Developing a Python Event Function
You can develop a Python event function locally and upload the code file, or create a function on the FunctionGraph console and edit code online.
For details about the syntax and SDK APIs of Python functions, see Function Development Overview.
Constraints
- FunctionGraph can return only the following types of values:
- None: The HTTP response body is empty.
- String: The content in this string is the body of an HTTP response.
- Other: For a value rather than None or String, FunctionGraph encodes the value in JSON, and uses the encoded object as the body of an HTTP response. The Content-Type header of the HTTP response is set to application/json.
- When calling a function using APIG, isBase64Encoded is valued true by default, indicating that the request body transferred to FunctionGraph is encoded using Base64 and must be decoded for processing.
The function must return characters strings by using the following structure.
{ "isBase64Encoded": true|false, "statusCode": httpStatusCode, "headers": {"headerName":"headerValue",...}, "body": "..." } - When you write code in Python, do not name your package with the same suffix as a standard Python library, such as json, lib, and os. Otherwise, an error will be reported indicating a module loading failure.
Step 1: Creating a Python Function Project
- Write code for printing text helloworld.
Open the text editor, compile a HelloWorld function, and save the code file as helloworld.py. The code is as follows:
def print hello(): print('Hello world!') - Define a FunctionGraph function.
Open the text editor, write the function code, and save the function file as index.py under the same directory as the helloworld.py file. The function code is as follows:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import json import helloworld def handler (event, context): output =json.dumps(event) helloworld.printhello() return output - Package the project files.
After creating the function project, you get the following directory. Select all files under the directory and package them into the fss_examples_python3.zip file, as shown in Figure 1. Ensure that the function handler is under the root directory after the ZIP file is decompressed.
You can also download the Python function sample project package and use it directly.
Step 2: Creating a Function
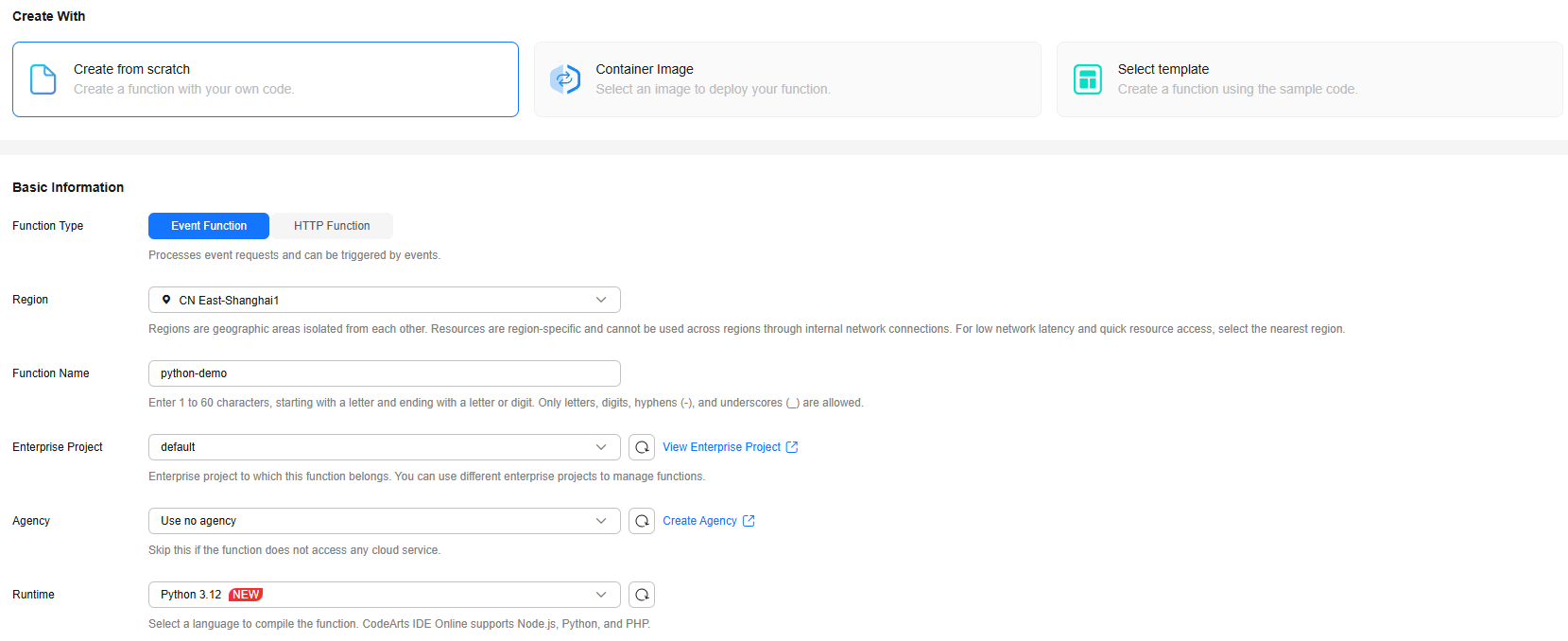
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console and click Create Function in the upper right corner.
- Create a Python event function from scratch and click Create Now as shown inFigure 2. The function details page is displayed.
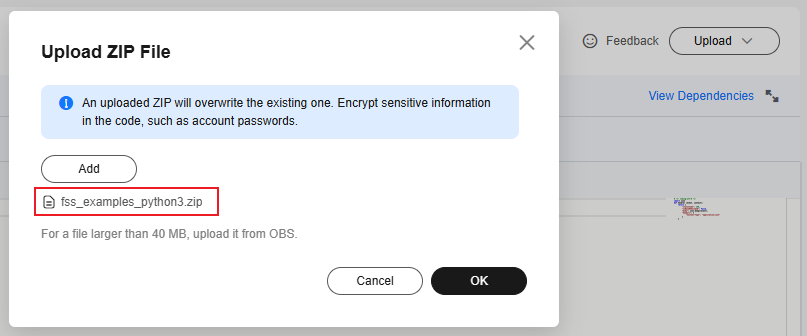
- Upload the ZIP file packed in Step 1: Creating a Python Function Project on the Code tab, as shown in Figure 3.
The uploaded code will be automatically deployed on the FunctionGraph console. If you have modified the code, click Deploy again.
Modifying the function handler:
In the navigation pane on the left of the FunctionGraph console, choose Functions > Function List. Click the name of the function to be set. On the function details page that is displayed, choose Configuration > Basic Settings and set the Handler parameter, as shown in Figure 4.Figure 4 Function handler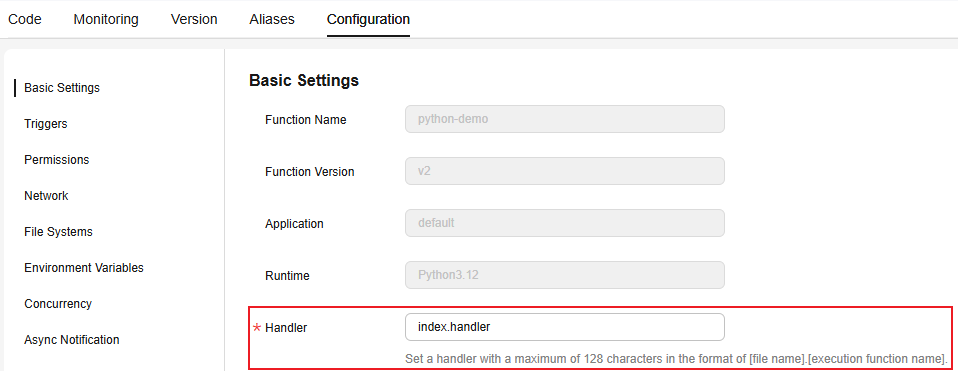
- The index of the handler must be consistent with the name of the file created in Step 1: Creating a Python Function Project, because the file name will help to locate the function file.
- The handler is a function name. It is used to find the handler of the function.
After you upload the fss_examples_python3.zip file to OBS, when the function is triggered, FunctionGraph decompresses the file to locate the function file through index and locate the function defined in the index.py file through handler, and then executes the function.
Step 3: Testing the Function
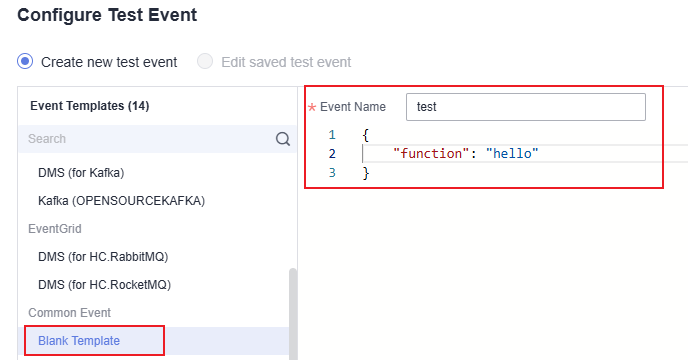
- On the Code tab, click Test. In the displayed Configure Test Event dialog box, select Blank Template. Configure the test event test as shown in Figure 5. Click Create.
- Select the configured test event test and click Test.
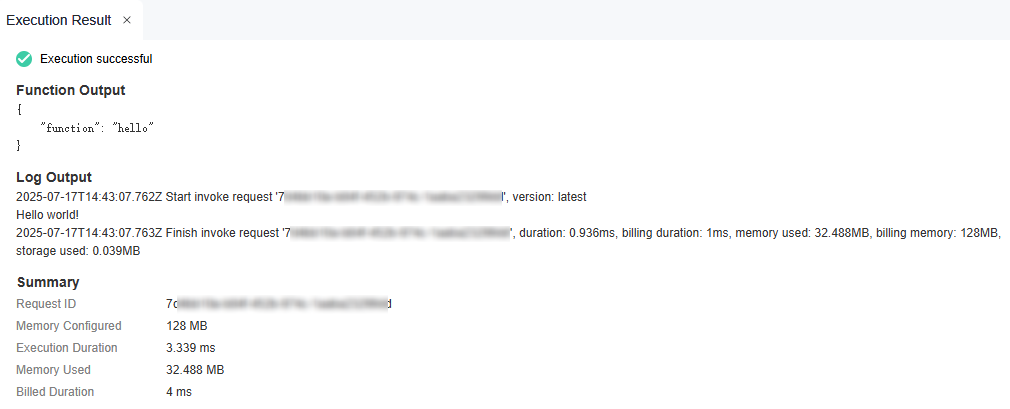
- As shown in Figure 6, the Execution Result window is displayed on the right. You can check whether the function is executed successfully.
Function Execution Result
The execution result consists of the function output, summary, and log output.
|
Parameter |
Successful Execution |
Failed Execution |
|---|---|---|
|
Function Output |
The defined function output information is returned. |
A JSON file that contains errorMessage, errorType, and stackTrace is returned. The format is as follows: {
"errorMessage": "",
"errorType": "",
"stackTrace": []
}
errorMessage: Error message returned by the runtime. errorType: Error type. stackTrace: Stack error information returned by the runtime. |
|
Summary |
Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. |
Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. |
|
Log Output |
Function logs are printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. |
Error information is printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. |
Helpful Links
- For details about how to create a Python function dependency, see Creating a Dependency for a Python Function.
- For more information about function development, such as the supported runtimes, trigger events, function project packaging specifications, and DLL referencing, see Function Development Overview.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot