Initialization
This section describes how to configure function initialization on the FunctionGraph console.
Overview
Function initialization refers to the process of performing setup tasks when a function is invoked, including setting its initial state, allocating resources, and assigning initial values to variables within the function.
The initialization is executed after an instance is started. The instance starts to process requests only after the initialization is executed.
The initialization is executed only once during the lifecycle of a function instance. Initialization will be billed in the same way as function request processing.
The service logic shared by multiple requests can be implemented in the initializer to reduce the latency. For example, the logic of loading a deep learning model with large specifications or building a connection pool for databases. For details about how to use initializers to develop functions, see Initializer .
Notes and Constraints
- Initialization is enabled by default for HTTP functions and cannot be disabled.
- Ensure that the function initializer and handler are in the same file.
- Set the initializer in the same way as the handler. For more information about the handler, see Table 1.
- Initialization is not supported for event functions based on custom images.
- Do not read or write data on disks in the initializer. Otherwise, the function cannot read data on disks.
Configuring Initialization
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console. In the navigation pane, choose Functions > Function List.
- Click the name of a function.
- Choose Configuration > Lifecycle.
- On the displayed page, enable Initialization, set initialization parameters by referring to Table 1, and click Save.
Figure 1 Enabling initialization
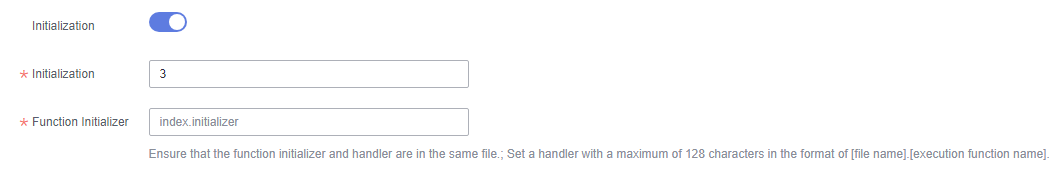
Table 1 Parameter configuration Parameter
Description
Initialization Timeout (s)
The value ranges from 1s to 300s.
Initializer
This parameter is available only for event functions and is not displayed for HTTP functions.
Ensure that the function initializer and handler are in the same file. The initializer must be named in the same way as the handler. For example, for a Node.js or Python function, set an initializer name in the format of [file name].[initialization function name]. The name can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
NOTE:For details on how to configure the code, see Configuring Function Code.
Initializer Code Example
- Node.js (Initializer introduction)
exports.initializer = function(context, callback) { callback(null, ''); }; - Python (Initializer introduction)
def my_initializer(context): print("hello world!") - Java (Initializer introduction)
public void my_initializer(Context context) { RuntimeLogger log = context.getLogger(); log.log(String.format("ak:%s", context.getSecurityAccessKey())); } - PHP (Initializer introduction)
<?php Function my_initializer($context) { echo 'hello world' . PHP_EOL; } ?>
Helpful Links
Manage the function lifecycle using APIs. For details, see Function Lifecycle Management APIs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





