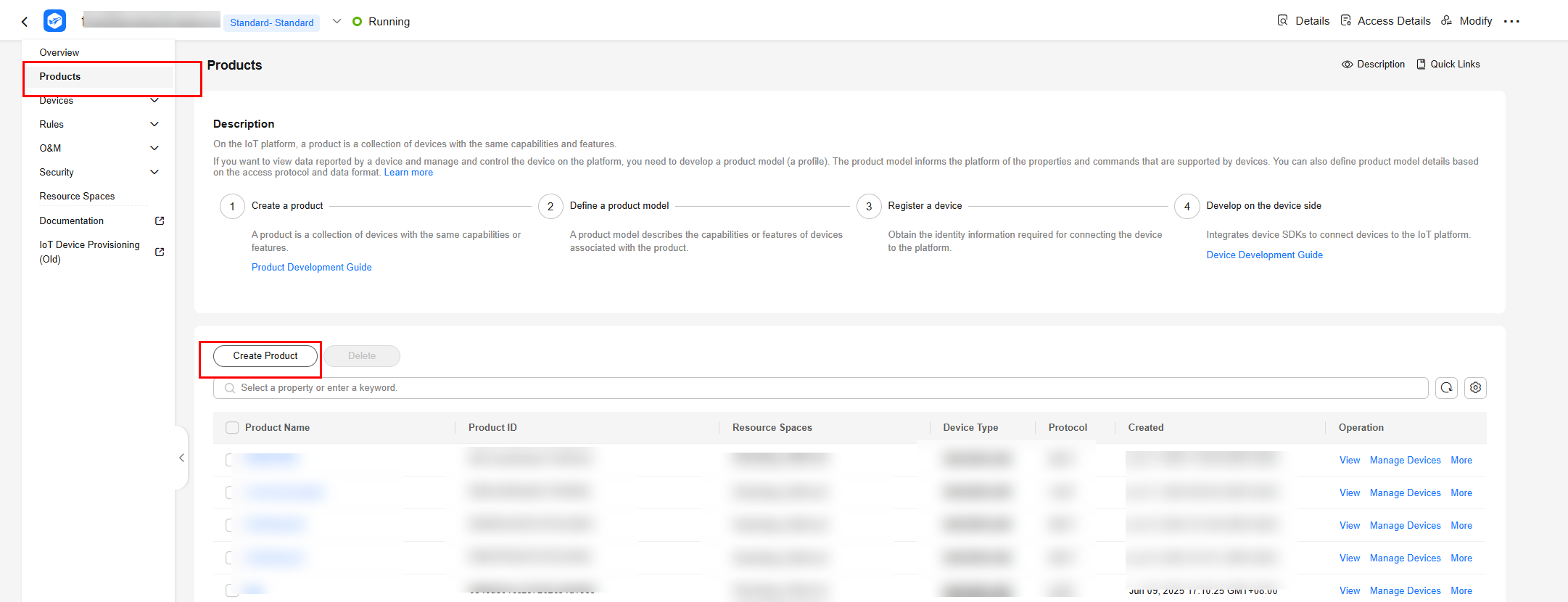
- Choose Products in the navigation pane and click Create Product.
Figure 1 Creating a product
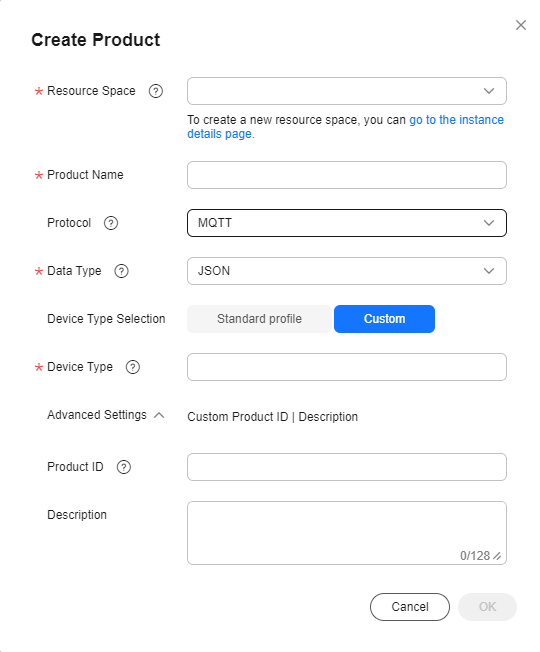
- In the displayed dialog box, set parameters based on your requirements.
Figure 2 Creating a product - MQTT
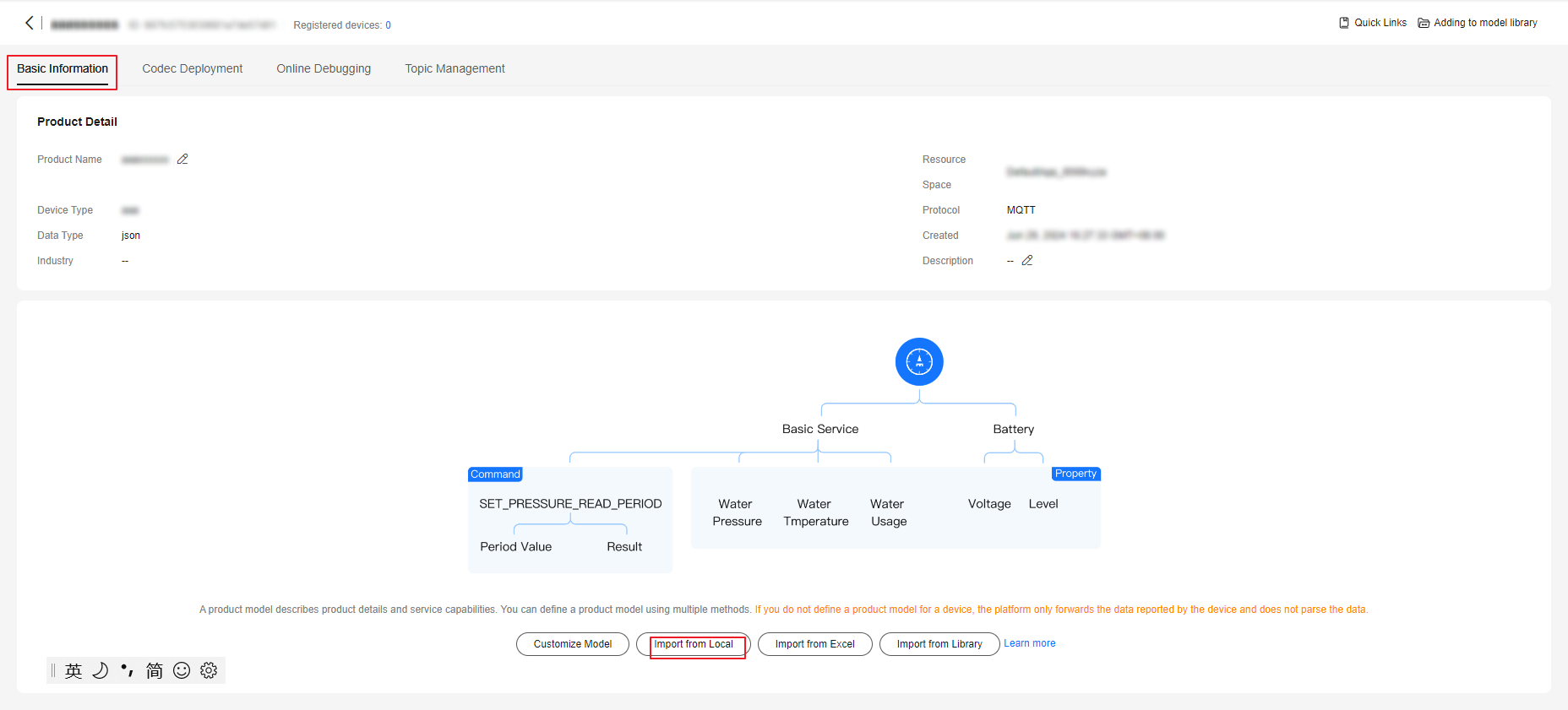
- Download the model file. For details about the development process, see Developing a Product Model Online.
- After the product is created, click the product, and then click Import from Local to upload the downloaded model file. The model file does not need to be decompressed, and the package name cannot contain brackets.
Figure 3 Uploading a product model - MQTT
Creating a Device
- In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices, and click Register Device.
Figure 4 Registering a device

- In the displayed dialog box, configure the parameters by referring to the following figure (select the created product), and click OK. If you do not specify Secret, a secret will be automatically generated by the platform. In this example, the secret is automatically generated.
Figure 5 Registering a device - test

- After the device is created, save the device ID and secret, which will be used for device connection.
Figure 6 Device - Device registered

Importing Sample Code
- Download the sample code quickStart(C).
- Copy the code to the Linux runtime environment. The following figure shows the code file hierarchy.
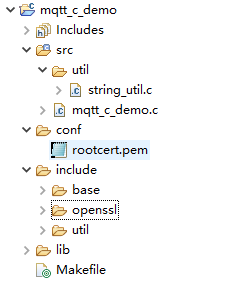
Description of the directories:
- src: source code directory
mqtt_c_demo: core source code of the demo
util/string_util.c: utility resource file
- conf: certificate directory
rootcert.pem: certificate used by the device to verify the platform identity. It is used for login authentication when the device connects to the platform.
- include: header files
base: dependent Paho header files
openssl: dependent OpenSSL header files
util: header files of the dependent tool resources
- lib: dependent library file
libcrypto.so*/libssl.so*: OpenSSL library file
libpaho-mqtt3as.so*: Paho library file
- Makefile: Makefile
- src: source code directory
Compiling Library Files
- Compiling the OpenSSL library
- Download OpenSSL, upload it to any directory on the Linux compiler, and run the following command to decompress it:
tar -zxvf openssl-1.1.1d.tar.gz
- Generate a makefile.
Run the following command to access the OpenSSL source code directory:
cd openssl-1.1.1d
Create a directory (for example, /home/test) for OpenSSL compilation.mkdir /home/test
Create a directory for OpenSSL compilation.mkdir /home/test/openssl
Create a configuration file directory.mkdir /home/test/openssl/ssl
Run the following configuration command:./config shared --prefix=/home/test/openssl --openssldir=/home/test/openssl/ssl
In this command, prefix is the installation directory, openssldir is the configuration file directory, and shared is used to generate a dynamic-link library (.so library).
If an exception occurs during the compilation, add no-asm to the configuration command (indicating that the assembly code is not used).
./config no-asm shared --prefix=/home/test/openssl --openssldir=/home/test/openssl/ssl

- Generate library files.
Run the following command in the OpenSSL source code directory:
make depend
Run the following command for compilation:
make
Install OpenSSL.
make install
Find the lib directory in home/test/openssl under the OpenSSL installation directory.
The library files libcrypto.so.1.1, libssl.so.1.1, libcrypto.so, and libssl.so are generated. Copy these files to the lib folder of quickStart(C) and copy the content in /home/test/openssl/include/openssl to include/openssl of quickStart(C).
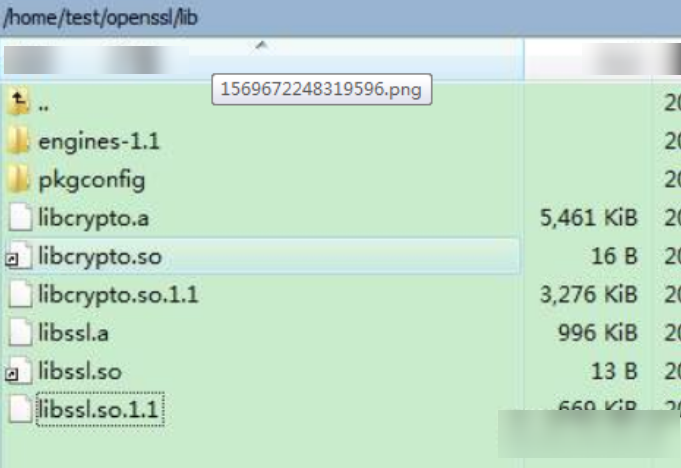
Note: Some compilation tools are 32-bit. If these tools are used on a 64-bit Linux computer, delete -m64 from the makefile before the compilation.
- Download OpenSSL, upload it to any directory on the Linux compiler, and run the following command to decompress it:
- Compiling the Eclipse Paho library file
- Download the paho.mqtt.c source code.
- Decompress the package and upload it to the Linux compiler.
- Modify the makefile.
- Run the following command to edit the makefile:
vim Makefile
- Run the following command to display the number of lines:
:set nu
- Add the following two lines (customized OpenSSL header files and library files) after line 129:
CFLAGS += -I/home/test/openssl/include LDFLAGS += -L/home/test/openssl/lib -lrt
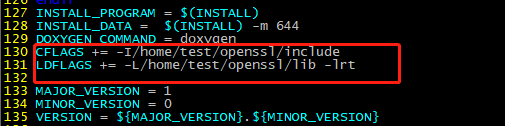
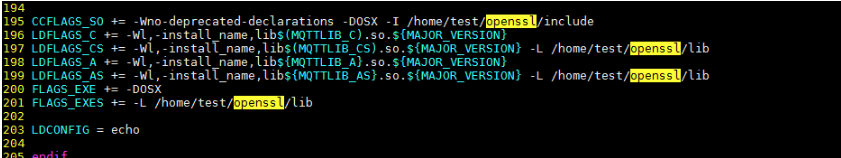
- Change the addresses in lines 195, 197, 199, and 201 to the corresponding addresses.
- Run the following command to edit the makefile:
- Start the compilation.
- Run the following command:
make clean
- Run the following command:
make
- Run the following command:
- After the compilation is complete, you can view the libraries that are compiled in the build/output directory.
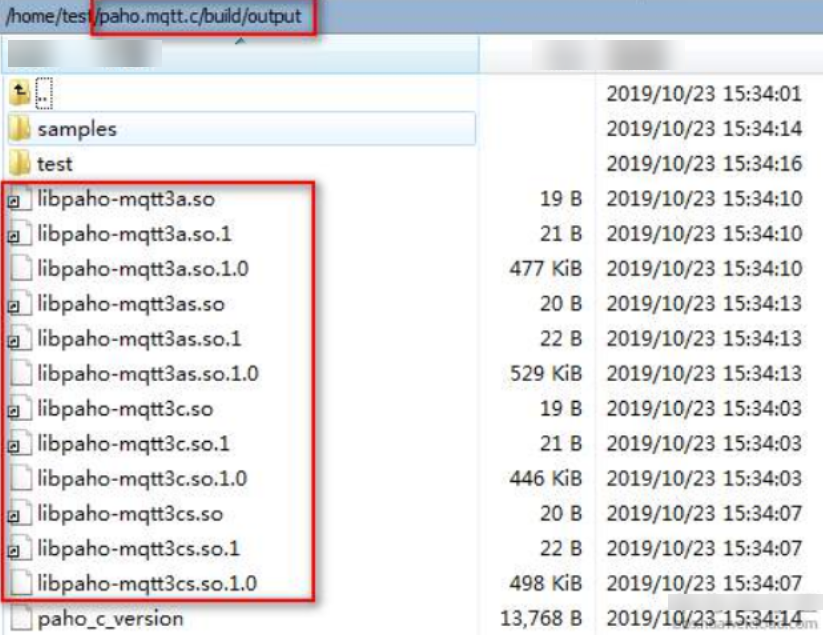
- Copy the Paho library file.
Currently, only libpaho-mqtt3as is used in the SDK. Copy the libpaho-mqtt3as.so and libpaho-mqtt3as.so.1 files to the lib folder of quickStart(C). Go back to the Paho source code directory, and copy MQTTAsync.h, MQTTClient.h, MQTTClientPersistence.h, MQTTProperties.h, MQTTReasonCodes.h, and MQTTSubscribeOpts.h in the src directory to the include/base directory of quickStart(C).
Establishing a Connection
To connect a device or gateway to the platform, upload the device information to bind the device or gateway to the platform.
- Configure the parameters. Change the values of username and password only. For details, see Obtaining Resources.
- Start the connection.
- Run the make command for compilation. Delete -m64 from the makefile in a 32-bit OS.
- Run export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib/ to load the library file.
- Run ./MQTT_Demo.o.
- If the connection is successful, the message "connect success" is displayed. The device is also displayed as Online on the console.
 Figure 7 Device list - Device online status
Figure 7 Device list - Device online status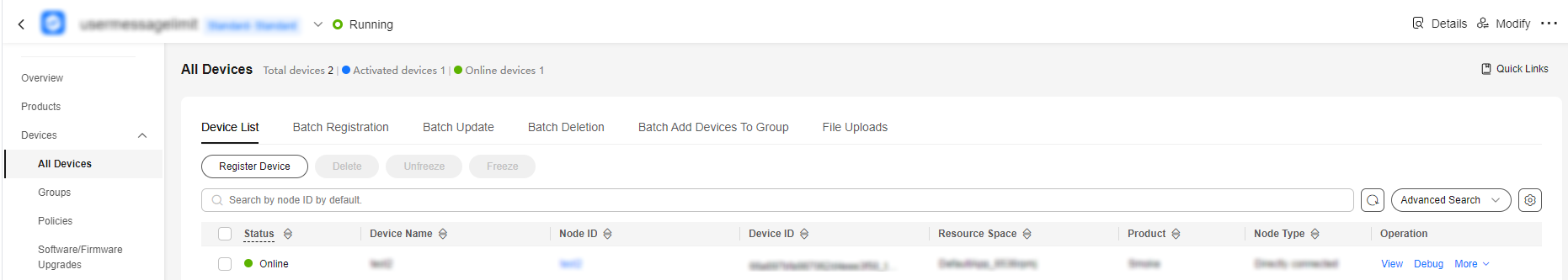
Reporting Properties
A device reports its properties to IoTDA. The sample code implements scheduled reporting. You can view the data reported by the device in IoTDA. For details, see Device Reporting Properties.
1 2 |
//publish data char *payload = "{\"services\":[{\"service_id\":\"BasicData\",\"properties\":{\"luminance\":32},\"eventTime\":NULL}]}"; |
- The message body payload is assembled in JSON format, and service_id must be the same as that defined in the product model. properties indicates a device property.
- luminance indicates the street light brightness.
- eventTime indicates the UTC time when the device reports data. If this parameter is not specified, the system time is used by default.
If the property reporting is successful, the message "publish success" is displayed in the demo.
The reported properties are displayed on the device details page.

Receiving a Command
After subscribing to a command topic, you can deliver a synchronous command on the console. For details, see Synchronous Command Delivery to an Individual MQTT Device.
If the command delivery is successful, the command received is displayed in the demo:

Obtaining Data Reported by a Device from the Cloud
After the platform receives, an application can receive push messages using AMQP. For details, see Obtaining Data Reported by a Device from the Cloud.
Additional Information
For more development guides, see Device SDKs and Access Using MQTT Demos.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot